Neonatal Med.
2019 Feb;26(1):55-62. 10.5385/nm.2019.26.1.55.
Risk Factors for Brain Damage in Preterm Infants After Late-Onset Circulatory Collapse Events
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. inasohn@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2440701
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2019.26.1.55
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed to identify risk factors for brain damage in infants with late-onset circulatory collapse (LCC), a circulatory failure that responds to glucocorticoid therapy.
METHODS
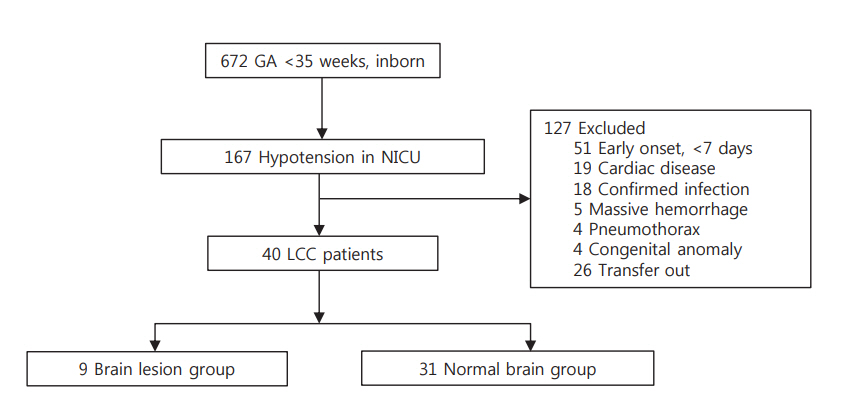
We retrospectively reviewed 167 infants (gestational age < 35 weeks) who had hypotension between April 2009 and March 2017 at Boramae Medical Center. Forty infants were diagnosed with LCC and divided into two groups based on ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging findings: infants with periventricular leukomalacia (n=9) and those with normal images (n=31) after LCC. The clinical factors of these two groups, including perinatal characteristics, clinical features during the LCC period, and neonatal morbidities, were compared.
RESULTS
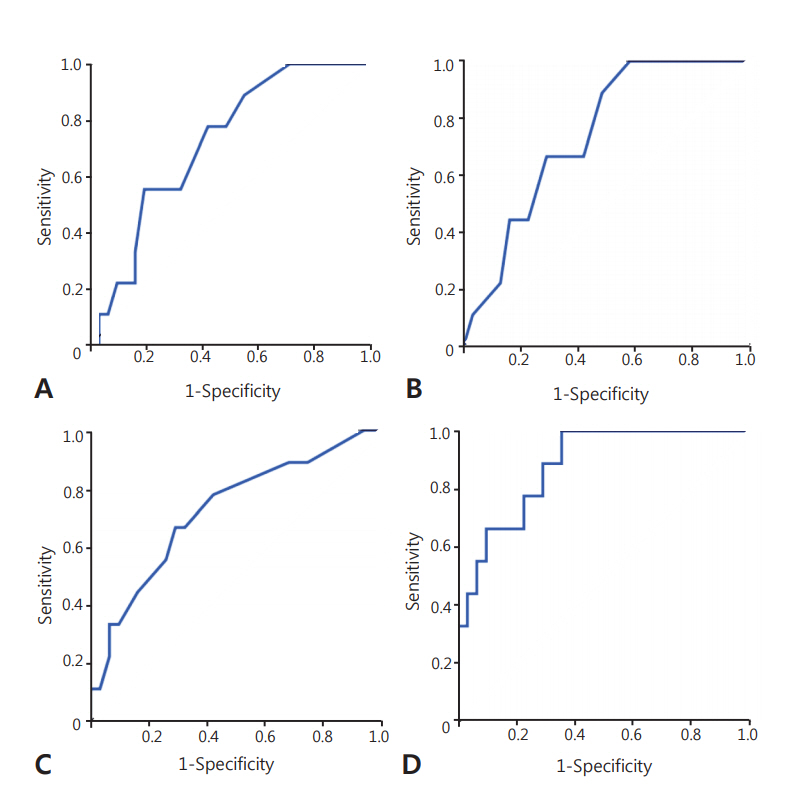
There were no significant differences in perinatal characteristics and postnatal morbidities between the two groups. Postnatal age was greater in the group with brain damage (16 days vs. 24 days, P=0.047). The lowest mean blood pressure (MBP) and lowest serum sodium concentration were significantly lower in the brain damage group (19 mm Hg vs. 22 mm Hg, P=0.034; 125 mmol/L vs. 129 mmol/L, P=0.043). There were no significant differences in other clinical factors, including cortisol levels, and inotrope and hydrocortisone use. In multivariate logistic regression, older postnatal age (odds ratio [OR], 1.147; P=0.049), lower MBP (OR, 0.616; P=0.031), and lower sodium concentration (OR, 0.728; P=0.037) during the LCC period highly predicted brain damage in infants with LCC (area under the curve 0.882, P=0.001).
CONCLUSION
Close monitoring of LCC signs even in long-term stable preterm infants and management for preventing severe hyponatremia and hypotension are important to minimize the occurrence of brain damage in infants with LCC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ng PC, Lee CH, Lam CW, Ma KC, Fok TF, Chan IH, et al. Transient adrenocortical insufficiency of prematurity and systemic hypotension in very low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2004; 89:F119–26.2. Shimokaze T, Akaba K, Saito E. Late-onset glucocorticoidresponsive circulatory collapse in preterm infants: clinical characteristics of 14 patients. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2015; 235:241–8.3. Kawai M. Late-onset circulatory collapse of prematurity. Pediatr Int. 2017; 59:391–6.4. Washio Y, Uchiyama A, Nakanishi H, Totsu S, Masumoto K, Kusuda S. Hemodynamic analysis in infants with late-onset circulatory collapse. Pediatr Int. 2013; 55:582–8.5. Young RS, Hernandez MJ, Yagel SK. Selective reduction of blood flow to white matter during hypotension in newborn dogs: a possible mechanism of periventricular leukomalacia. Ann Neurol. 1982; 12:445–8.6. Shin SM, Chai JW. Brain ultrasonographic findings of late-onset circulatory dysfunction due to adrenal insufficiency in preterm infants. Ultrasonography. 2016; 35:258–64.7. Nakanishi H, Yamanaka S, Koriyama T, Shishida N, Miyagi N, Kim TJ, et al. Clinical characterization and long-term prognosis of neurological development in preterm infants with late-onset circulatory collapse. J Perinatol. 2010; 30:751–6.8. Fernandez E, Schrader R, Watterberg K. Prevalence of low cortisol values in term and near-term infants with vasopressor-resistant hypotension. J Perinatol. 2005; 25:114–8.9. Kluckow M. Low systemic blood flow and pathophysiology of the preterm transitional circulation. Early Hum Dev. 2005; 81:429–37.10. Munro MJ, Walker AM, Barfield CP. Hypotensive extremely low birth weight infants have reduced cerebral blood flow. Pediatrics. 2004; 114:1591–6.11. Kobayashi S, Fujimoto S, Koyama N, Fukuda S, Iwaki T, Tanaka T, et al. Late-onset circulatory dysfunction of premature infants and late-onset periventricular leukomalacia. Pediatr Int. 2008; 50:225–31.12. Kinney HC. The near-term (late preterm) human brain and risk for periventricular leukomalacia: a review. Semin Perinatol. 2006; 30:81–8.13. Victor S, Marson AG, Appleton RE, Beirne M, Weindling AM. Relationship between blood pressure, cerebral electrical activity, cerebral fractional oxygen extraction, and peripheral blood flow in very low birth weight newborn infants. Pediatr Res. 2006; 59:314–9.14. Tsuji M, Saul JP, du Plessis A, Eichenwald E, Sobh J, Crocker R, et al. Cerebral intravascular oxygenation correlates with mean arterial pressure in critically ill premature infants. Pediatrics. 2000; 106:625–32.15. Greisen G. Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in newborn babies. Early Hum Dev. 2005; 81:423–8.16. Oelkers W. Hyponatremia and inappropriate secretion of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) in patients with hypopituitarism. N Engl J Med. 1989; 321:492–6.17. Ishikawa S, Schrier RW. Effect of arginine vasopressin antagonist on renal water excretion in glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid deficient rats. Kidney Int. 1982; 22:587–93.18. Wolfson B, Manning RW, Davis LG, Arentzen R, Baldino F Jr. Colocalization of corticotropin releasing factor and vasopressin mRNA in neurones after adrenalectomy. Nature. 1985; 315:59–61.19. Kalogeras KT, Nieman LK, Friedman TC, Doppman JL, Cutler GB Jr, Chrousos GP, et al. Inferior petrosal sinus sampling in healthy subjects reveals a unilateral corticotropin-releasing hormone-induced arginine vasopressin release associated with ipsilateral adrenocorticotropin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1996; 97:2045–50.20. Papanek PE, Raff H. Physiological increases in cortisol inhibit basal vasopressin release in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol. 1994; 266(6 Pt 2):R1744–51.21. Schrier RW. Body water homeostasis: clinical disorders of urinary dilution and concentration. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 17:1820–32.22. Adrogue HJ, Madias NE. Hyponatremia. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:1581–9.23. Sjoblom E, Hojer J, Ludwigs U, Pirskanen R. Fatal hyponatraemic brain oedema due to common gastroenteritis with accidental water intoxication. Intensive Care Med. 1997; 23:348–50.24. Ayus JC, Armstrong D, Arieff AI. Hyponatremia with hypoxia: effects on brain adaptation, perfusion, and histology in rodents. Kidney Int. 2006; 69:1319–25.25. Ayus JC, Achinger SG, Arieff A. Brain cell volume regulation in hyponatremia: role of sex, age, vasopressin, and hypoxia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008; 295:F619–24.26. Upadhyay A, Jaber BL, Madias NE. Incidence and prevalence of hyponatremia. Am J Med. 2006; 119(7 Suppl 1):S30–5.27. Giuliani C, Peri A. Effects of hyponatremia on the brain. J Clin Med. 2014; 3:1163–77.28. Kobayashi S, Fujimoto S, Fukuda S, Hattori A, Iwaki T, Koyama N, et al. Periventricular leukomalacia with late-onset circulatory dysfunction of premature infants: correlation with severity of magnetic resonance imaging findings and neurological outcomes. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2006; 210:333–9.29. Noori S, Friedlich P, Wong P, Ebrahimi M, Siassi B, Seri I. Hemodynamic changes after low-dosage hydrocortisone administration in vasopressor-treated preterm and term neonates. Pediatrics. 2006; 118:1456–66.30. Seri I, Tan R, Evans J. Cardiovascular effects of hydrocortisone in preterm infants with pressor-resistant hypotension. Pediatrics. 2001; 107:1070–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Features of Late-Onset Circulatory Collapse in Preterm Infants
- Late-onset Hypotension and Late Circulatory Collapse Due to Adrenal Insufficiency in Preterm Infants with Gestational Age Less than 32 Weeks
- Clinical Features of Late-onset Circulatory Collapse in Preterm Infants
- Brain ultrasonographic findings of late-onset circulatory dysfunction due to adrenal insufficiency in preterm infants
- Comparisons of Clinical Characteristics Affecting Readmission between Late Preterm Infants and Moderate Preterm Infants or Full-Term Infants