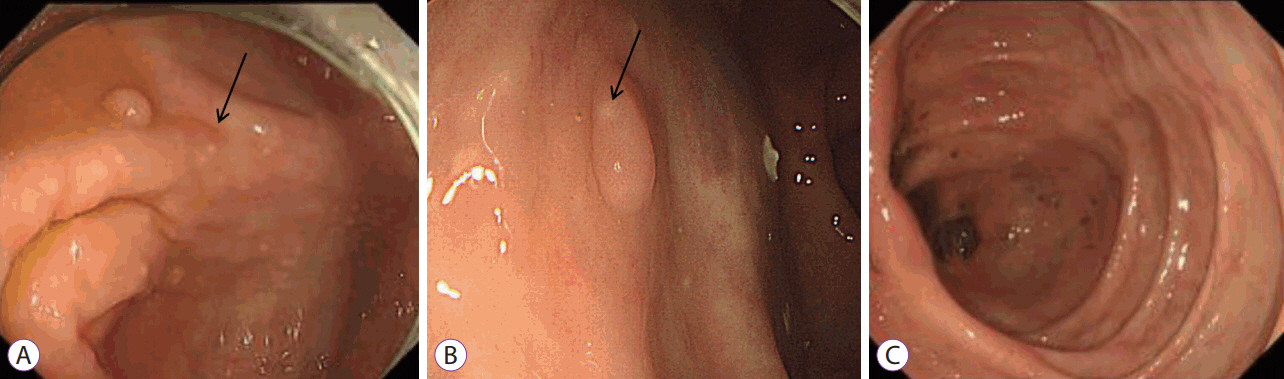
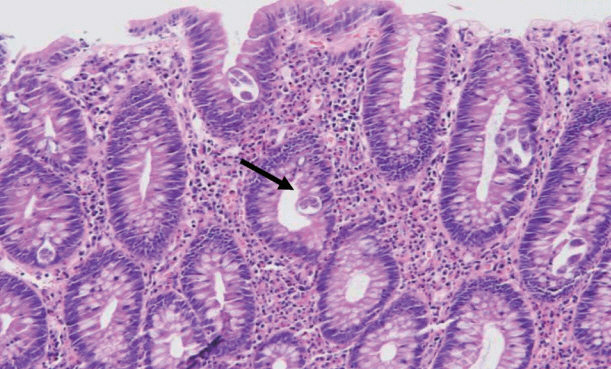
Clin Endosc.
2019 Jan;52(1):80-82. 10.5946/ce.2018.078.
Strongyloidiasis Presenting as Yellowish Nodules in Colonoscopy of an Immunocompetent Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University of Medical and Science, Incheon, Korea. drgreen@gilhospital.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Gachon University of Medical and Science, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2438150
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2018.078
Abstract
- Strongyloides stercoralis is endemic to tropical and subtropical regions, and infections are usually asymptomatic. However, immunocompromised patients, such as those receiving immunosuppressive therapy, high-dose steroids, or chemotherapy, can develop fatal hyperinfections. An 84-year-old man without any symptoms was diagnosed with strongyloidiasis during a regular screening colonoscopy. His medical history only involved a gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer 6 months previously. Few cases have been published about asymptomatic strongyloidiasis diagnosed in an immunocompetent host via endoscopic mucosal resection with characteristic colonoscopic findings. We report a case of colon-involved asymptomatic strongyloidiasis with specific colonic findings of yellowish-white nodules. This finding may be an important marker of S. stercoralis infection, which could prevent hyperinfections.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Buonfrate D, Baldissera M, Abrescia F, et al. Epidemiology of Strongyloides stercoralis in northern Italy: results of a multicentre case-control study, February 2013 to July 2014. Euro Surveill. 2016; 21.
Article2. Khieu V, Schär F, Forrer A, et al. High prevalence and spatial distribution of Strongyloides stercoralis in rural Cambodia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014; 8:e2854.
Article3. Yung EE, Lee CM, Boys J, Grabo DJ, Buxbaum JL, Chandrasoma PT. Strongyloidiasis hyperinfection in a patient with a history of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014; 91:806–809.
Article4. Greaves D, Coggle S, Pollard C, Aliyu SH, Moore EM. Strongyloides stercoralis infection. BMJ. 2013; 347:f4610.
Article5. Xouris D, Vafiadis-Zoumbulis I, Papaxoinis K, et al. Possible Strongyloides stercoralis infection diagnosed by videocapsule endoscopy in an immunocompetent patient with devastating diarrhea. Ann Gastroenterol. 2012; 25:268–270.6. Teixeira MC, Inês EJ, Pacheco FT, et al. Asymptomatic Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection in an alcoholic patient with intense anemia. J Parasitol. 2010; 96:833–835.
Article7. Kishimoto K, Hokama A, Hirata T, et al. Endoscopic and histopathological study on the duodenum of Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:1768–1773.
Article8. Thompson BF, Fry LC, Wells CD, et al. The spectrum of GI strongyloidiasis: an endoscopic-pathologic study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 59:906–910.
Article9. Minematsu H, Hokama A, Makishi T, Arakaki K, Kinjo F, Fujita J. Colonoscopic findings and pathologic characteristics of Strongyloides colitis: a case series. Digestion. 2011; 83:210–214.10. Sridhara S, Simon N, Raghuraman U, Crowson N, Aggarwal V. Strongyloides stercoralis pancolitis in an immunocompetent patient. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:196–199.
Article11. Mutreja D, Sivasami K, Tewari V, Nandi B, Nair GL, Patil SD. A 36-yearold man with vomiting, pain abdomen, significant weight loss, hyponatremia, and hypoglycemia. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2015; 58:500–505.
Article12. El-Sameed YA, Beejay N, Al Maashari R. Diffuse alveolar haemorrhage and severe hypoxemia from Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome. Clin Respir J. 2015; 9:489–492.13. Salvador F, Sulleiro E, Sánchez-Montalvá A, et al. Usefulness of Strongyloides stercoralis serology in the management of patients with eosinophilia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014; 90:830–834.
Article14. Buonfrate D, Formenti F, Perandin F, Bisoffi Z. Novel approaches to the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015; 21:543–552.
Article15. Dias C, Landaeta J, Armas V. Diagnostic endoscopy of intestinal Strongyloidiasis in an immunocompetent patient by single balloon enteroscopy. Advanced Research in Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2018; 8:555741.
Article16. Sato Y, Kobayashi J, Toma H, Shiroma Y. Efficacy of stool examination for detection of Strongyloides infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1995; 53:248–250.
Article17. Nam S-C, Han M-H, Kim Y-S, Kum Y-S, Suh I-S, Bae H-I. Two cases of Strongyloidiasis diagnosed by colonoscopic biopsy. Korean J Pathol. 2007; 41:343–346.18. Khieu V, Schär F, Marti H, et al. Diagnosis, treatment and risk factors of Strongyloides stercoralis in schoolchildren in Cambodia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013; 7:e2035.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Strongyloides Stercoralis Concurrently Invading the Stomach and Colon
- Strongyloidiasis associated with amebiasis and giardiaisis in an immunocompetent boy presented with acute abdomen
- Pulmonary embolism in an immunocompetent patient with acute cytomegalovirus colitis
- A case of strongyloidiasis with severe malnutrition
- A case of disseminated strongyloidiasis diagnosed by worms in the urinary sediment