Ann Dermatol.
2019 Apr;31(2):209-212. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.209.
Symmetrical Giant Facial Plaque-Type Juvenile Xanthogranuloma: A Case Report with a Successful Response to Fractional COâ‚‚ Laser Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Severance Hospital, Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ODDUNG93@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2439068
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.209
Abstract
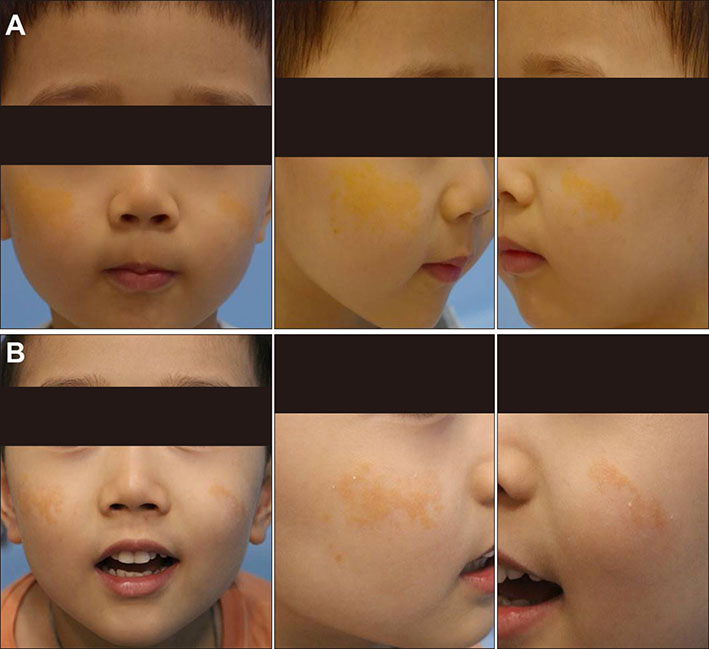
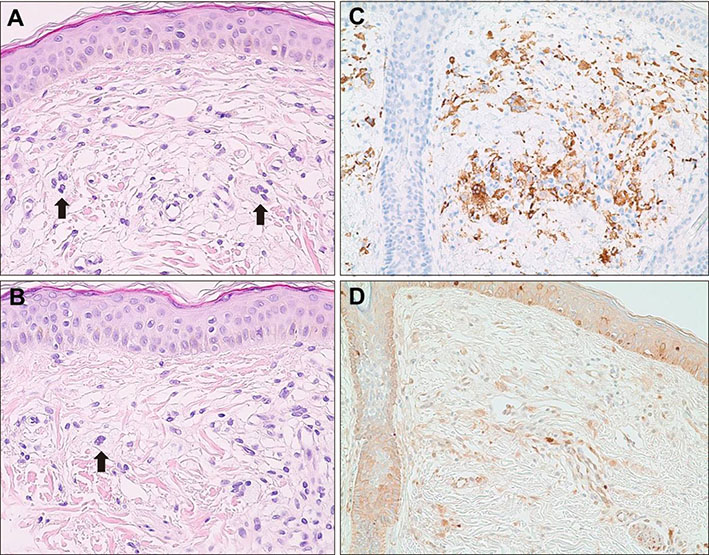
- Symmetrical giant facial plaque-type juvenile xanthogranuloma (SGFP-JXG) is a rare variant of juvenile xanthogranuloma, reported only in two cases in the literature. We report a case of a 3-year-old Korean boy who developed bilateral yellowish indurated plaques on both cheeks since 1 year after birth. A skin biopsy revealed numerous foam cells and Touton type giant cells throughout the upper dermis, and its immunohistochemical studies resulted positive for CD68 and negative for S-100. The boy was therefore diagnosed as a persistent SGFP-JXG. As the lesion did not show any signs of spontaneous regression, we performed a single session of fractional ablative COâ‚‚ laser, which resulted in a significant reduction of the lesion. This is the first case report of a persistent SGFP-JXG on which a single ablative laser therapy was performed with a successful outcome.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gunson TH, Birchall NM. Symmetrical giant facial plaque-type juvenile xanthogranuloma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 59:2 Suppl 1. S56–S57.
Article2. Szczerkowska-Dobosz A, Kozicka D, Purzycka-Bohdan D, Biernat W, Stawczyk M, Nowicki R. Juvenile xanthogranuloma: a rare benign histiocytic disorder. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014; 31:197–200.3. Dehner LP. Juvenile xanthogranulomas in the first two decades of life: a clinicopathologic study of 174 cases with cutaneous and extracutaneous manifestations. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003; 27:579–593.
Article4. Sangüeza OP, Salmon JK, White CR Jr, Beckstead JH. Juvenile xanthogranuloma: a clinical, histopathologic and immunohistochemical study. J Cutan Pathol. 1995; 22:327–335.
Article5. Yazganoglu KD, Erdem Y, Buyukbabani N, Baykal C. A giant congenital plaque. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012; 29:217–218.
Article6. Sugiura K, Hasegawa Y, Shimoyama Y, Hashizume H, Akiyama M. Symmetrical giant facial plaque-type juvenile xanthogranuloma persisting beyond 10 years of age. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014; 94:465–466.
Article7. Miyagawa F, Fukumoto T, Kobayashi N, Asada H. Successful treatment of diffuse normolipemic plane xanthoma with probucol. Case Rep Dermatol. 2013; 5:148–151.
Article8. Altman J, Winkelmann RK. Diffuse normolipemic plane xanthoma. Generalized xanthelasma. Arch Dermatol. 1962; 85:633–640.9. Oka M, Okamura A, Kawano S, Fukumoto T, Sakaguchi M, Nishigori C. Diffuse plane normolipemic xanthoma associated with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia-1. Eur J Dermatol. 2014; 24:112–113.
Article10. Vail JT Jr, Adler KR, Rothenberg J. Cutaneous xanthomas associated with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Arch Dermatol. 1985; 121:1318–1320.
Article11. Kim KJ, Lee DP, Suh HS, Lee MW, Choi JH, Moon KC, et al. Diffuse plane xanthoma in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia. J Dermatol. 2004; 31:503–505.
Article12. Lorenz S, Hohenleutner S, Hohenleutner U, Landthaler M. Treatment of diffuse plane xanthoma of the face with the Erbium:YAG laser. Arch Dermatol. 2001; 137:1413–1415.
Article13. Bragg J. Diffuse plane xanthomata. Dermatol Online J. 2005; 11:4.
Article14. Klemke CD, Held B, Dippel E, Goerdt S. Multiple juvenile xanthogranulomas successfully treated with CO laser. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2007; 5:30–33.15. Trelles MA, Leclère FM, Martínez-Carpio PA. Fractional carbon dioxide laser and acoustic-pressure ultrasound for transepidermal delivery of cosmeceuticals: a novel method of facial rejuvenation. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013; 37:965–972.
Article