Anat Cell Biol.
2019 Mar;52(1):43-47. 10.5115/acb.2019.52.1.43.
Magnetic resonance angiography of hypoplastic A1 segment of anterior cerebral artery at 3.0-Tesla in Andhra Pradesh population of India
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Narayana Medical College, Nellore, India.
- 2Department of Anatomy, Narayana Medical College, Nellore, India. lesanshar@gmail.com
- 3Department of Neurology, Narayana Medical College, Nellore, India.
- KMID: 2442328
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2019.52.1.43
Abstract
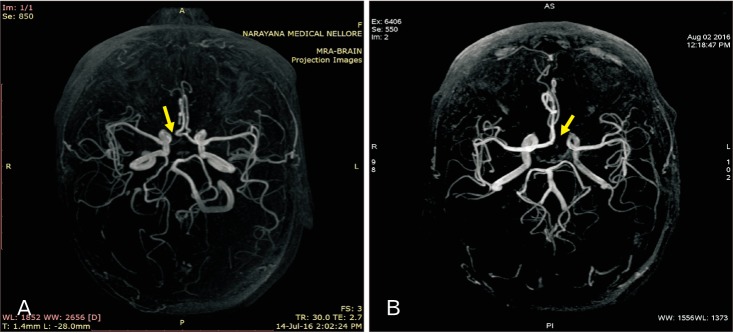
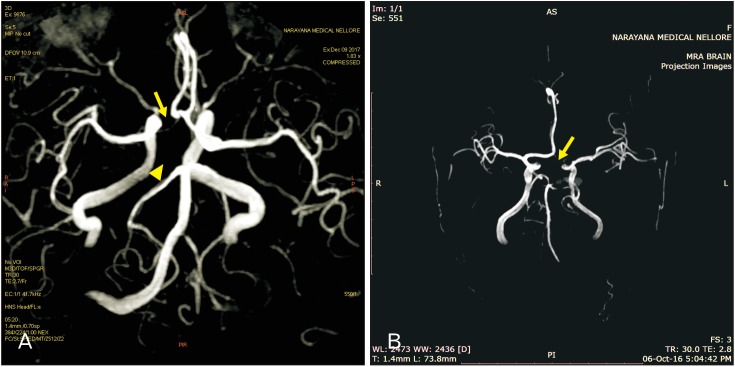
- Pre-communicating or A1 segment of anterior cerebral artery (A1ACA) hypoplasia can negotiate the anterior cerebral circulation. Not many studies have been examined the association of hypoplastic A1ACA and cerebral ischemic stroke (CIS). In this study the authors' want to accomplish the relationship between hypoplastic A1ACA and outcomes among the patients with CIS in Andhra Pradesh population of India. Retrospective review of prospectively identified 201 adult patients with CIS from 2015 to 2017 was achieved. Patients underwent 3.0T intracranial magnetic resonance angiography were compared with clinical and radiological aspects between male and female cases of A1ACA hypoplasia with associated variations in the circle of Willis. The obtained data was statistically analysed using SPSS software version 16.0 for Windows and P-value <0.05 was considered as significant. Chi-square test was applied to find out the association between the sex and incidence of hypoplastic A1ACA. Sixty-four of 201 patients with A1ACA hypoplasia with no aplastic cases were recorded. It was found to be more in males than females and common on right than left side. Frequent neurological indications such as headache, dizziness, visual instability, nausea, weakness of extremities and seizure were noted and most cases were associated with CIS. Hypoplastic A1ACA often associated with ischemia of terminal branches of ipsilateral ACA which is compromised by the blood flow via contralateral ACA. In this study, though the CIS is not directly related to hypoplastic A1ACA, any alterations in A1 segment is a considerable risk factor of stroke.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Incidence of hypoplastic posterior communicating artery and fetal posterior cerebral artery in Andhra population of India: a retrospective 3-Tesla magnetic resonance angiographic study
Sharmila P Bhanu, Suneetha Pentyala, Devi K Sankar
Anat Cell Biol. 2020;53(3):272-278. doi: 10.5115/acb.20.066.Magnetic resonance angiography in assessment of anomalies of anterior cerebral artery in adults
Noha Abdelfattah Ahmed Madkour
Anat Cell Biol. 2023;56(4):469-473. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.162.Azygos anterior cerebral artery associated with hypoplastic A1 fragment of right anterior cerebral artery
Omkar Patnaik, Preeti Shahane, Mrudula Chandrupatla, Punnapa Raviteja
Anat Cell Biol. 2023;56(4):575-578. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.177.
Reference
-
1. Orlandini GE, Ruggiero C, Orlandini SZ, Gulisano M. Blood vessel size of circulus arteriosus cerebri (circle of Willis): a statistical research on 100 human subjects. Acta Anat (Basel). 1985; 123:72–76. PMID: 4050309.2. Krabbe-Hartkamp MJ, van der, de Leeuw FE, de Groot JC, Algra A, Hillen B, Breteler MM, Mali WP. Circle of Willis: morphologic variation on three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiograms. Radiology. 1998; 207:103–111. PMID: 9530305.3. Chuang YM, Liu CY, Pan PJ, Lin CP. Anterior cerebral artery A1 segment hypoplasia may contribute to A1 hypoplasia syndrome. Eur Neurol. 2007; 57:208–211. PMID: 17268201.4. Kang DW, Chu K, Ko SB, Kwon SJ, Yoon BW, Roh JK. Lesion patterns and mechanism of ischemia in internal carotid artery disease: a diffusion-weighted imaging study. Arch Neurol. 2002; 59:1577–1582. PMID: 12374495.5. Caplan LR, Hennerici M. Impaired clearance of emboli (washout) is an important link between hypoperfusion, embolism, and ischemic stroke. Arch Neurol. 1998; 55:1475–1482. PMID: 9823834.6. Wang CX, Todd KG, Yang Y, Gordon T, Shuaib A. Patency of cerebral microvessels after focal embolic stroke in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001; 21:413–421. PMID: 11323527.7. Liebeskind DS. Collateral circulation. Stroke. 2003; 34:2279–2284. PMID: 12881609.8. Uchino A, Nomiyama K, Takase Y, Kudo S. Anterior cerebral artery variations detected by MR angiography. Neuroradiology. 2006; 48:647–652. PMID: 16786350.9. Stefani MA, Schneider FL, Marrone AC, Severino AG, Jackowski AP, Wallace MC. Anatomic variations of anterior cerebral artery cortical branches. Clin Anat. 2000; 13:231–236. PMID: 10873213.10. Gunnal SA, Wabale RN, Farooqui MS. Variations of anterior cerebral artery in human cadavers. Neurol Asia. 2013; 18:249–259.11. Ugur HC, Kahilogullari G, Esmer AF, Comert A, Odabasi AB, Tekdemir I, Elhan A, Kanpolat Y. A neurosurgical view of anatomical variations of the distal anterior cerebral artery: an anatomical study. J Neurosurg. 2006; 104:278–284. PMID: 16509502.12. Lehecka M, Dashti R, Hernesniemi J, Niemelä M, Koivisto T, Ronkainen A, Rinne J, Jääskeläinen J. Microneurosurgical management of aneurysms at A3 segment of anterior cerebral artery. Surg Neurol. 2008; 70:135–151. PMID: 18482754.13. Steven DA, Ferguson GG. Winn HR, editor. Distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysms. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co.;2004. p. 1945–1957.14. Schomer DF, Marks MP, Steinberg GK, Johnstone IM, Boothroyd DB, Ross MR, Pelc NJ, Enzmann DR. The anatomy of the posterior communicating artery as a risk factor for ischemic cerebral infarction. N Engl J Med. 1994; 330:1565–1570. PMID: 8177246.15. Maurer J, Maurer E, Perneczky A. Surgically verified variations in the A1 segment of the anterior cerebral artery. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1991; 75:950–953. PMID: 1823542.16. Niederberger E, Gauvrit JY, Morandi X, Carsin-Nicol B, Gauthier T, Ferré JC. Anatomic variants of the anterior part of the cerebral arterial circle at multidetector computed tomography angiography. J Neuroradiol. 2010; 37:139–147. PMID: 20346510.17. Ansari S, Dadmehr M, Eftekhar B, McConnell DJ, Ganji S, Azari H, Kamali-Ardakani S, Hoh BL, Mocco J. A simple technique for morphological measurement of cerebral arterial circle variations using public domain software (Osiris). Anat Cell Biol. 2011; 44:324–330. PMID: 22254161.18. De Silva KR, Silva R, Gunasekera WS, Jayesekera RW. Prevalence of typical circle of Willis and the variation in the anterior communicating artery: a study of a Sri Lankan population. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2009; 12:157–161. PMID: 20174495.19. Shaban A, Albright K, Gouse B, George A, Monlezun D, Boehme A, Beasley TM, Martin-Schild S. The impact of absent A1 segment on ischemic stroke characteristics and outcomes. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015; 24:171–175. PMID: 25440333.20. Lakhotia M, Pahadiya HR, Prajapati GR, Choudhary A, Gandhi R, Jangid H. A case of anterior cerebral artery A1 segment hypoplasia syndrome presenting with right lower limb monoplegia, abulia, and urinary incontinence. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2016; 7:189–191. PMID: 26933381.21. Honig A, Eliahou R, Auriel E. Confined anterior cerebral artery infarction manifesting as isolated unilateral axial weakness. J Neurol Sci. 2017; 373:18–20. PMID: 28131184.22. Dimmick SJ, Faulder KC. Normal variants of the cerebral circulation at multidetector CT angiography. Radiographics. 2009; 29:1027–1043. PMID: 19605654.23. Okahara M, Kiyosue H, Mori H, Tanoue S, Sainou M, Nagatomi H. Anatomic variations of the cerebral arteries and their embryology: a pictorial review. Eur Radiol. 2002; 12:2548–2561. PMID: 12271398.24. Henderson RD, Eliasziw M, Fox AJ, Rothwell PM, Barnett HJ. Angiographically defined collateral circulation and risk of stroke in patients with severe carotid artery stenosis. North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) Group. Stroke. 2000; 31:128–132. PMID: 10625727.25. Hendrikse J, Eikelboom BC, van der Grond J. Magnetic resonance angiography of collateral compensation in asymptomatic and symptomatic internal carotid artery stenosis. J Vasc Surg. 2002; 36:799–805. PMID: 12368718.26. Hoksbergen AW, Legemate DA, Csiba L, Csáti G, Síró P, Fülesdi B. Absent collateral function of the circle of Willis as risk factor for ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2003; 16:191–198. PMID: 12865604.27. Gerstner E, Liberato B, Wright CB. Bi-hemispheric anterior cerebral artery with drop attacks and limb shaking TIAs. Neurology. 2005; 65:174. PMID: 16009921.28. Han YK, Kim S, Yoon CS, Lee YM, Kang HC, Lee JS, Kim HD. A1 segment hypoplasia/aplasia detected by magnetic resonance angiography in neuropediatric patients. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2011; 19:231–239.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incidence of hypoplastic posterior communicating artery and fetal posterior cerebral artery in Andhra population of India: a retrospective 3-Tesla magnetic resonance angiographic study
- Azygos anterior cerebral artery associated with hypoplastic A1 fragment of right anterior cerebral artery
- Aneurysms of the Proximal Anterior Cerebral Artery
- Fusiform Aneurysm of Proximal Anterior Cerebral Artery: Case Report
- Aneurysms of Proximal(A1) Segment of Anterior Cerebral Artery