Hip Pelvis.
2017 Mar;29(1):15-23. 10.5371/hp.2017.29.1.15.
Comprehensive Review of Advancements in Hip Arthroscopy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. dshwang@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2371763
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2017.29.1.15
Abstract
- Hip arthroscopy is currently being leveraged in the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of hip joint problems. In fact, great advancements in hip arthroscopy have resulted in an ever-expanding number of indications to which it is being applied. Minimally invasive hip arthroscopy allows for quicker initiation of rehabilitation and has attracted much attention as the field becomes increasingly focused on surgeries designed to preserve joints. This review aims to summarize the recent advances, applications, and impact of hip arthroscopy.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burman MS. Arthroscopy or the direct visualization of joints: an experimental cadaver study. 1931. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; (390):5–9.2. Takagi K. The classic. Arthroscope. Kenji Takagi. J. Jap. Orthop. Assoc., 1939. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982; (167):6–8.3. Gross R. Arthroscopy in hip disorders in children. Orthop Rev. 1977; 9:43–49.4. Johnson LL. Diagnostic and surgical arthroscopy. Clin Symp. 1982; 34:2–32.5. Eriksson E, Arvidsson I, Arvidsson H. Diagnostic and operative arthroscopy of the hip. Orthopedics. 1986; 9:169–176.
Article6. Glick JM, Sampson TG, Gordon RB, Behr JT, Schmidt E. Hip arthroscopy by the lateral approach. Arthroscopy. 1987; 3:4–12.
Article7. Sampson TG. Complications of hip arthroscopy. Clin Sports Med. 2001; 20:831–835.
Article8. Villar RN. Hip arthroscopy. Br J Hosp Med. 1992; 47:763–766.9. Conn KS, Villar RN. [Labrum lesions from the viewpoint of arthroscopic hip surgery]. Orthopade. 1998; 27:699–703. German.10. Dameron TB Jr. Bucket-handle tear of acetabular labrum accompanying posterior dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959; 41-A:131–134.
Article11. Petersilge CA, Haque MA, Petersilge WJ, Lewin JS, Lieberman JM, Buly R. Acetabular labral tears: evaluation with MR arthrography. Radiology. 1996; 200:231–235.
Article12. Santori N, Villar RN. Acetabular labral tears: result of arthroscopic partial limbectomy. Arthroscopy. 2000; 16:11–15.
Article13. Okada Y, Awaya G, Ikeda T, Tada H, Kamisato S, Futami T. Arthroscopic surgery for synovial chondromatosis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989; 71:198–199.
Article14. Byrd JW. Hip arthroscopy: patient assessment and indications. Instr Course Lect. 2003; 52:711–719.15. Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, Leunig M, Nötzli H, Siebenrock KA. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (417):112–120.16. Byrd JW. Hip arthroscopy. The supine position. Clin Sports Med. 2001; 20:703–731.17. Philippon MJ, Schenker ML. Arthroscopy for the treatment of femoroacetabular impingement in the athlete. Clin Sports Med. 2006; 25:299–308. ix
Article18. Philippon MJ, Stubbs AJ, Schenker ML, Maxwell RB, Ganz R, Leunig M. Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: osteoplasty technique and literature review. Am J Sports Med. 2007; 35:1571–1580.
Article19. Bardakos NV, Vasconcelos JC, Villar RN. Early outcome of hip arthroscopy for femoroacetabular impingement: the role of femoral osteoplasty in symptomatic improvement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90:1570–1575.20. Sampson TG. Arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2008; 37:608–612.
Article21. Byrd JW, Jones KS. Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: minimum 2-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:1379–1388.
Article22. Trompeter A, Colegate-Stone T, Khakha R, Hull J. Hip arthroscopy for femoroacetabular impingement: results of 118 consecutive cases in a district general hospital. Hip Int. 2013; 23:400–405.
Article23. Philippon MJ, Schenker ML, Briggs KK, Kuppersmith DA, Maxwell RB, Stubbs AJ. Revision hip arthroscopy. Am J Sports Med. 2007; 35:1918–1921.
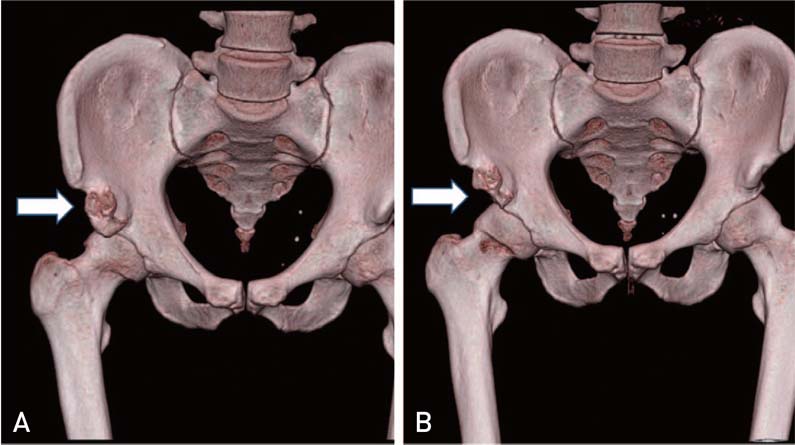
Article24. Hetsroni I, Larson CM, Dela Torre K, Zbeda RM, Magennis E, Kelly BT. Anterior inferior iliac spine deformity as an extraarticular source for hip impingement: a series of 10 patients treated with arthroscopic decompression. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28:1644–1653.
Article25. Hetsroni I, Poultsides L, Bedi A, Larson CM, Kelly BT. Anterior inferior iliac spine morphology correlates with hip range of motion: a classification system and dynamic model. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471:2497–2503.
Article26. Pan H, Kawanabe K, Akiyama H, Goto K, Onishi E, Nakamura T. Operative treatment of hip impingement caused by hypertrophy of the anterior inferior iliac spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90:677–679.
Article27. Larson CM, Kelly BT, Stone RM. Making a case for anterior inferior iliac spine/subspine hip impingement: three representative case reports and proposed concept. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:1732–1737.
Article28. Hapa O, Bedi A, Gursan O, et al. Anatomic footprint of the direct head of the rectus femoris origin: cadaveric study and clinical series of hips after arthroscopic anterior inferior iliac spine/subspine decompression. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29:1932–1940.
Article29. Ward WT, Fleisch ID, Ganz R. Anatomy of the iliocapsularis muscle. Relevance to surgery of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; (374):278–285.30. Tanzer M, Noiseux N. Osseous abnormalities and early osteoarthritis: the role of hip impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; (429):170–177.31. Taher RT, Power RA. Iliopsoas tendon dysfunction as a cause of pain after total hip arthroplasty relieved by surgical release. J Arthroplasty. 2003; 18:387–388.
Article32. Jacobson T, Allen WC. Surgical correction of the snapping iliopsoas tendon. Am J Sports Med. 1990; 18:470–474.
Article33. Allen WC, Cope R. Coxa saltans: the snapping hip revisited. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1995; 3:303–308.
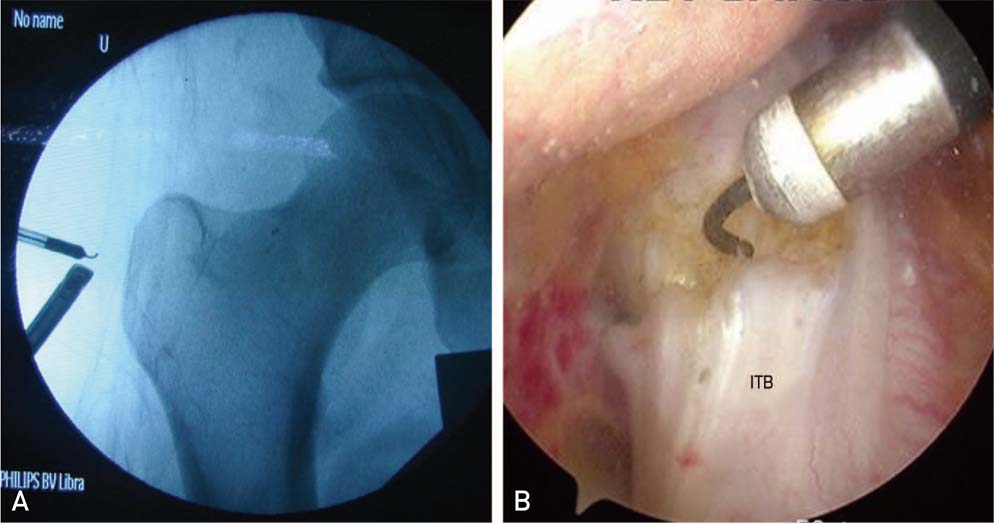
Article34. Provencher MT, Hofmeister EP, Muldoon MP. The surgical treatment of external coxa saltans (the snapping hip) by Z-plasty of the iliotibial band. Am J Sports Med. 2004; 32:470–476.
Article35. Ilizaliturri VM Jr, Martinez-Escalante FA, Chaidez PA, Camacho-Galindo J. Endoscopic iliotibial band release for external snapping hip syndrome. Arthroscopy. 2006; 22:505–510.
Article36. White RA, Hughes MS, Burd T, Hamann J, Allen WC. A new operative approach in the correction of external coxa saltans: the snapping hip. Am J Sports Med. 2004; 32:1504–1508.
Article37. McCrory P, Bell S. Nerve entrapment syndromes as a cause of pain in the hip, groin and buttock. Sports Med. 1999; 27:261–274.
Article38. Robinson DR. Pyriformis syndrome in relation to sciatic pain. Am J Surg. 1947; 73:355–358.
Article39. Filler AG, Haynes J, Jordan SE, et al. Sciatica of nondisc origin and piriformis syndrome: diagnosis by magnetic resonance neurography and interventional magnetic resonance imaging with outcome study of resulting treatment. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005; 2:99–115.
Article40. Martin HD, Shears SA, Johnson JC, Smathers AM, Palmer IJ. The endoscopic treatment of sciatic nerve entrapment/deep gluteal syndrome. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:172–181.
Article41. Puranen J, Orava S. The hamstring syndrome. A new diagnosis of gluteal sciatic pain. Am J Sports Med. 1988; 16:517–521.42. Young IJ, van Riet RP, Bell SN. Surgical release for proximal hamstring syndrome. Am J Sports Med. 2008; 36:2372–2378.
Article43. Cox JM, Bakkum BW. Possible generators of retrotrochanteric gluteal and thigh pain: the gemelli-obturator internus complex. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2005; 28:534–538.
Article44. Meknas K, Kartus J, Letto JI, Christensen A, Johansen O. Surgical release of the internal obturator tendon for the treatment of retro-trochanteric pain syndrome: a prospective randomized study, with long-term follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009; 17:1249–1256.
Article45. Benson ER, Schutzer SF. Posttraumatic piriformis syndrome: diagnosis and results of operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:941–949.46. Papadopoulos EC, Khan SN. Piriformis syndrome and low back pain: a new classification and review of the literature. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004; 35:65–71.
Article47. Dezawa A, Kusano S, Miki H. Arthroscopic release of the piriformis muscle under local anesthesia for piriformis syndrome. Arthroscopy. 2003; 19:554–557.
Article48. Lee WY, Hwang DS, Kang C, Zheng L. Entrapment neuropathy of the sciatic nerve caused by a paralabral cyst: three cases treated arthroscopically. JBJS Case Connect. 2016; 6:e82.
Article49. Young NP, Spinner RJ. Nerve cysts and joint relationship. In : Tubbs RS, Rizk E, Shoja MM, Loukas M, Barbaro N, Spinner RJ, editors. Nerves and nerve injuries. Vol. 2. Philadelpiha: Acdemic Press, Elsevier;2015. p. 935–943.50. Byrd JW. Hip arthroscopy for posttraumatic loose fragments in the young active adult: three case reports. Clin J Sport Med. 1996; 6:129–133. discussion 133-4.51. Mullis BH, Dahners LE. Hip arthroscopy to remove loose bodies after traumatic dislocation. J Orthop Trauma. 2006; 20:22–26.
Article52. Lansford T, Munns SW. Arthroscopic treatment of Pipkin type I femoral head fractures: a report of 2 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2012; 26:e94–e96.53. Evans CH, Mazzocchi RA, Nelson DD, Rubash HE. Experimental arthritis induced by intraarticular injection of allogenic cartilaginous particles into rabbit knees. Arthritis Rheum. 1984; 27:200–207.
Article54. Park MS, Yoon SJ, Choi SM. Hip Arthroscopic management for femoral head fractures and posterior acetabular wall fractures (Pipkin Type IV). Arthrosc Tech. 2013; 2:e221–e225.
Article55. Hwang JM, Hwang DS, Lee WY, Noh CK, Zheng L. Hip Arthroscopy for incarcerated acetabular labrum following reduction of traumatic hip dislocation: Three case reports. Hip Pelvis. 2016; 28:164–168.
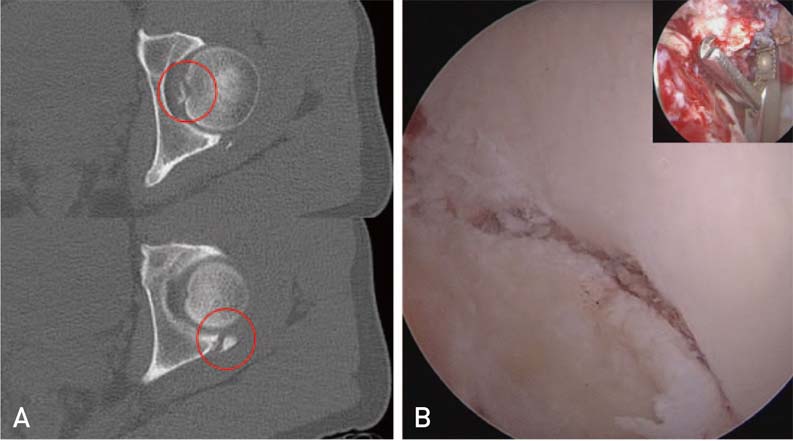
Article56. Matsuda DK. A rare fracture, an even rarer treatment: the arthroscopic reduction and internal fixation of an isolated femoral head fracture. Arthroscopy. 2009; 25:408–412.
Article57. Yang JH, Chouhan DK, Oh KJ. Percutaneous screw fixation of acetabular fractures: applicability of hip arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2010; 26:1556–1561.
Article58. Kim H, Baek JH, Park SM, Ha YC. Arthroscopic reduction and internal fixation of acetabular fractures. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014; 22:867–870.
Article59. Guanche CA, Sikka RS. Acetabular labral tears with underlying chondromalacia: a possible association with high-level running. Arthroscopy. 2005; 21:580–585.
Article60. Martin HD, Savage A, Braly BA, Palmer IJ, Beall DP, Kelly B. The function of the hip capsular ligaments: a quantitative report. Arthroscopy. 2008; 24:188–195.
Article61. Leunig M, Beck M, Stauffer E, Hertel R, Ganz R. Free nerve endings in the ligamentum capitis femoris. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000; 71:452–454.
Article62. Haviv B, O'Donnell J. Arthroscopic debridement of the isolated Ligamentum Teres rupture. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19:1510–1513.
Article63. Kivlan BR, Richard Clemente F, Martin RL, Martin HD. Function of the ligamentum teres during multi-planar movement of the hip joint. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013; 21:1664–1668.
Article64. Philippon MJ, Pennock A, Gaskill TR. Arthroscopic reconstruction of the ligamentum teres: technique and early outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012; 94:1494–1498.65. Simpson JM, Field RE, Villar RN. Arthroscopic reconstruction of the ligamentum teres. Arthroscopy. 2011; 27:436–441.
Article66. Amenabar T, O'Donnell J. Arthroscopic ligamentum teres reconstruction using semitendinosus tendon: surgical technique and an unusual outcome. Arthrosc Tech. 2012; 1:e169–e174.
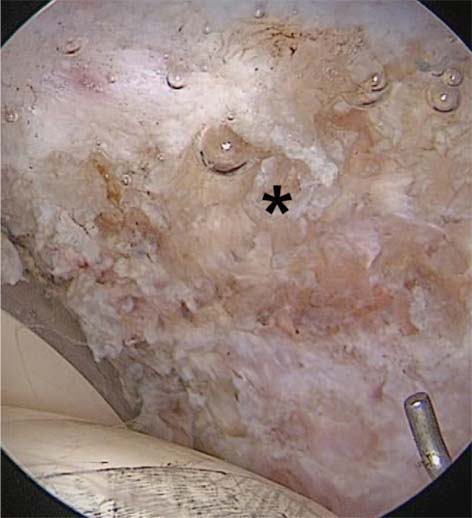
Article67. Lindner D, Sharp KG, Trenga AP, Stone J, Stake CE, Domb BG. Arthroscopic ligamentum teres reconstruction. Arthrosc Tech. 2012; 2:e21–e25.
Article68. Field RE, Rajakulendran K. The labro-acetabular complex. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:Suppl 2. 22–27.
Article69. Crawford MJ, Dy CJ, Alexander JW, et al. The 2007 Frank Stinchfield Award. The biomechanics of the hip labrum and the stability of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 465:16–22.
Article70. McCarthy JC, Noble PC, Schuck MR, Wright J, Lee J. The Otto E. Aufranc Award: The role of labral lesions to development of early degenerative hip disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; (393):25–37.71. Philippon MJ, Briggs KK, Hay CJ, Kuppersmith DA, Dewing CB, Huang MJ. Arthroscopic labral reconstruction in the hip using iliotibial band autograft: technique and early outcomes. Arthroscopy. 2010; 26:750–756.
Article72. Geyer MR, Philippon MJ, Fagrelius TS, Briggs KK. Acetabular labral reconstruction with an iliotibial band autograft: outcome and survivorship analysis at minimum 3-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41:1750–1756.
Article