Korean J Gastroenterol.
2019 Mar;73(3):186-189. 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.3.186.
Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Critically Ill Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. whpaik@snuh.org
- KMID: 2442086
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2019.73.3.186
Abstract
- No abstract available.
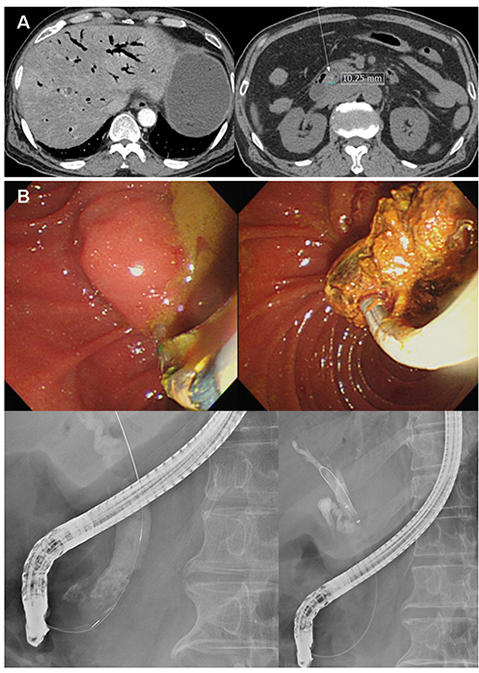
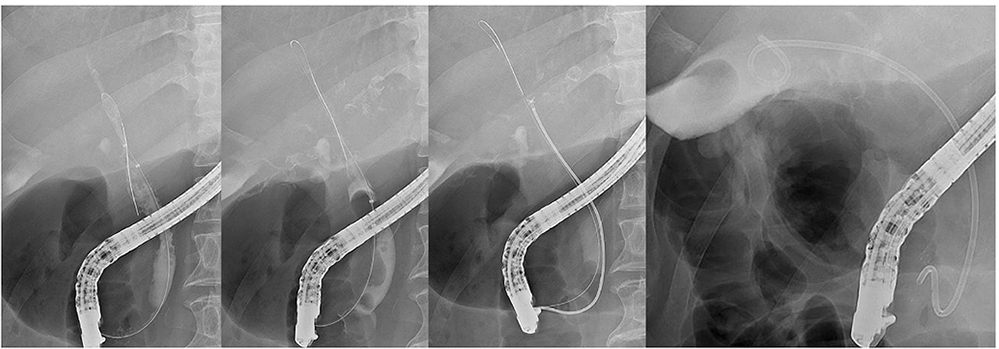
Figure
Reference
-
1. Imam MH, Talwalkar JA, Lindor KD. Secondary sclerosing cholangitis: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Clin Liver Dis. 2013; 17:269–277.2. Forbes A, Blanshard C, Gazzard B. Natural history of AIDS related sclerosing cholangitis: a study of 20 cases. Gut. 1993; 34:116–121.
Article3. Björnsson E, Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Lindor K. Immunoglobulin G4 associated cholangitis: description of an emerging clinical entity based on review of the literature. Hepatology. 2007; 45:1547–1554.
Article4. Benninger J, Grobholz R, Oeztuerk Y, et al. Sclerosing cholangitis following severe trauma: description of a remarkable disease entity with emphasis on possible pathophysiologic mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:4199–4205.
Article5. Gudnason HO, Björnsson ES. Secondary sclerosing cholangitis in critically ill patients: current perspectives. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2017; 10:105–111.
Article6. Voigtländer T, Negm AA, Schneider AS, et al. Secondary sclerosing cholangitis in critically ill patients: model of end-stage liver disease score and renal function predict outcome. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:1055–1058.
Article7. Ben-Ari Z, Levingston D, Weitzman E, et al. Secondary sclerosing cholangitis following major burn. Ann Hepatol. 2015; 14:695–701.
Article8. Leonhardt S, Veltzke-Schlieker W, Adler A, et al. Trigger mechanisms of secondary sclerosing cholangitis in critically ill patients. Crit Care. 2015; 19:131.
Article9. Cheon YK. Malignant masquerade at the bile duct. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 41:Suppl 1. 120–123.10. Mourad MM, Liossis C, Gunson BK, et al. Etiology and management of hepatic artery thrombosis after adult liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2014; 20:713–723.
Article11. Popov Y, Patsenker E, Fickert P, Trauner M, Schuppan D. Mdr2 (Abcb4)-/- mice spontaneously develop severe biliary fibrosis via massive dysregulation of pro- and antifibrogenic genes. J Hepatol. 2005; 43:1045–1054.
Article12. Leonhardt S, Veltzke-Schlieker W, Adler A, et al. Secondary sclerosing cholangitis in critically Ill patients: clinical presentation, cholangiographic features, natural history, and outcome: a series of 16 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e2188.13. Gossard AA, Angulo P, Lindor KD. Secondary sclerosing cholangitis: a comparison to primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:1330–1333.
Article14. Engler S, Elsing C, Flechtenmacher C, Theilmann L, Stremmel W, Stiehl A. Progressive sclerosing cholangitis after septic shock: a new variant of vanishing bile duct disorders. Gut. 2003; 52:688–693.
Article15. Kulaksiz H, Heuberger D, Engler S, Stiehl A. Poor outcome in progressive sclerosing cholangitis after septic shock. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:214–218.
Article16. Kirchner GI, Scherer MN, Obed A, et al. Outcome of patients with ischemic-like cholangiopathy with secondary sclerosing cholangitis after liver transplantation. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:471–478.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- Biliary Cast Formation with Sclerosing Cholangitis in Critically Ill Patient: Case Report and Literature Review
- Biliary Tract & Pancreas; A Case of Cholangiocarcinoma Suggested as Developing in the Patient with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: Two Case Reports
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: One Case Report