Acute Crit Care.
2018 Nov;33(4):246-251. 10.4266/acc.2018.00192.
Comparison between Gel Pad Cooling Device and Water Blanket during Target Temperature Management in Cardiac Arrest Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kanesu@gmail.com
- 2Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Emergency Medicine, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2441242
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2018.00192
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Target temperature management (TTM) improves neurological outcomes for comatose survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. We compared the efficacy and safety of a gel pad cooling device (GP) and a water blanket (WB) during TTM.
METHODS
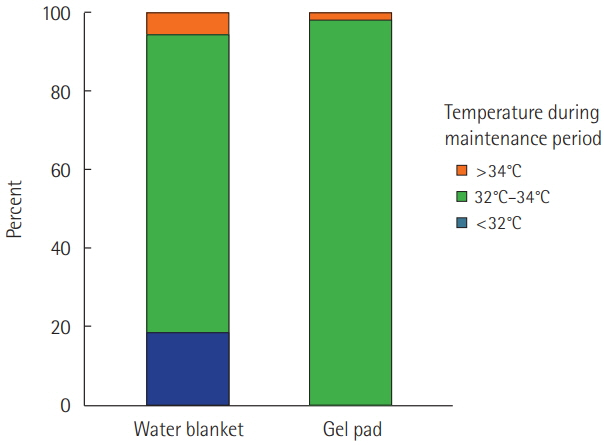
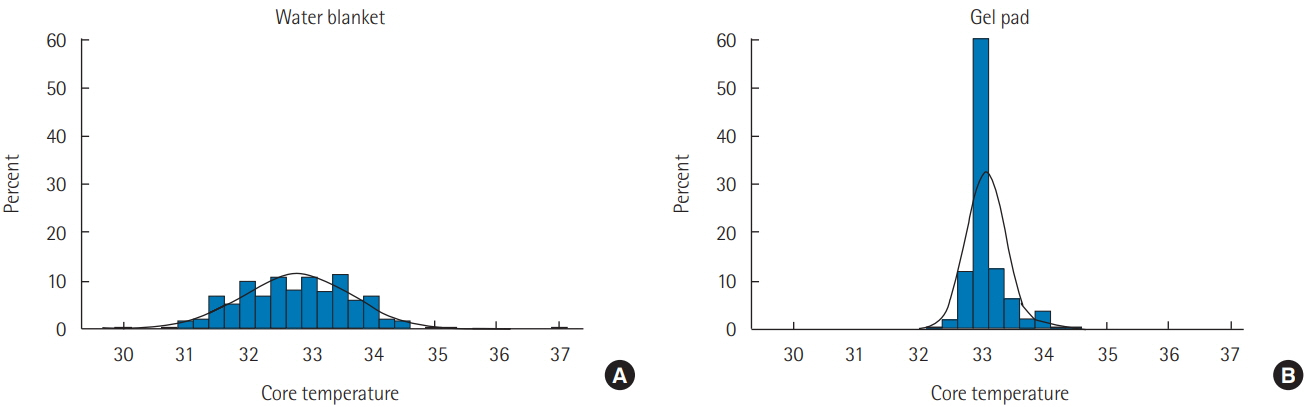
We performed a retrospective analysis in a single hospital, wherein we measured the time to target temperature ( < 34℃) after initiation of cooling to evaluate the effectiveness of the cooling method. The temperature farthest from 33℃ was selected every hour during maintenance. Generalized estimation equation analysis was used to compare the absolute temperature differences from 33℃ during the maintenance period. If the selected temperature was not between 32℃ and 34℃, the hour was considered a deviation from the target. We compared the deviation rates during hypothermia maintenance to evaluate the safety of the different methods.
RESULTS
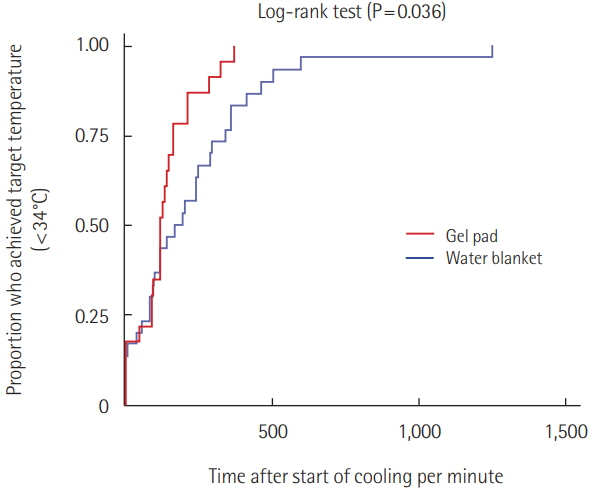
A GP was used for 23 patients among of 53 patients, and a WB was used for the remaining. There was no difference in baseline temperature at the start of cooling between the two patient groups (GP, 35.7℃ vs. WB, 35.6℃; P=0.741). The time to target temperature (134.2 minutes vs. 233.4 minutes, P=0.056) was shorter in the GP patient group. Deviation from maintenance temperature (2.0% vs. 23.7%, P < 0.001) occurred significantly more frequently in the WB group. The mean absolute temperature difference from 33℃ during the maintenance period was 0.19℃ (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.17℃ to 0.21℃) in the GP group and 0.76℃ (95% CI, 0.71℃ to 0.80℃) in the WB group. GP significantly decreased this difference by 0.59℃ (95% CI, 0.44℃ to 0.75℃; P < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
The GP was superior to the WB for strict temperature control during TTM.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lim C, Alexander MP, LaFleche G, Schnyer DM, Verfaellie M. The neurological and cognitive sequelae of cardiac arrest. Neurology. 2004; 63:1774–8.
Article2. Wachelder EM, Moulaert VR, van Heugten C, Verbunt JA, Bekkers SC, Wade DT. Life after survival: long-term daily functioning and quality of life after an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2009; 80:517–22.
Article3. Bernard SA, Gray TW, Buist MD, Jones BM, Silvester W, Gutteridge G, et al. Treatment of comatose survivors of out-ofhospital cardiac arrest with induced hypothermia. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:557–63.
Article4. Hypothermia after Cardiac Arrest Study Group. Mild therapeutic hypothermia to improve the neurologic outcome after cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:549–56.5. Callaway CW, Donnino MW, Fink EL, Geocadin RG, Golan E, Kern KB, et al. Part 8: post-cardiac arrest care: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines update for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation. 2015; 132(18 Suppl 2):S465–82.6. Holzer M, Müllner M, Sterz F, Robak O, Kliegel A, Losert H, et al. Efficacy and safety of endovascular cooling after cardiac arrest: cohort study and Bayesian approach. Stroke. 2006; 37:1792–7.7. Flint AC, Hemphill JC, Bonovich DC. Therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest: performance characteristics and safety of surface cooling with or without endovascular cooling. Neurocrit Care. 2007; 7:109–18.
Article8. Polderman KH. Application of therapeutic hypothermia in the intensive care unit: opportunities and pitfalls of a promising treatment modality. Part 2: practical aspects and side effects. Intensive Care Med. 2004; 30:757–69.9. Merchant RM, Abella BS, Peberdy MA, Soar J, Ong ME, Schmidt GA, et al. Therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest: unintentional overcooling is common using ice packs and conventional cooling blankets. Crit Care Med. 2006; 34(12 Suppl):S490–4.
Article10. Hoedemaekers CW, Ezzahti M, Gerritsen A, van der Hoeven JG. Comparison of cooling methods to induce and maintain normo- and hypothermia in intensive care unit patients: a prospective intervention study. Crit Care. 2007; 11:R91.
Article11. Gillies MA, Pratt R, Whiteley C, Borg J, Beale RJ, Tibby SM. Therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest: A retrospective comparison of surface and endovascular cooling techniques. Resuscitation. 2010; 81:1117–22.
Article12. Haugk M, Sterz F, Grassberger M, Uray T, Kliegel A, Janata A, et al. Feasibility and efficacy of a new non-invasive surface cooling device in post-resuscitation intensive care medicine. Resuscitation. 2007; 75:76–81.
Article13. Carroll M, Beek O. Protection against hippocampal CA1 cell loss by post-ischemic hypothermia is dependent on delay of initiation and duration. Metab Brain Dis. 1992; 7:45–50.14. Kuboyama K, Safar P, Radovsky A, Tisherman SA, Stezoski SW, Alexander H. Delay in cooling negates the beneficial effect of mild resuscitative cerebral hypothermia after cardiac arrest in dogs: a prospective, randomized study. Crit Care Med. 1993; 21:1348–58.15. Coppler PJ, Sawyer KN, Youn CS, Choi SP, Park KN, Kim YM, et al. Variability of Post-Cardiac Arrest Care Practices Among Cardiac Arrest Centers: United States and South Korean Dual Network Survey of Emergency Physician Research Principal Investigators. Ther Hypothermia Temp Manag. 2017; 7:30–5.
Article16. Heard KJ, Peberdy MA, Sayre MR, Sanders A, Geocadin RG, Dixon SR, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing the Arctic Sun to standard cooling for induction of hypothermia after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2010; 81:9–14.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Hydrogel Pad and Conventional Method on the Induction Time of Therapeutic Hypothermia in Patients with Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
- The Mechanism of Low Temperature Burn and Clinical Cases
- Effect of cooling water temperature on the temperature changes in pulp chamber and at handpiece head during high-speed tooth preparation
- Targeted temperature management for postcardiac arrest syndrome
- Deep Hypothermia for Total Correction of Tetralogy of Fallot