Neonatal Med.
2019 Feb;26(1):34-40. 10.5385/nm.2019.26.1.34.
Clinical Characteristics of Infantile Colic
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Inha University Hospital, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. juyounglee@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2440698
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2019.26.1.34
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To diagnose infantile colic from parent questionnaires, as well as investigating the risk factors and clinical course of infantile colic.
METHODS
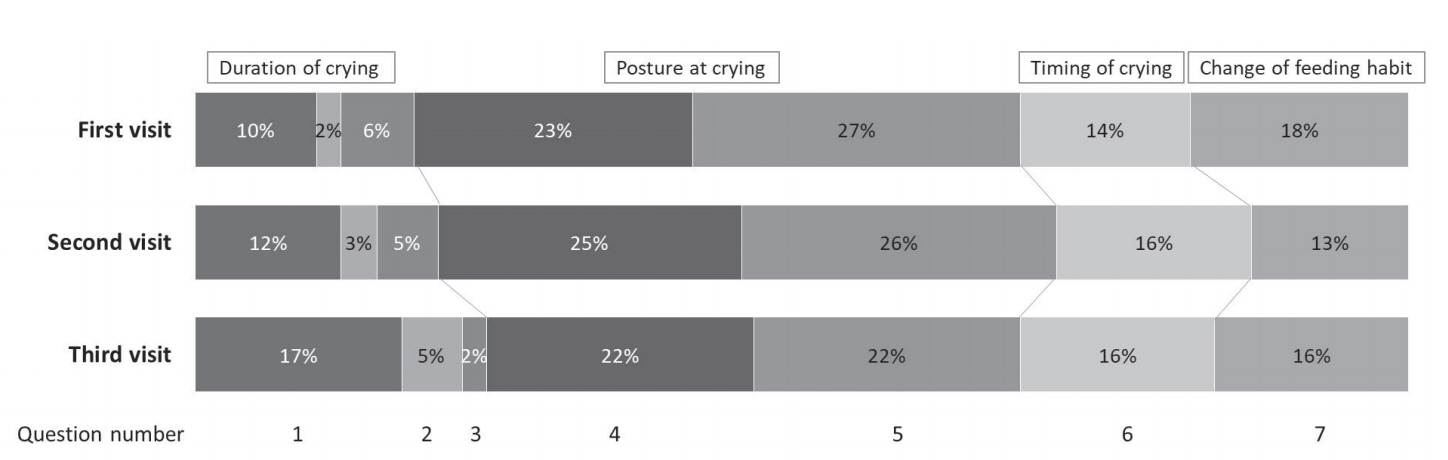
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 462 infants, with a corrected age of < 4 months at the time of visiting Inha University Hospital from January to December 2017. Parents responded to a 10-line questionnaire consisting of seven items relating to colic symptoms and three further items relating to underlying disease. The score was based on the number of days each symptom was evident during the preceding week. We defined infantile colic as the sum total being greater than seven points; if at least one of the three symptoms suggesting underlying disease was present, the infant was excluded from the diagnosis.
RESULTS
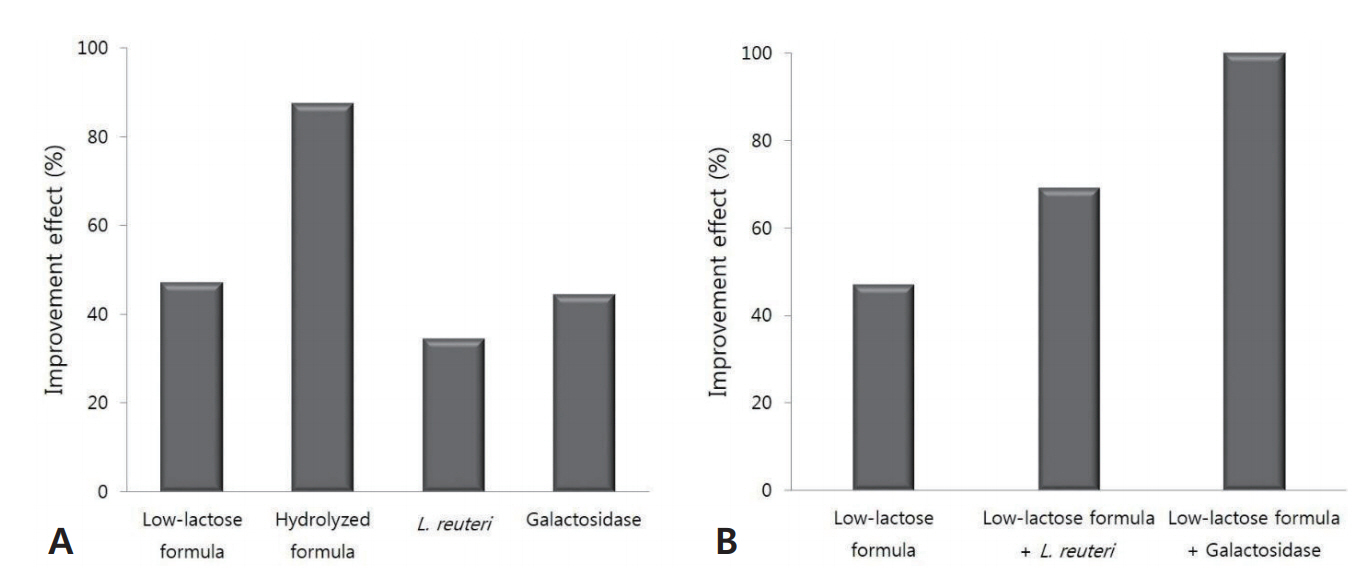
One hundred and sixty-seven infants (36.1%) satisfied the criteria. The lower the gestational age, the more infantile colic they developed (P < 0.001). The prevalence of colic was higher in infants born with a birth weight < 2.5 kg (62.7% vs. 24.4%, P < 0.001) and in infants small for their gestational age, in the < 10th percentile (54.5% vs. 33.7%, P=0.003). The prevalence of colic was significantly different according to the type of feeding (P=0.001), being the lowest in breast-only feeding (29.8%), 32.8% in mixed feeding with breast milk and formula, and 49.7% in formula-only feeding. Colic symptoms improved by administering hydrolyzed formula (87.5%), low-lactose formula (47.1%), galactosidase (44.4%), and the probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri (34.5%).
CONCLUSION
The prevalence of infantile colic was over 30%. Prematurity, lower birth weight, and small for gestational age were the risk factors of infantile colic. Clinical improvement was observed when active intervention was performed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Illingworth RS. Infantile colic revisited. Arch Dis Child. 1985; 60:981–5.2. Lindberg T. Infantile colic: aetiology and prognosis. Acta Paediatr. 2000; 89:1–2.3. Wessel MA, Cobb JC, Jackson EB, Harris GS Jr, Detwiler AC. Paroxysmal fussing in infancy, sometimes called colic. Pediatrics. 1954; 14:421–35.4. Canivet C, Hagander B, Jakobsson I, Lanke J. Infantile colic: less common than previously estimated? Acta Paediatr. 1996; 85:454–8.5. Raiha H, Lehtonen L, Korhonen T, Korvenranta H. Family life 1 year after infantile colic. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1996; 150:1032–6.6. Forsyth BW. Colic and the effect of changing formulas: a doubleblind, multiple-crossover study. J Pediatr. 1989; 115:521–6.7. Treem WR, Hyams JS, Blankschen E, Etienne N, Paule CL, Borschel MW. Evaluation of the effect of a fiber-enriched formula on infant colic. J Pediatr. 1991; 119:695–701.8. Miller AR, Barr RG. Infantile colic. Is it a gut issue? Pediatr Clin North Am. 1991; 38:1407–23.9. Treem WR. Infant colic. A pediatric gastroenterologist's perspective. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1994; 41:1121–38.10. Geertsma MA, Hyams JS. Colic: a pain syndrome of infancy? Pediatr Clin North Am. 1989; 36:905–19.11. Balon AJ. Management of infantile colic. Am Fam Physician. 1997; 55:235–46.12. Savino F, Castagno E, Bretto R, Brondello C, Palumeri E, Oggero R. A prospective 10-year study on children who had severe infantile colic. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 2005; 94:129–32.13. Hill DJ, Roy N, Heine RG, Hosking CS, Francis DE, Brown J, et al. Effect of a low-allergen maternal diet on colic among breastfed infants: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2005; 116:e709–15.14. Savino F, Cordisco L, Tarasco V, Palumeri E, Calabrese R, Oggero R, et al. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 in infantile colic: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2010; 126:e526–33.15. Szajewska H, Gyrczuk E, Horvath A. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 for the management of infantile colic in breastfed infants: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Pediatr. 2013; 162:257–62.16. Sung V, Collett S, de Gooyer T, Hiscock H, Tang M, Wake M. Probiotics to prevent or treat excessive infant crying: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2013; 167:1150–7.17. Anabrees J, Indrio F, Paes B, AlFaleh K. Probiotics for infantile colic: a systematic review. BMC Pediatr. 2013; 13:186.18. Sung V, Hiscock H, Tang ML, Mensah FK, Nation ML, Satzke C, et al. Treating infant colic with the probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri: double blind, placebo controlled randomised trial. BMJ. 2014; 348:g2107.19. Urbanska M, Szajewska H. The efficacy of Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 in infants and children: a review of the current evidence. Eur J Pediatr. 2014; 173:1327–37.20. Johnson JD, Cocker K, Chang E. Infantile colic: recognition and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2015; 92:577–82.21. Chau K, Lau E, Greenberg S, Jacobson S, Yazdani-Brojeni P, Verma N, et al. Probiotics for infantile colic: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial investigating Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938. J Pediatr. 2015; 166:74–8.22. Blass EM, Hoffmeyer LB. Sucrose as an analgesic for newborn infants. Pediatrics. 1991; 87:215–8.23. Haouari N, Wood C, Griffiths G, Levene M. The analgesic effect of sucrose in full term infants: a randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 1995; 310:1498–500.24. Lucassen PL, Assendelft WJ, van Eijk JT, Gubbels JW, Douwes AC, van Geldrop WJ. Systematic review of the occurrence of infantile colic in the community. Arch Dis Child. 2001; 84:398–403.25. Saavedra MA, da Costa JS, Garcias G, Horta BL, Tomasi E, Mendonca R. Infantile colic incidence and associated risk factors: a cohort study. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2003; 79:115–22.26. Fazil M. Prevalence and risk factors for infantile colic in District Mansehra. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2011; 23:115–7.27. Talachian E, Bidari A, Rezaie MH. Incidence and risk factors for infantile colic in Iranian infants. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:4662–6.28. Milidou I, Sondergaard C, Jensen MS, Olsen J, Henriksen TB. Gestational age, small for gestational age, and infantile colic. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2014; 28:138–45.29. Sondergaard C, Skajaa E, Henriksen TB. Fetal growth and infantile colic. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2000; 83:F44–7.30. Belson A, Shetty AK, Yorgin PD, Bujanover Y, Peled Y, Dar MH, et al. Colonic hydrogen elimination and methane production in infants with and without infantile colic syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2003; 48:1762–6.31. Rautava P, Helenius H, Lehtonen L. Psychosocial predisposing factors for infantile colic. BMJ. 1993; 307:600–4.32. Miller JJ, McVeagh P, Fleet GH, Petocz P, Brand JC. Breath hydrogen excretion in infants with colic. Arch Dis Child. 1989; 64:725–9.33. Roggero P, Mosca F, Motta G, Mangiaterra V, Perazzani M, Offredi ML, et al. Sugar absorption in healthy preterm and full-term infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1986; 5:214–9.34. Barr RG, Hanley J, Patterson DK, Wooldridge J. Breath hydrogen excretion in normal newborn infants in response to usual feeding patterns: evidence for "functional lactase insufficiency" beyond the first month of life. J Pediatr. 1984; 104:527–33.35. Infante Pina D, Badia Llach X, Arino-Armengol B, Villegas Iglesias V. Prevalence and dietetic management of mild gastrointestinal disorders in milk-fed infants. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:248–54.36. Valeur N, Engel P, Carbajal N, Connolly E, Ladefoged K. Colonization and immunomodulation by Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 in the human gastrointestinal tract. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004; 70:1176–81.37. Spinler JK, Taweechotipatr M, Rognerud CL, Ou CN, Tumwasorn S, Versalovic J. Human-derived probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri demonstrate antimicrobial activities targeting diverse enteric bacterial pathogens. Anaerobe. 2008; 14:166–71.38. Hunter C, Dimaguila MA, Gal P, Wimmer JE Jr, Ransom JL, Carlos RQ, et al. Effect of routine probiotic, Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938, use on rates of necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates with birthweight < 1000 grams: a sequential analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2012; 12:142.39. Weizman Z, Asli G, Alsheikh A. Effect of a probiotic infant formula on infections in child care centers: comparison of two probiotic agents. Pediatrics. 2005; 115:5–9.40. Savino F, Pelle E, Palumeri E, Oggero R, Miniero R. Lactobacillus reuteri (American Type Culture Collection Strain 55730) versus simethicone in the treatment of infantile colic: a prospective randomized study. Pediatrics. 2007; 119:e124. –30.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incidence and Associated Factors of Infantile Colic in Thai Infants
- Efficacy of probiotics for managing infantile colic due to their anti-inflammatory properties: a meta-analysis and systematic review
- Infantile Colic and the Subsequent Development of the Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Analgesic Effect of Sugar Solution in Infantile Colic
- Infantile Colic: A Survey of Physicians in Pakistan