Intest Res.
2016 Apr;14(2):187-190. 10.5217/ir.2016.14.2.187.
Pulmonary embolism in an immunocompetent patient with acute cytomegalovirus colitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, China Medical University Hospital, School of Medicine, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, Republic of China. codecol80@gmail.com
- KMID: 2425293
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2016.14.2.187
Abstract
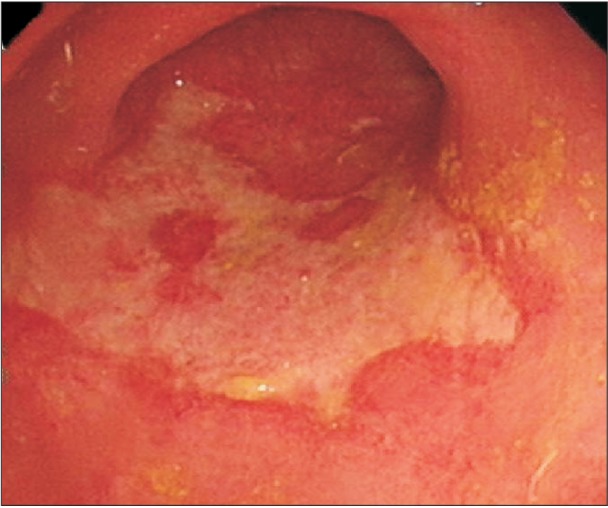
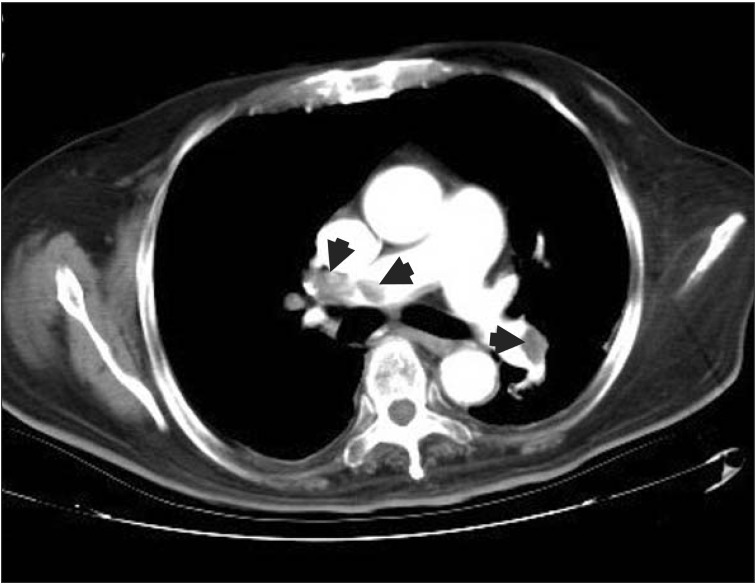
- Acute cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection occurs commonly in immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients, but is usually asymptomatic in the latter. Vascular events associated with acute CMV infection have been described, but are rare. Hence, such events are rarely reported in the literature. We report a case of pulmonary embolism secondary to acute CMV colitis in an immunocompetent 78-year-old man. The patient presented with fever and diarrhea. Colonic ulcers were diagnosed based on colonoscopy findings, and CMV was the proven etiology on pathological examination. The patient subsequently experienced acute respiratory failure. Pulmonary embolism was diagnosed based on the chest radiography and computed tomography findings. A diagnosis of acute CMV colitis complicated by pulmonary embolism was made. The patient was successfully treated with intravenous administration of unfractionated heparin and intravenous ganciclovir.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Staras SA, Dollard SC, Radford KW, Flanders WD, Pass RF, Cannon MJ. Seroprevalence of cytomegalovirus infection in the United States, 1988-1994. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 43:1143–1151. PMID: 17029132.
Article2. Rafailidis PI, Mourtzoukou EG, Varbobitis IC, Falagas ME. Severe cytomegalovirus infection in apparently immunocompetent patients: a systematic review. Virol J. 2008; 5:47. DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-5-47. PMID: 18371229.
Article3. Goodgame RW. Gastrointestinal cytomegalovirus disease. Ann Intern Med. 1993; 119:924–935. PMID: 8215005.
Article4. Jenkins RE, Peters BS, Pinching AJ. Thromboembolic disease in AIDS is associated with cytomegalovirus disease. AIDS. 1991; 5:1540–1542. PMID: 1667576.
Article5. Bauduer F, Blanc A, Cordon B. Deep vein thrombosis and acute cytomegalovirus infection: case report and review of the literature. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2003; 14:489–491. PMID: 12851536.6. Abgueguen P, Delbos V, Chennebault JM, Payan C, Pichard E. Vascular thrombosis and acute cytomegalovirus infection in immunocompetent patients: report of 2 cases and literature review. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 36:E134–E139. PMID: 12766855.
Article7. Fridlender ZG, Khamaisi M, Leitersdorf E. Association between cytomegalovirus infection and venous thromboembolism. Am J Med Sci. 2007; 334:111–114. PMID: 17700200.
Article8. Abgueguen P, Delbos V, Ducancelle A, Jomaa S, Fanello S, Pichard E. Venous thrombosis in immunocompetent patients with acute cytomegalovirus infection: a complication that may be underestimated. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010; 16:851–854. PMID: 19686279.
Article9. Rahbar A, Söderberg-Nauclér C. Human cytomegalovirus infection of endothelial cells triggers platelet adhesion and aggregation. J Virol. 2005; 79:2211–2220. PMID: 15681423.
Article10. Delbos V, Abgueguen P, Chennebault JM, Fanello S, Pichard E. Acute cytomegalovirus infection and venous thrombosis: role of antiphospholipid antibodies. J Infect. 2007; 54:e47–e50. PMID: 16701900.
Article11. Zhou YF, Yu ZX, Wanishsawad C, Shou M, Epstein SE. The immediate early gene products of human cytomegalovirus increase vascular smooth muscle cell migration, proliferation, and expression of PDGF beta-receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999; 256:608–613. PMID: 10080946.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cytomegalovirus Colitis in an Immunocompetent Adult
- A Case of Cytomegalovirus and Pseudomembranous Colitis in an Immunocompetent Adult
- Cytomegalovirus Colitis with Ulcerative Colitis in the Steroid Naive Immunocompetent Patient
- Cytomegalovirus colitis in immunocompetent patients
- A case of cytomegalovirus colitis in an immunocompetent adult presenting as pancolitis