Ann Dermatol.
2019 Apr;31(2):133-138. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.133.
A Face-Split Study to Evaluate the Effects of Microneedle Radiofrequency with Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser for the Treatment of Melasma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. ryoo111@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2439058
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.133
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Laser toning using a low-fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser is one of the most frequently used treatment modalities for melasma. However, this therapy is time consuming because it requires a lot of treatment sessions. Recently, it has been reported that transdermal radiofrequency (RF) is effective for the treatment of melasma.
OBJECTIVE
To determine whether microneedle RF conduction could be an adjunct therapy for melasma, we have studied the effect of simultaneous treatments with laser toning and RF for melasma.
METHODS
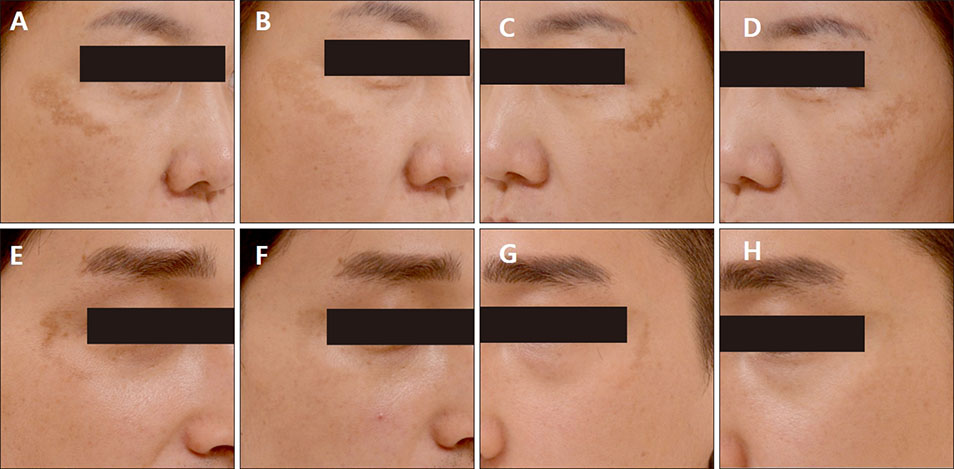
Fifteen patients with melasma underwent five sessions of laser toning and microneedle RF on the right side of the face, and only laser toning on the left side. Responses to treatments were evaluated using the Mexameter® (Courage Khazaka, Germany) score, the pigmentation and severity index (PSI) score, and the patient's overall assessment. Additionally, an electron microscopic study of a skin biopsy was performed.
RESULTS
Both laser toning and combination therapy showed significant decreases in the Mexameter® and PSI score after five treatment sessions. Combination therapy showed a more significant improvement of melasma than laser toning. No remarkable side effects were reported. Electron microscopic analysis showed a greater number of vacuolar changes and increased loosening of melanocytes and adjacent epidermal cells after combination therapy.
CONCLUSION
The combination treatment of laser toning and microneedle RF therapy showed a better therapeutic effect for melasma than laser toning alone. Therefore, the microneedle RF technique could be a new and safe adjunct therapy for the treatment of melasma.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee AY. Recent progress in melasma pathogenesis. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2015; 28:648–660.
Article2. Handel AC, Miot LD, Miot HA. Melasma: a clinical and epidemiological review. An Bras Dermatol. 2014; 89:771–782.
Article3. Trivedi MK, Yang FC, Cho BK. A review of laser and light therapy in melasma. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2017; 3:11–20.
Article4. Manaloto RM, Alster T. Erbium:YAG laser resurfacing for refractory melasma. Dermatol Surg. 1999; 25:121–123.
Article5. Gokalp H, Akkaya AD, Oram Y. Long-term results in low-fluence 1064-nm Q-Switched Nd:YAG laser for melasma: is it effective? J Cosmet Dermatol. 2016; 15:420–426.
Article6. Lolis MS, Goldberg DJ. Radiofrequency in cosmetic dermatology: a review. Dermatol Surg. 2012; 38:1765–1776.
Article7. Choi M, Choi SH, Kang JS, Cho SB. Successful treatment of refractory melasma using invasive micro-pulsed electric signal device. Med Laser. 2015; 4:39–44.
Article8. Krueger N, Sadick NS. New-generation radiofrequency technology. Cutis. 2013; 91:39–46.9. Cohen BE, Elbuluk N. Microneedling in skin of color: a review of uses and efficacy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016; 74:348–355.
Article10. Clinard V, Smith JD. Drug-induced skin disorder. US Pharm. 2012; 37:HS11–HS18.11. Matias AR, Ferreira M, Costa P, Neto P. Skin colour, skin redness and melanin biometric measurements: comparison study between Antera(®) 3D, Mexameter(®) and Colorimeter(®). Skin Res Technol. 2015; 21:346–362.
Article12. Na J, Zheng Z, Dannaker C, Lee SE, Kang JS, Cho SB. Electromagnetic initiation and propagation of bipolar radiofrequency tissue reactions via invasive non-insulated microneedle electrodes. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:16735.
Article13. Harth Y, Frank I. In vivo histological evaluation of non-insulated microneedle radiofrequency applicator with novel fractionated pulse mode. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013; 12:1430–1433.14. Kim JE, Lee HW, Kim JK, Moon SH, Ko JY, Lee MW, et al. Objective evaluation of the clinical efficacy of fractional radiofrequency treatment for acne scars and enlarged pores in Asian skin. Dermatol Surg. 2014; 40:988–995.
Article15. Kwon SH, Hwang YJ, Lee SK, Park KC. Heterogeneous pathology of melasma and its clinical implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17:E824.
Article16. Kang WH, Yoon KH, Lee ES, Kim J, Lee KB, Yim H, et al. Melasma: histopathological characteristics in 56 Korean patients. Br J Dermatol. 2002; 146:228–237.
Article17. Park SY, Kwon HH, Yoon JY, Min S, Suh DH. Clinical and histologic effects of fractional microneedling radiofrequency treatment on rosacea. Dermatol Surg. 2016; 42:1362–1369.
Article18. Mun JY, Jeong SY, Kim JH, Han SS, Kim IH. A low fluence Q-switched Nd:YAG laser modifies the 3D structure of melanocyte and ultrastructure of melanosome by subcellular-selective photothermolysis. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 2011; 60:11–18.
Article19. Sandby-Møller J, Poulsen T, Wulf HC. Epidermal thickness at different body sites: relationship to age, gender, pigmentation, blood content, skin type and smoking habits. Acta Derm Venereol. 2003; 83:410–413.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Split-face Comparison of Pulse-in-pulse Type Intense Pulsed Light Versus Low-fluence Multi-pass 1064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG Laser in the Treatment of Facial Melasma
- Treatment of Melasma with Pulsed-Dye Laser and 1,064-nm Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser: A Split-Face Study
- Treatment of Melasma with the Photoacoustic Twin Pulse Mode of Low-Fluence 1,064 nm Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser
- New Melasma Treatment by Collimated Low Fluence Q-switched Nd : YAG Laser
- A split-face study evaluating the efficacy of a topical antioxidant cream containing tocotrienol after 1064-nm picosecond Nd:YAG laser treatment for environment-induced skin pigmentation