Korean J Gastroenterol.
2019 Mar;73(3):167-176. 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.3.167.
Efficacy and Safety of Combined Radiofrequency Ablation with Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage A Hepatocellular Carcinoma Ineligible for Curative Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sykwonmd@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2442083
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2019.73.3.167
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Surgical resection or ablation is recommended for the treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), whereas transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is frequently used in early HCC ineligible for curative resection. We evaluated the clinical effects and safety of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) shortly after TACE in patients with Barcelona clinic liver cancer (BCLC) stage A HCC.
METHODS
Sixty-seven BCLC stage A HCC patients who failed to achieve complete response to TACE as either a first line treatment and who subsequently received RFA at the Konkuk University Medical Center from January 2005 to December 2017 were included. Evaluation indices included treatment response, overall survival rate, recurrence-free survival, prognostic factors, and procedure-related complications.
RESULTS
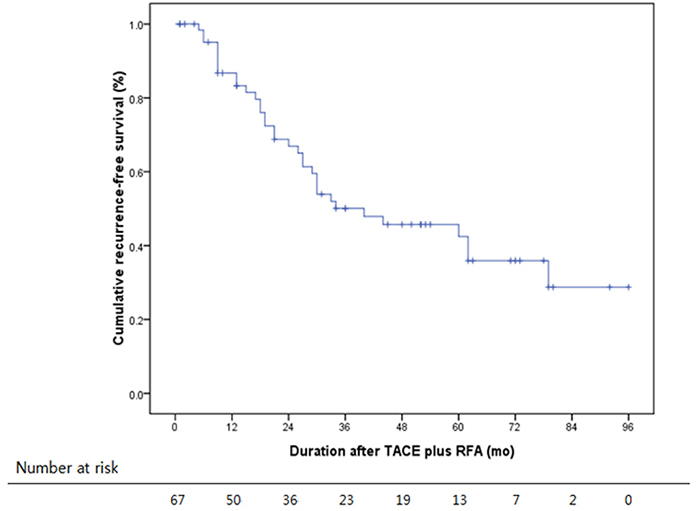
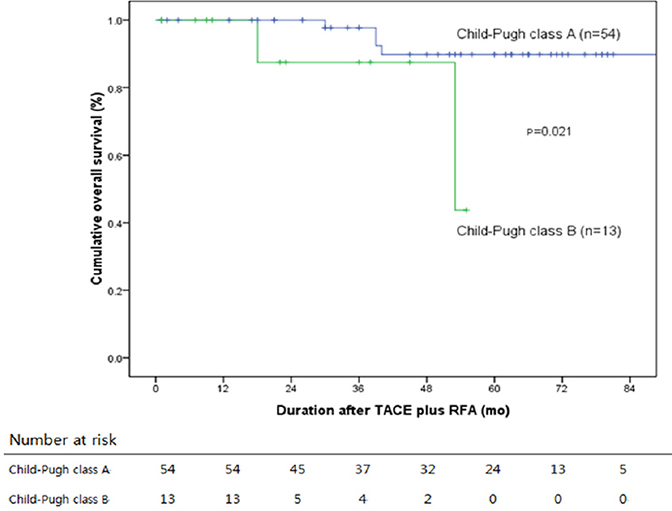
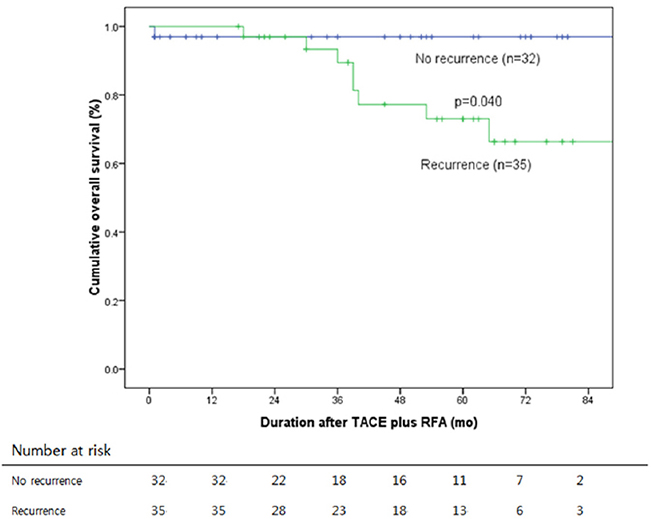
Median follow-up was 46.9 months. Fifty-four (80.6%) patients were of Child-Pugh class A, and 13 (19.4%) were of class B. Modified UICC stages were I in 10 (14.9%), II in 46 (68.7%), and III in 11 (16.4%) patients. In the 67 study subjects, cumulative recurrence-free survival rates were 86.8%, 55.9% and 29.7% at 1, 3, and 5 years, respectively, and overall survival rates were 100%, 93.4%, and 83.5% at 1, 3, and 5 years, respectively. Tumor size significantly predicted recurrence. No treatment-related death occurred.
CONCLUSIONS
Combination of RFA was an efficient and safe treatment for BCLC stage A HCC patients that failed to achieve complete response to initial TACE. We suggest TACE plus RFA be considered as a curative option for early HCC patients ineligible for curative resection of RFA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M, et al. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology. 2008; 47:82–89.
Article2. Han K, Kim JH. Transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: barcelona clinic liver cancer staging system. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:10327–10335.
Article3. Kim SE, Lee HC, Kim KM, et al. Applicability of the BCLC staging system to patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in Korea: analysis at a single center with a liver transplant center. Korean J Hepatol. 2011; 17:113–119.
Article4. Peng ZW, Zhang YJ, Chen MS, et al. Radiofrequency ablation with or without transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:426–432.
Article5. Georgiades CS, Hong K, Geschwind JF. Radiofrequency ablation and chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer J. 2008; 14:117–122.
Article6. Lee HJ, Kim JW, Hur YH, et al. Combined therapy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection for single 2-3 cm hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity-score matching analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017; 28:1240–1247.e3.7. Rossi S, Ravetta V, Rosa L, et al. Repeated radiofrequency ablation for management of patients with cirrhosis with small hepatocellular carcinomas: a long-term cohort study. Hepatology. 2011; 53:136–147.
Article8. Morimoto M, Numata K, Kondou M, Nozaki A, Morita S, Tanaka K. Midterm outcomes in patients with intermediate-sized hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized controlled trial for determining the efficacy of radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Cancer. 2010; 116:5452–5460.9. Choe WH, Kim YJ, Park HS, Park SW, Kim JH, Kwon SY. Short-term interval combined chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:12588–12594.
Article10. Thomas MB, Jaffe D, Choti MM, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: consensus recommendations of the national cancer institute clinical trials planning meeting. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:3994–4005.
Article11. Shibata T, Isoda H, Hirokawa Y, Arizono S, Shimada K, Togashi K. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: is radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization more effective than radiofrequency ablation alone for treatment? Radiology. 2009; 252:905–913.
Article12. Schwartz M, Weintraub J. Combined transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2008; 5:630–631.
Article13. Lencioni R, Cioni D, Donati F, Bartolozzi C. Combination of interventional therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2001; 48:8–14.14. Ravaioli M, Grazi GL, Piscaglia F, et al. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: results of down-staging in patients initially outside the Milan selection criteria. Am J Transplant. 2008; 8:2547–2557.
Article15. N’Kontchou G, Mahamoudi A, Aout M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results and prognostic factors in 235 Western patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2009; 50:1475–1483.
Article16. Zhu AX, Salem R. Combining transarterial chemoembolization with radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: one step forward? J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:406–408.
Article17. Xie H, Wang H, An W, et al. The efficacy of radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for primary hepatocellular carcinoma in a cohort of 487 patients. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e89081.
Article18. Song MJ, Bae SH, Lee JS, et al. Combination transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation therapy for early hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Intern Med. 2016; 31:242–252.
Article19. Pan T, Mu LW, Wu C, et al. Comparison of combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and CT-guided radiofrequency ablation with surgical resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within the up-to-seven criteria: a multicenter case-matched study. J Cancer. 2017; 8:3506–3513.
Article20. Takuma Y, Takabatake H, Morimoto Y, et al. Comparison of combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation with surgical resection by using propensity score matching in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria. Radiology. 2013; 269:927–937.
Article21. Kagawa T, Koizumi J, Kojima S, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization plus radiofrequency ablation therapy for early stage hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with surgical resection. Cancer. 2010; 116:3638–3644.22. Sohn W, Choi MS, Cho JY, et al. Role of radiofrequency ablation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who undergo prior transarterial chemoembolization: long-term outcomes and predictive factors. Gut Liver. 2014; 8:543–551.
Article23. Chang NK, Shin SS, Kim JW, et al. Effect of ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation in incompletely treated hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:Suppl 1. S104–S111.
Article24. Kim JH, Yim HJ, Lee KG, et al. Recurrence rates and factors for recurrence after radiofrequency ablation combined with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. Hepatol Int. 2012; 6:505–510.
Article25. Tang C, Shen J, Feng W, et al. Combination therapy of radiofrequency ablation and transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e3754.26. Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Takaki H, et al. Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization versus hepatectomy. Radiology. 2008; 247:260–266.
Article27. Kim JW, Shin SS, Kim JK, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for the treatment of single hepatocellular carcinoma of 2 to 5 cm in diameter: comparison with surgical resection. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:626–635.
Article28. Guo W, He X, Li Z, Li Y. Combination of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) vs. surgical resection (SR) on survival outcome of early hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2015; 62:710–714.29. Kim MY, Kim JW, Myung DS, et al. Outcomes of transarterial chemoembolization with or without additional radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma of 2 to 5 cm in diameter. Iran J Radiology. 2017; 14:e39515.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Combination of Transarterial Chemoebolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment
- Evaluation of the Outcome after Transarterial Chemoembolization; Refinement of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage-B from Eastern Point of View
- Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Status and Future Directions
- Efficacy of Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Refractory to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Vascular Variation: A Case Study
- Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation is the best option for the local treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma?