J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2017 Apr;52(2):146-152. 10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.2.146.
The Effectiveness of Arthroscopy in Borderline Hip Dysplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Carollo Hospital, Suncheon, Korea. wctoilets@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2438979
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.2.146
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The outcome of hip arthroscopy as a treatment of patients with hip dysplasia is variable. In patients with severe hip dysplasia, arthroscopy has the potential to exacerbate instability and unfavorable outcome. To the best of out knowledge, there has not been a report regarding arthroscopic treatment in patients with borderline hip dysplasia in Korea. We favorable outcome with using arthroscopy to treat symptomatic borderline hip dysplasia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
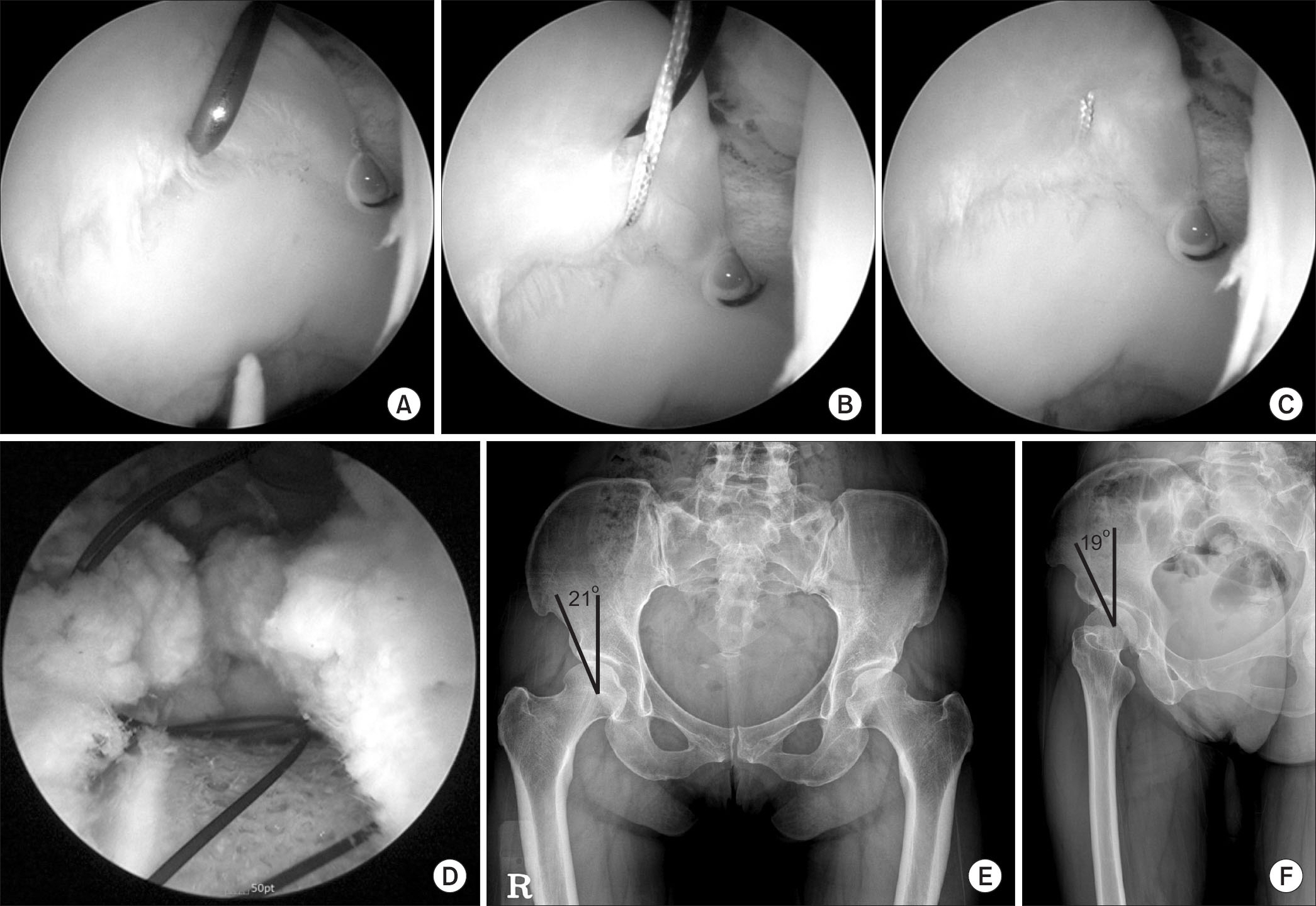
Between August 2010 and February 2015, 143 patients undergoing hip arthroscopy for intra-articular hip disorder were retrospectively enrolled. From this cohort, a borderline dysplasia group compromising 29 patient with lateral center edge angle (LCEA) >18° and <25° and a minimum of 1 years follow-up, was identified. Patient-reported outcome scores, including modified Harris hip score, the hip outcome score-activity of daily living, the sport-specific subscale, visual analogue scale (VAS) and satisfaction survey were obtained preoperatively and at postoperative 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 2 years, and 3 years. Revision surgery and complications were recorded for each group.
RESULTS
The mean age was 35.7 years (range, 16-63 years) years respectively. There were 16 females (55.2%) and 13 males (44.8%). The mean LCEA was 22.0° (range, 18°-25°) and the mean Tönnis angle was 6.1° (range, 0°-18°). The mean follow-up was 20.2 months (range, 12-39 months), and at the 1 year follow-up, there was significant improvement (p<0.001) in all patient reported outcome scores and VAS. Satisfaction survey showed an average score of 7.7.
CONCLUSION
In patients with borderline hip dysplasia, if there is an occurrence of symptomatic labral tear, arthroscopic labral refixation has a good short-term result. Therefore, if patients have no response to conservative treatment or have severe pain, arthroscopic labral refixation is a useful treatment options to relieve symptom.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goldstein RY, Kaye ID, Slover J, Feldman D. Hip dysplasia in the skeletally mature patient. Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013). 2014; 72:28–42.2. Wiberg G. Studies on dysplastic acetabula and congenital subluxation of the hip joint: with special reference to the complication of osteoarthritis. Acta Chir Scand. 1939; 83:S5–135.3. Dorrell JH, Catterall A. The torn acetabular labrum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986; 68:400–3.
Article4. Klaue K, Durnin CW, Ganz R. The acetabular rim syndrome. A clinical presentation of dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:423–9.
Article5. Nishina T, Saito S, Ohzono K, Shimizu N, Hosoya T, Ono K. Chiari pelvic osteotomy for osteoarthritis. The influence of the torn and detached acetabular labrum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990; 72:765–9.
Article6. Byrd JWT, Jones KS. Inverted acetabular labrum and secondary osteoarthritis: radiographic diagnosis and arthroscopic treatment. Arthroscopy. 2000; 16:417.7. Clohisy JC, Schutz AL, St. John L, Schoenecker PL, Wright RW. Periacetabular osteotomy: a systematic literature review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:2041–52.
Article8. Cooperman DR, Wallensten R, Stulberg SD. Acetabular dysplasia in the adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; 175:79–85.
Article9. Agricola R, Heijboer MP, Roze RH. . Pincer deformity does not lead to osteoarthritis of the hip whereas acetabular dysplasia does: acetabular coverage and development of osteoarthritis in a nationwide prospective cohort study (CHECK). Osteoarthr Cartil. 2013; 21:1514–21.
Article10. Jo S, Lee SH, Wang SI, Smith B, O'Donnell J. The role of arthroscopy in the dysplastic hip-a systematic review of the intra-articular findings, and the outcomes utilizing hip ar-throscopic surgery. J Hip Preserv Surg. 2016; 3:171–80.
Article11. Parvizi J, Bican O, Bender B. . Arthroscopy for labral tears in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip: a cautionary note. J Arthroplast. 2009; 24:S110–3.
Article12. Mei-Dan O, McConkey MO, Brick M. . Catastrophic failure of hip arthroscopy due to iatrogenic instability: can partial division of the ligamentum teres and iliofemoral ligament cause subluxation? Arthroscopy. 2012; 28:440–5.
Article13. Byrd JW, Jones KS. Hip arthroscopy in the presence of dysplasia. Arthroscopy. 2003; 19:1055–60.
Article14. Yamamoto Y, Ide T, Nakamura M, Hamada Y, Usui I. Ar-throscopic partial limbectomy in hip joints with acetabular hypoplasia. Arthroscopy. 2005; 21:586–91.
Article15. Larson CM, Ross JR, Stone RM. . Arthroscopic management of dysplastic hip deformities: predictors of success and failures with comparison to an arthroscopic FAI cohort. Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44:447–53.16. Nawabi DH, Degen RM, Fields KG. . Outcomes after arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement for patients with borderline hip dysplasia. Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44:1017–23.
Article17. Yeung M, Kowalczuk M, Simunovic N, Ayeni OR. Hip ar-throscopy in the setting of hip dysplasia: a systematic review. Bone Joint Res. 2016; 5:225–31.18. Domb BG, Stake CE, Lindner D, El-Bitar Y, Jackson TJ. Arthroscopic capsular plication and labral preservation in borderline hip dysplasia: two-year clinical outcomes of a surgical approach to a challenging problem. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41:2591–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hip Arthroscopy of a Painful Hip with Borderline Dysplasia: Letter to the Editor
- Hip Arthroscopy of a Painful Hip with Borderline Dysplasia
- Comprehensive Review of Advancements in Hip Arthroscopy
- Minimum Five-Year Results of Arthroscopic Management with Labral Preservation in Borderline Hip Dysplasia
- Arthroscopy of the Hip Joint: Diagnosis and Treatment