Korean J Orthod.
2018 Jan;48(1):48-56. 10.4041/kjod.2018.48.1.48.
Effect of carbonated water manufactured by a soda carbonator on etched or sealed enamel
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, Wonkwang University School of Dentistry, Iksan, Korea. sangkim@wku.ac.kr
- KMID: 2441441
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2018.48.1.48
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of carbonated water on etched or sealed enamel according to the carbonation level and the presence of calcium ions.
METHODS
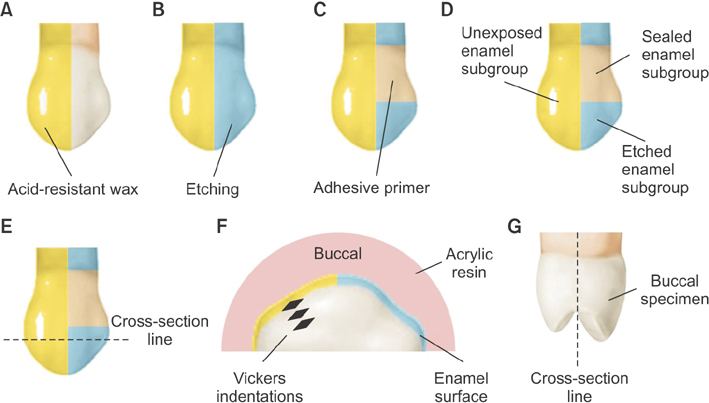
Carbonated water with different carbonation levels was manufactured by a soda carbonator. Seventy-five premolar teeth were randomly divided into a control group and 4 experimental groups in accordance with the carbonation level and the presence of calcium ions in the test solutions. After specimen preparation of the Unexposed, Etched, and Sealed enamel subgroups, all the specimens were submerged in each test solution for 15 minutes three times a day during 7 days. Microhardness tests on the Unexposed and Etched enamel subgroups were performed with 10 specimens from each group. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) tests on the Unexposed, Etched, and Sealed enamel subgroups were performed with 5 specimens from each group. Microhardness changes in different groups were statistically compared using paired t-tests, the Wilcoxon signed rank test, and the Kruskal-Wallis test.
RESULTS
The microhardness changes were significantly different between the groups (p = 0.000). The microhardness changes in all experimental groups except Group 3 (low-level carbonated water with calcium ions) were significantly greater than those in the Control group. SEM showed that etched areas of the specimen were affected by carbonated water and the magnitude of destruction varied between groups. Adhesive material was partially removed in groups exposed to carbonated water.
CONCLUSIONS
Carbonated water has negative effects on etched or sealed enamel, resulting in decreased microhardness and removal of the adhesive material.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jeoung JY, Min KJ, Chae HK. Analysis of high school science textual descriptions of scientifically debatable compounds according to the experimental results by MBL: a case study of carbonic acid in water and aqueous solution of carbon dioxide. J Korean Chem Soc. 2010; 54:479–486.
Article2. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Food and drug statistical yearbook. Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2014.3. ten Cate JM, Imfeld T. Dental erosion, summary. Eur J Oral Sci. 1996; 104:241–244.
Article4. Oncag G, Tuncer AV, Tosun YS. Acidic soft drinks effects on the shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets and a scanning electron microscopy evaluation of the enamel. Angle Orthod. 2005; 75:247–253.5. Barrett RD, Bishara SE, Quinn JK. Biodegradation of orthodontic appliances. Part I. Biodegradation of nickel and chromium in vitro. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1993; 103:8–14.
Article6. Hall AF, Buchanan CA, Millett DT, Creanor SL, Strang R, Foye RH. The effect of saliva on enamel and dentine erosion. J Dent. 1999; 27:333–339.
Article7. Lee HO. Effects of sparkling water on the surface of composite resin [dissertation]. Gwangju: Chonnam National Uni;2016.8. Kim SK, Park SW, Kang SM, Kwon HK, Kim BI. Assessment of the erosive potential of carbonated waters. J Korean Acad Oral Health. 2015; 39:273–279.
Article9. Steffen JM. The effects of soft drinks on etched and sealed enamel. Angle Orthod. 1996; 66:449–456.10. Pasha A, Sindhu D, Nayak RS, Mamatha J, Chaitra KR, Vishwakarma S. The effect of two soft drinks on bracket bond strength and on intact and sealed enamel: an in vitro study. J Int Oral Health. 2015; 7:Suppl 2. 26–33.11. Dinçer B, Hazar S, Sen BH. Scanning electron microscope study of the effects of soft drinks on etched and sealed enamel. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002; 122:135–141.
Article12. Navarro R, Vicente A, Ortiz AJ, Bravo LA. The effects of two soft drinks on bond strength, bracket microleakage, and adhesive remnant on intact and sealed enamel. Eur J Orthod. 2011; 33:60–65.
Article13. Cardoso CA, Magalhães AC, Rios D, Lima JE. Cross-sectional hardness of enamel from human teeth at different posteruptive ages. Caries Res. 2009; 43:491–494.
Article14. Li X, Wang J, Joiner A, Chang J. The remineralisation of enamel: a review of the literature. J Dent. 2014; 42:Suppl 1. S12–S20.
Article15. Grenby TH. Methods of assessing erosion and erosive potential. Eur J Oral Sci. 1996; 104:207–214.
Article16. Wongkhantee S, Patanapiradej V, Maneenut C, Tantbirojn D. Effect of acidic food and drinks on surface hardness of enamel, dentine, and tooth-coloured filling materials. J Dent. 2006; 34:214–220.
Article17. Brown CJ, Smith G, Shaw L, Parry J, Smith AJ. The erosive potential of flavoured sparkling water drinks. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2007; 17:86–91.
Article18. Meurman JH, ten Cate JM. Pathogenesis and modifying factors of dental erosion. Eur J Oral Sci. 1996; 104:199–206.
Article19. Zero DT. Etiology of dental erosion--extrinsic factors. Eur J Oral Sci. 1996; 104:162–177.20. Parry J, Shaw L, Arnaud MJ, Smith AJ. Investigation of mineral waters and soft drinks in relation to dental erosion. J Oral Rehabil. 2001; 28:766–772.
Article21. Lim DS, Ban YH, Min YE, Park JJ, Yu YJ, In SR, et al. The effect of carbonated water on bovine enamel erosion and plaque adhesion. J Dent Hyg Sci. 2015; 15:437–444.
Article22. Shinohara MS, de Oliveira MT, Di Hipólito V, Giannini M, de Goes MF. SEM analysis of the acid-etched enamel patterns promoted by acidic monomers and phosphoric acids. J Appl Oral Sci. 2006; 14:427–435.
Article23. Ozdemir F, Cakan U, Gonul N, Germec Cakan D. Orthodontic bonding to acid- or laser-etched prebleached enamel. Korean J Orthod. 2013; 43:141–146.
Article24. Türköz C, Ulusoy C. Evaluation of different enamel conditioning techniques for orthodontic bonding. Korean J Orthod. 2012; 42:32–38.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effects of salivary contamination of acid-etched enamel on bracket bond strength
- The effect of washing phosphoric acid etchant on shear bond strength of an orthodontic adhesive
- The effects of surface treatments on shear bond strengths of light-cured and chemically cured glass ionomer cements to enamel
- In vitro study on the effects of the flouride on the remineralization of acid etched enamel
- Prediction of Normal Values of Vital Capacity in Teenagers