Intest Res.
2019 Jan;17(1):63-69. 10.5217/ir.2018.00077.
Hypoalbuminemia as a risk factor for thromboembolic events in inflammatory bowel disease inpatients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Gastroenterology Unit, Department of Internal Medicine, Department of Surgery, University of Campinas (UNICAMP), Campinas, Brazil. marcelloir@hotmail.com
- 2Colorectal Surgery Unit, Department of Surgery, University of Campinas (UNICAMP), Campinas, Brazil.
- 3Colorectal Surgery Unit, IBD Outpatients Clinic, Cajuru University Hospital, Catholic University of Parana (PUCPR), Curitiba, Brazil.
- KMID: 2438444
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2018.00077
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
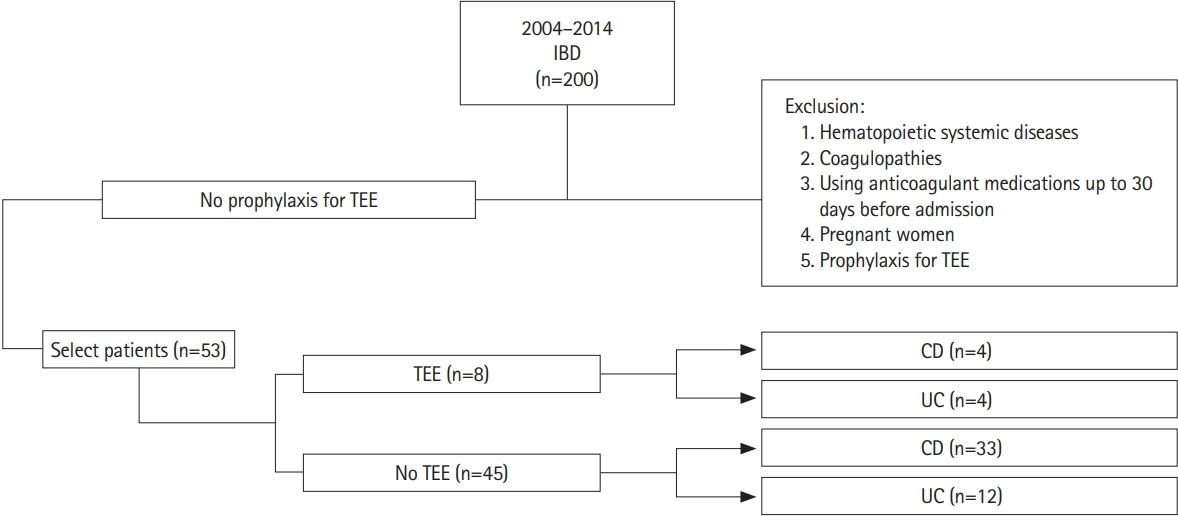
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are chronic entities characterized by local and systemic inflammation and may be associated with thrombosis. The aim of this study was to identify the prevalence of thromboembolic events (TEE) in hospitalized IBD patients and identify risk factors for their occurrence.
METHODS
This retrospective, single-center study included patients treated at a Brazilian IBD referral unit between 2004 and 2014. Patients hospitalized for more than 48 hours due to active IBD and who did not receive prophylaxis for TEE during hospitalization were included. Patients were allocated to 2 groups: those with TEE up to 30 days or at the time of hospitalization (TEE-group) and patients without TEE (control-group). Clinical and laboratory characteristics were evaluated.
RESULTS
Of 53 patients evaluated, 69,8% with Crohn's disease (CD) and 30.2% with ulcerative colitis (UC). The prevalence of TEE 30 days before or during hospitalization was 15.1%, with 10.8% in CD and 25% in UC. In the TEE group, mean serum albumin was 2.06 g/dL versus 3.30 g/dL in the control group. Patients with albumin levels below 2.95 g/dL (43.18%) had a higher risk of developing TEE (relative risk, 1.72; 95% confidence interval, 1.17-2.53) (P < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Albumin levels were significantly lower in patients with TEE, and hypoalbuminemia was considered a risk factor for the development of TEE in this population.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Risk of venous thromboembolism with a central venous catheter in hospitalized Japanese patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a propensity score-matched cohort study
Yasuhiro Aoki, Hiroki Kiyohara, Yohei Mikami, Kosaku Nanki, Takaaki Kawaguchi, Yusuke Yoshimatsu, Shinya Sugimoto, Tomohisa Sujino, Kaoru Takabayashi, Naoki Hosoe, Haruhiko Ogata, Yasushi Iwao, Takanori Kanai
Intest Res. 2023;21(3):318-327. doi: 10.5217/ir.2022.00116.
Reference
-
1. Giannotta M, Tapete G, Emmi G, Silvestri E, Milla M. Thrombosis in inflammatory bowel diseases: what’s the link? Thromb J. 2015; 13:14.
Article2. Bargen JA, Barker NW. Extensive arterial and venous thrombosis complicating chronic ulcerative colitis. Arch Intern Med. 1936; 58:17–31.
Article3. Miehsler W, Reinisch W, Valic E, et al. Is inflammatory bowel disease an independent and disease specific risk factor for thromboembolism? Gut. 2004; 53:542–548.
Article4. Irving PM, Pasi KJ, Rampton DS. Thrombosis and inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 3:617–628.
Article5. Papa A, Gerardi V, Marzo M, Felice C, Rapaccini GL, Gasbarrini A. Venous thromboembolism in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: focus on prevention and treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:3173–3179.
Article6. Silverberg MS, Satsangi J, Ahmad T, et al. Toward an integrated clinical, molecular and serological classification of inflammatory bowel disease: report of a Working Party of the 2005 Montreal World Congress of Gastroenterology. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005; 19 Suppl A:5A–36A.
Article7. Nguyen GC, Bernstein CN, Bitton A, et al. Consensus statements on the risk, prevention, and treatment of venous thromboembolism in inflammatory bowel disease: Canadian Association of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2014; 146:835–848.
Article8. Harvey RF, Bradshaw JM. A simple index of Crohn’s-disease activity. Lancet. 1980; 1:514.
Article9. Truelove SC, Witts LJ. Cortisone in ulcerative colitis; final report on a therapeutic trial. Br Med J. 1955; 2:1041–1048.10. Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1995; 854:1–452.11. Nguyen GC, Sharma S. Feasibility of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis during inflammatory bowel disease flares in the outpatient setting: a decision analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:2182–2189.
Article12. Olson NC, Cushman M, Lutsey PL, et al. Inflammation markers and incident venous thromboembolism: the Reasons for Geographic And Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) cohort. J Thromb Haemost. 2014; 12:1993–2001.
Article13. Paar M, Rossmann C, Nusshold C, et al. Anticoagulant action of low, physiologic, and high albumin levels in whole blood. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0182997.
Article14. Jørgensen KA, Stoffersen E. On the inhibitory effect of albumin on platelet aggregation. Thromb Res. 1980; 17:13–18.
Article15. Folsom AR, Lutsey PL, Heckbert SR, Cushman M. Serum albumin and risk of venous thromboembolism. Thromb Haemost. 2010; 104:100–104.
Article16. Winstedt D, Hanna J, Schött U. Albumin-induced coagulopathy is less severe and more effectively reversed with fibrinogen concentrate than is synthetic colloid-induced coagulopathy. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2013; 73:161–169.
Article17. Geerts WH, Bergqvist D, Pineo GF, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008; 133(6 Suppl):381S–453S.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chronic Kidney Disease as an Independent Risk Factor for Thromboembolism in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
- The incidence and risk factors of venous thromboembolism in Japanese inpatients with inflammatory bowel disease: a retrospective cohort study
- Inflammatory bowel disease is no longer a risk factor of viral hepatitis infection in Asia
- Is Indefinite Dysplasia a Risk Factor for Advanced Colorectal Neoplasia in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
- Predictors of Small Bowel Transit Time for Capsule Endoscopy in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease