Korean J Gastroenterol.
2019 Feb;73(2):114-117. 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.2.114.
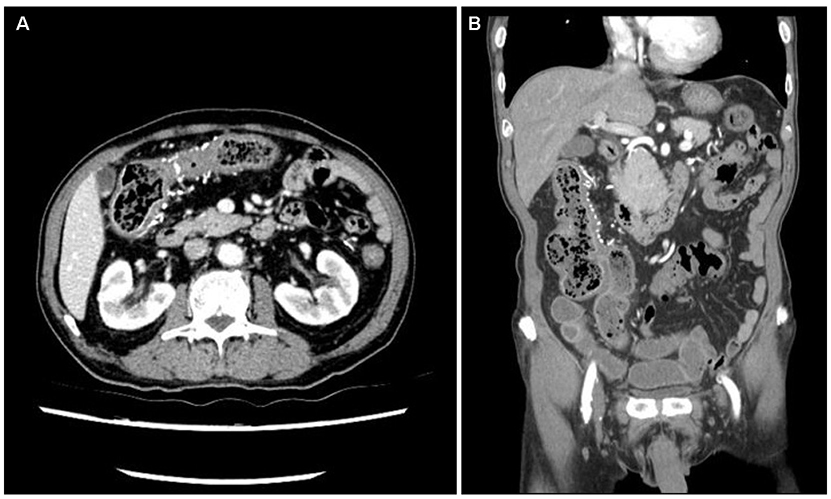
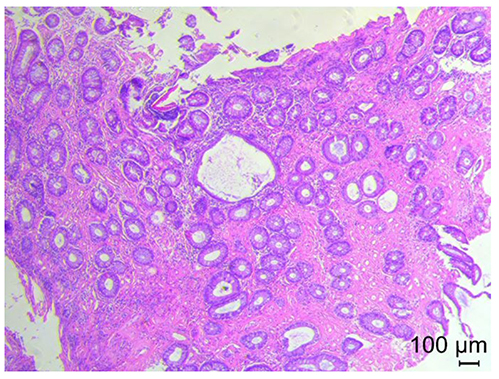
Phlebosclerotic Colitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2438712
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2019.73.2.114
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brandt LJ, Boley SJ. AGA technical review on intestinal ischemia. American gastrointestinal association. Gastroenterology. 2000; 118:954–968.2. Yao T, Iwashita A, Hoashi T, et al. Phlebosclerotic colitis: value of radiography in diagnosis--report of three cases. Radiology. 2000; 214:188–192.
Article3. Choi JM, Lee KN, Kim HS, et al. Idiopathic phlebosclerotic colitis: a rare entity of chronic ischemic colitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2014; 63:183–186.
Article4. Kang HY, Noh R, Kim SM, Shin HD, Yun SY, Song IH. Phlebosclerotic colitis in a cirrhotic patient with portal hypertension: the first case in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:1195–1199.
Article5. Song JH, Kim JI, Jung JH, et al. A case of phlebosclerotic colitis in a hemodialysis patient. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012; 59:40–43.
Article6. Chang KM. New histologic findings in idiopathic mesenteric phlebosclerosis: clues to its pathogenesis and etiology--probably ingested toxic agent-related. J Chin Med Assoc. 2007; 70:227–235.
Article7. Yeh HJ, Lin PY, Kao WY, Kun CH, Chang CC. Idiopathic mesenteric phlebosclerosis associated with long-term use of Chinese herbal medicine. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2018; 29:140–142.
Article8. Hiramatsu K, Sakata H, Horita Y, et al. Mesenteric phlebosclerosis associated with long-term oral intake of geniposide, an ingredient of herbal medicine. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 36:575–586.
Article9. Kato T, Miyazaki K, Nakamura T, Tan KY, Chiba T, Konishi F. Perforated phlebosclerotic colitis--description of a case and review of this condition. Colorectal Dis. 2010; 12:149–151.10. Iwashita A, Yao T, Schlemper RJ, et al. Mesenteric phlebosclerosis: a new disease entity causing ischemic colitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003; 46:209–220.11. Chen MT, Yu SL, Yang TH. A case of phlebosclerotic colitis with involvement of the entire colon. Chang Gung Med J. 2010; 33:581–585.12. Hu P, Deng L. Phlebosclerotic colitis: three cases and literature review. Abdom Imaging. 2013; 38:1220–1224.
Article13. Yu CJ, Wang HH, Chou JW, et al. Phlebosclerotic colitis with nonsurgical treatment. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009; 24:1241–1242.
Article14. Fang YL, Hsu HC, Chou YH, Wu CC, Chou YY. Phlebosclerotic colitis: a case report and review of the literature. Exp Ther Med. 2014; 7:583–586.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Idiopathic Phlebosclerotic Colitis: A Rare Entity of Chronic Ischemic Colitis
- A Case of Phlebosclerotic Colitis in a Hemodialysis Patient
- Phlebosclerotic Colitis in a Healthy Young Woman
- A Case of Phlebosclerotic Colitis in a Patient of Chronic Renal Failure
- Phlebosclerotic Colitis in a Healthy Young Female with Long-term Herbal Medicine Use