Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Feb;43(1):1-10. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.1.1.
Effect of Task-Specific Lower Extremity Training on Cognitive and Gait Function in Stroke Patients: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. vcdnhic@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2440946
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.1.1
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To elucidate the effect of task-specific lower extremity training (TSLET) on cognitive and gait function in stroke patients.
METHODS
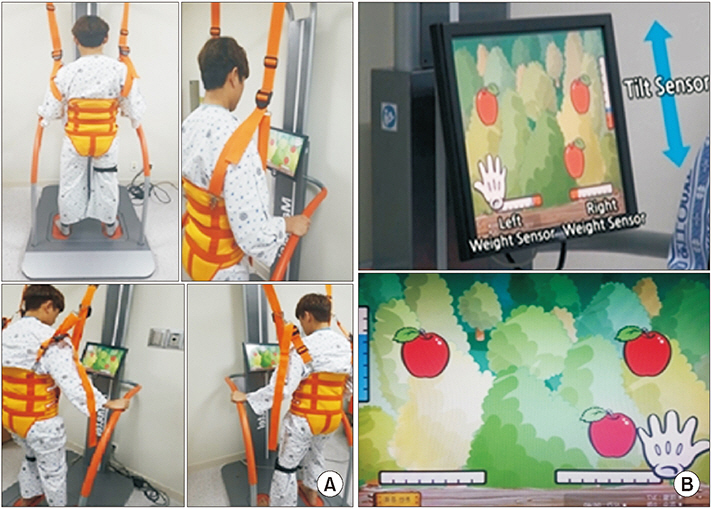
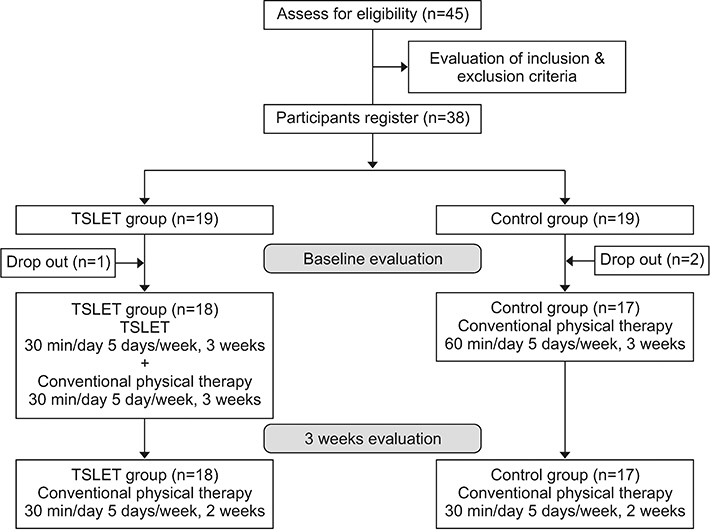
Thirty-eight patients were assigned to either the TSLET group or the control group. The individuals of TSLET group went through a TSLET plus conventional physical therapy. The control group received two sessions of conventional physical therapy. The primary outcome involved the assessment with visual and auditory digit span test. The secondary outcome was evaluated by the Korean version of Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) and Global Deterioration Scale (GDS) for cognitive function, Berg Balance Scale (BBS), Time Up and Go Test (TUG), 10 meters Walking Test (10mWT), 6 minutes Walking Test (6MWT), and Korean version of Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI) for gait, balance, and functional ability.
RESULTS
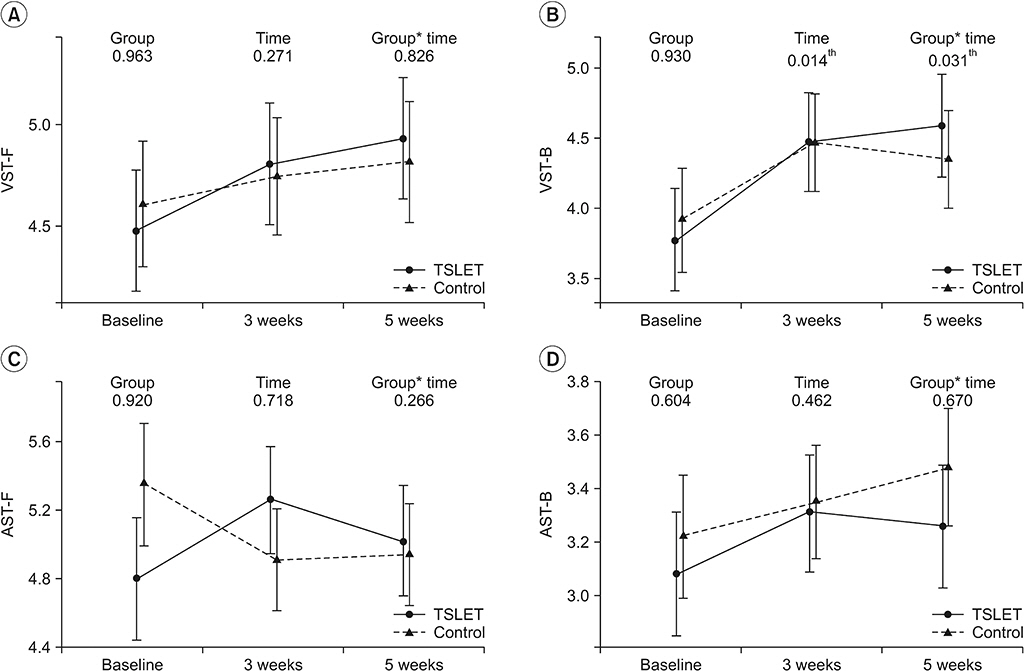
After intervention (3 weeks) and 2 weeks of follow-up, the TSLET group showed statistically significant improvement in the visual digit span test backwards compared with the control group. In secondary outcome, a significant improvement was observed in GDS, BBS, TUG, and 10mWT in the TSLET group. There was no significant difference between the two groups concerning visual digit span test forward, auditory forward and backward digit span tests, K-MMSE, 6MWT, and K-MBI.
CONCLUSION
TSLET could be a useful alternative strategy for improving cognitive and gait function in stroke patients.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tatemichi TK, Desmond DW, Stern Y, Paik M, Sano M, Bagiella E. Cognitive impairment after stroke: frequency, patterns, and relationship to functional abilities. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994; 57:202–7.
Article2. Jin YP, Di Legge S, Ostbye T, Feightner JW, Hachinski V. The reciprocal risks of stroke and cognitive impairment in an elderly population. Alzheimers Dement. 2006; 2:171–8.
Article3. Mok VC, Wong A, Lam WW, Fan YH, Tang WK, Kwok T, et al. Cognitive impairment and functional outcome after stroke associated with small vessel disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004; 75:560–6.
Article4. Tatemichi TK, Paik M, Bagiella E, Desmond DW, Pirro M, Hanzawa LK. Dementia after stroke is a predictor of long-term survival. Stroke. 1994; 25:1915–9.
Article5. Haggard P, Cockburn J, Cock J, Fordham C, Wade D. Interference between gait and cognitive tasks in a rehabilitating neurological population. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000; 69:479–86.
Article6. El-Tamawy MS, Abd-Allah F, Ahmed SM, Darwish MH, Khalifa HA. Aerobic exercises enhance cognitive functions and brain derived neurotrophic factor in ischemic stroke patients. NeuroRehabilitation. 2014; 34:209–13.
Article7. Fernandez-Gonzalo R, Fernandez-Gonzalo S, Turon M, Prieto C, Tesch PA, Garcia-Carreira Mdel C. Muscle, functional and cognitive adaptations after flywheel resistance training in stroke patients: a pilot randomized controlled trial. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2016; 13:37.
Article8. Wayne PM, Walsh JN, Taylor-Piliae RE, Wells RE, Papp KV, Donovan NJ, et al. Effect of tai chi on cognitive performance in older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014; 62:25–39.
Article9. Huh JS, Lee YS, Kim CH, Min YS, Kang MG, Jung TD. Effects of balance control training on functional outcomes in subacute hemiparetic stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2015; 39:995–1001.
Article10. Hung JW, Chou CX, Chang HF, Wu WC, Hsieh YW, Chen PC, et al. Cognitive effects of weight-shifting controlled exergames in patients with chronic stroke: a pilot randomized comparison trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2017; 53:694–702.
Article11. Kim YH, Shin SH, Park SH, Ko MH. Cognitive assessment for patient with brain injury by computerized neuropsychological test. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2001; 25:209–16.12. Kool W, Conway AR, Turk-Browne NB. Sequential dynamics in visual short-term memory. Atten Percept Psychophys. 2014; 76:1885–901.
Article13. Hirayama S, Terasawa K, Rabeler R, Hirayama T, Inoue T, Tatsumi Y, et al. The effect of phosphatidylserine administration on memory and symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2014; 27 Suppl 2:284–91.
Article14. Oh E, Kang Y, Shin JH, Yeon BK. A validity study of KMMSE as a screening test for dementia: comparison against a comprehensive neuropsychological evaluation. Dement Neurocognitive Disord. 2010; 9:8–12.15. Kang Y, Na DL, Hahn S. A validity study on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997; 15:300–8.16. Eisdorfer C, Cohen D, Paveza GJ, Ashford JW, Luchins DJ, Gorelick PB, et al. An empirical evaluation of the Global Deterioration Scale for staging Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Psychiatry. 1992; 149:190–4.17. Blum L, Korner-Bitensky N. Usefulness of the Berg Balance Scale in stroke rehabilitation: a systematic review. Phys Ther. 2008; 88:559–66.
Article18. Yelnik A, Bonan I. Clinical tools for assessing balance disorders. Neurophysiol Clin. 2008; 38:439–45.
Article19. Pohl PS, Duncan PW, Perera S, Liu W, Lai SM, Studenski S, et al. Influence of stroke-related impairments on performance in 6-minute walk test. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2002; 39:439–44.20. Jung HY, Park BK, Shin HS, Kang YK, Pyun SB, Paik NJ, et al. Development of the Korean version of Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI): multi-center study for subjects with stroke. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2007; 31:283–97.21. Bramell-Risberg E, Jarnlo GB, Elmstahl S. Separate physical tests of lower extremities and postural control are associated with cognitive impairment: results from the general population study Good Aging in Skane (GAS-SNAC). Clin Interv Aging. 2012; 7:195–205.22. Cotman CW, Berchtold NC, Christie LA. Exercise builds brain health: key roles of growth factor cascades and inflammation. Trends Neurosci. 2007; 30:464–72.
Article23. Gomez-Pinilla F, Vaynman S, Ying Z. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor functions as a metabotrophin to mediate the effects of exercise on cognition. Eur J Neurosci. 2008; 28:2278–87.
Article24. Vaynman S, Ying Z, Gomez-Pinilla F. Hippocampal BDNF mediates the efficacy of exercise on synaptic plasticity and cognition. Eur J Neurosci. 2004; 20:2580–90.
Article25. Colcombe SJ, Erickson KI, Raz N, Webb AG, Cohen NJ, McAuley E, et al. Aerobic fitness reduces brain tissue loss in aging humans. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2003; 58:176–80.
Article26. Gordon BA, Rykhlevskaia EI, Brumback CR, Lee Y, Elavsky S, Konopack JF, et al. Neuroanatomical correlates of aging, cardiopulmonary fitness level, and education. Psychophysiology. 2008; 45:825–38.
Article27. Erickson KI, Prakash RS, Voss MW, Chaddock L, Hu L, Morris KS, et al. Aerobic fitness is associated with hippocampal volume in elderly humans. Hippocampus. 2009; 19:1030–9.
Article28. Kattenstroth JC, Kolankowska I, Kalisch T, Dinse HR. Superior sensory, motor, and cognitive performance in elderly individuals with multi-year dancing activities. Front Aging Neurosci. 2010; 2:31.
Article29. Hufner K, Binetti C, Hamilton DA, Stephan T, Flanagin VL, Linn J, et al. Structural and functional plasticity of the hippocampal formation in professional dancers and slackliners. Hippocampus. 2011; 21:855–65.
Article30. Warburton DE, Bredin SS, Horita LT, Zbogar D, Scott JM, Esch BT, et al. The health benefits of interactive video game exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2007; 32:655–63.
Article31. Barker-Collo S, Feigin V. The impact of neuropsychological deficits on functional stroke outcomes. Neuropsychol Rev. 2006; 16:53–64.
Article32. Liu-Ambrose T, Pang MY, Eng JJ. Executive function is independently associated with performances of balance and mobility in community-dwelling older adults after mild stroke: implications for falls prevention. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2007; 23:203–10.
Article33. Lesniak M, Bak T, Czepiel W, Seniow J, Czlonkowska A. Frequency and prognostic value of cognitive disorders in stroke patients. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2008; 26:356–63.
Article34. Schofield NJ, Ashman AF. The relationship between digit span and cognitive processing across ability groups. Intelligence. 1986; 10:59–73.
Article35. Tombaugh TN, McIntyre NJ. The mini-mental state examination: a comprehensive review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992; 40:922–35.
Article36. Kim CH, Byun SD, Shin OS, Kim TG, Kwon SM, Noh JH, et al. Effect of the balance control of the affected lower extremity on balance and gait in hemiparetic patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2008; 32:394–9.37. Hyun CW, Han EY, Im SH, Choi JC, Kim BR, Yoon HM, et al. Hemiparetic knee extensor strength and balance function are predictors of ambulatory function in subacute stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2015; 39:577–85.
Article38. Graham JE, Ostir GV, Fisher SR, Ottenbacher KJ. Assessing walking speed in clinical research: a systematic review. J Eval Clin Pract. 2008; 14:552–62.
Article39. Solway S, Brooks D, Lacasse Y, Thomas S. A qualitative systematic overview of the measurement properties of functional walk tests used in the cardiorespiratory domain. Chest. 2001; 119:256–70.
Article40. Balami JS, Chen RL, Buchan AM. Stroke syndromes and clinical management. QJM. 2013; 106:607–15.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of activities of daily living-based dual-task training on upper extremity function, cognitive function, and quality of life in stroke patients
- Dual-Task Training Effect on Cognitive and Body Function, β-amyloid Levels in Alzheimer’s Dementia Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Dual Task Training Effects on Upper Extremity Functions and Performance of Daily Activities of Chronic Stroke Patients
- The Impact of Mental Practice on Motor Function in Patients With Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- The Effects of Task-Oriented Circuit Training Using Rehabilitation Tools on the Upper-Extremity Functions and Daily Activities of Patients with Acute Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial