Yonsei Med J.
2019 May;60(5):487-489. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.5.487.
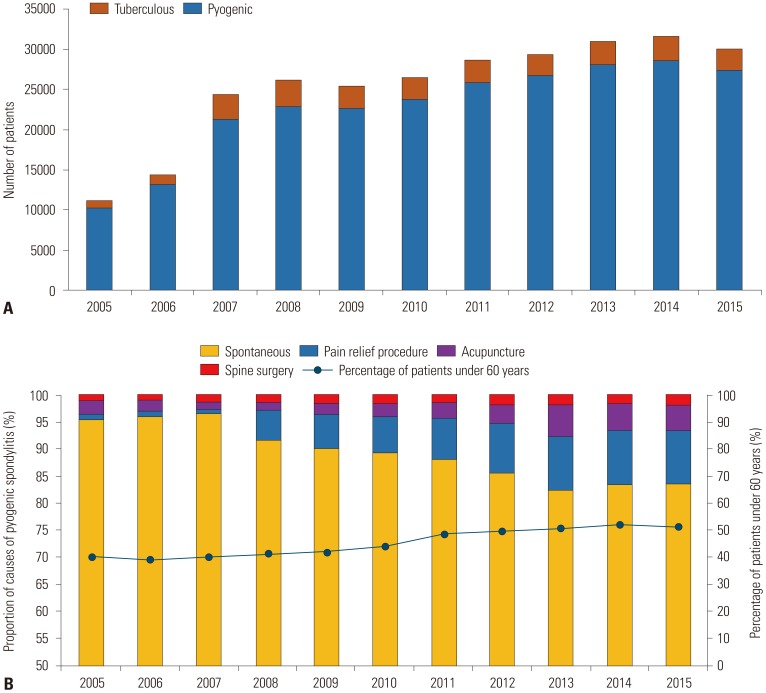
Changes in Trends of Spondylitis in Korea Based on a Nationwide Database
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. hyzhang@nhimc.or.kr
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Policy Research Affairs, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Spine and Spinal Cord Institute, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. DKCHIN@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2443255
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.5.487
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Change of Pyogenic and Tuberculous Spondylitis between 2007 and 2016 Year : A Nationwide Study
Yeon Jee Kim, Je Beom Hong, Yeo Song Kim, Jeeeun Yi, Jung Min Choi, Seil Sohn
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2020;63(6):784-793. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2020.0013.
Reference
-
1. Vergne P, Trèves R. Infectious spondylodiscitis. etiology, diagnosis, progression and treatment. Rev Prat. 1998; 48:2065–2071. PMID: 9881020.2. Kaufman DM, Kaplan JG, Litman N. Infectious agents in spinal epidural abscesses. Neurology. 1980; 30:844–850. PMID: 7191067.
Article3. Lee Y, Kim BJ, Kim SH, Lee SH, Kim WH, Jin SW. Comparative analysis of spontaneous infectious spondylitis: pyogenic versus tuberculous. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2018; 61:81–88. PMID: 29354239.4. Seong SC, Kim YY, Khang YH, Park JH, Kang HJ, Lee H, et al. [Data resource profile: the National Health Information Database of the National Health Insurance Service in South Korea.]. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 46:799–800. PMID: 27794523.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Change of Pyogenic and Tuberculous Spondylitis between 2007 and 2016 Year : A Nationwide Study
- Epidemiologic Trends and Socioeconomic Disparities of Ankylosing Spondylitis in South Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Study, 2010–2021
- Comparison of Pyogenic Spondylitis and Tuberculous Spondylitis
- Trends and Characteristics of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography: A Nationwide Database Study in Korea
- Streptococcus Spondylitis Concomitant Infectious Endocarditis: A Case Report