J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2019 Feb;60(2):126-134. 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.2.126.
Accuracy of Astigmatic Correction Using Toric Intraocular Lens by Position and Size of Corneal Incision
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea. eunchol@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2438071
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2019.60.2.126
Abstract
- PURPOSE
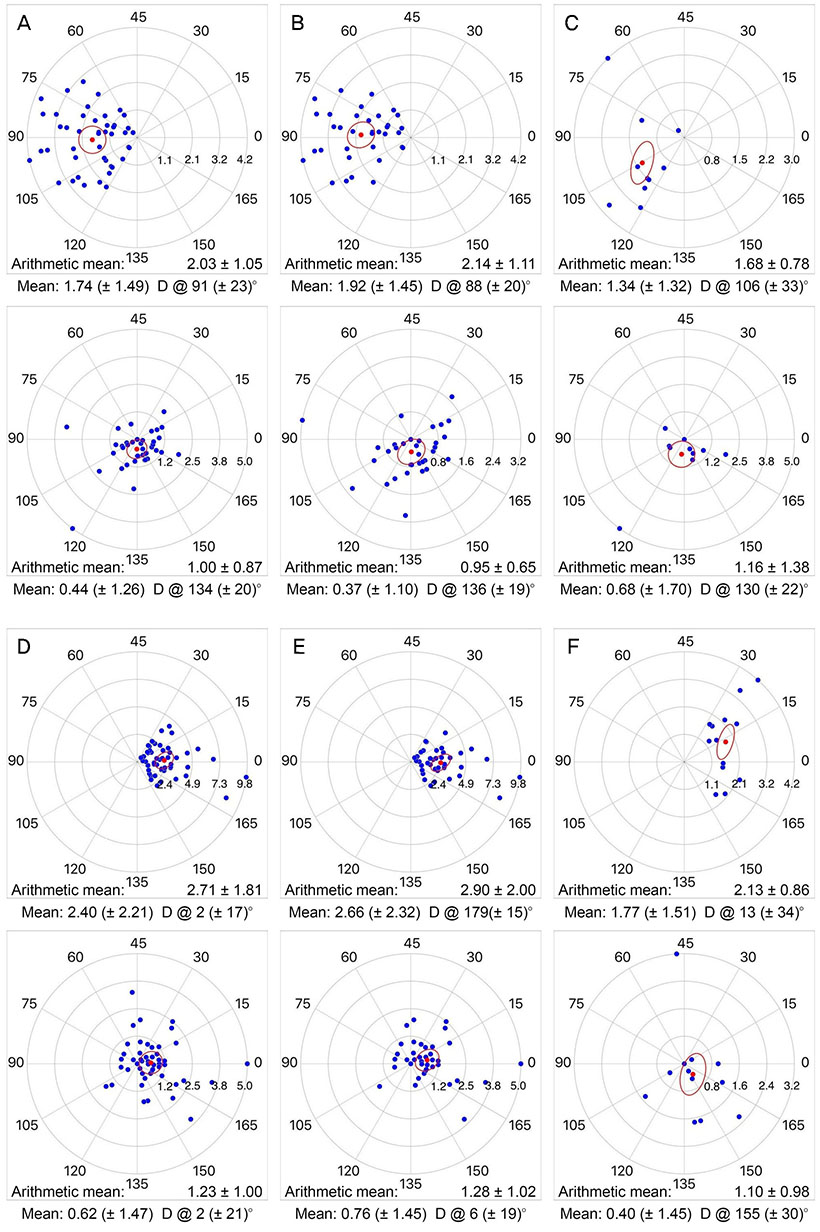
To assess the accuracy of toric intraocular lens (IOL) implantation by the location and size of the corneal incision.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 98 patients (98 eyes) who underwent phacoemulsification with toric IOL implantation from January 2014 to March 2017. The patients were divided into two groups: group 1 got an incision of the superior side of the cornea (n = 54) and group 2 received an incision on the temporal side of the eye (n = 44). For both groups, incisions were made at their steep corneal astigmatism axises. Each group was further divided into subgroups for whom different sized blades were employed (2.75 vs. 2.2 mm widths). We measured the refractive index and autokeratometric parameters. We postoperatively assessed residual astigmatism and any reduction thereof.
RESULTS
In both groups, uncorrected and best-corrected visual acuity, refraction cylinder astigmatism, and autokeratometric astigmatism improved statistically. Between two groups, corneal astigmatism decrease was not significant. Residual astigmatism also showed no significant differences between the two. Patients in both groups treated using 2.75 mm wide blades exhibited greater increases in corneal astigmatism.
CONCLUSIONS
During cataract surgery, precise correction of astigmatism via toric IOL implantation is possible when surgically induced astigmatism is minimized by careful choice of the location and size of the corneal incision.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hoffmann PC, Hütz WW. Analysis of biometry and prevalence data for corneal astigmatism in 23,239 eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1479–1485.2. He W, Zhu X, Du Y, et al. Clinical efficacy of implantation of toric intraocular lenses with different incision positions: a comparative study of steep-axis incision and non-steep-axis incision. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017; 17:132.
Article3. Shimizu K, Misawa A, Suzuki Y. Toric intraocular lenses: correcting astigmatism while controlling axis shift. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1994; 20:523–526.
Article4. Ahmed II, Rocha G, Slomovic AR, et al. Visual function and patient experience after bilateral implantation of toric intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:609–616.
Article5. Bauer NJ, de Vries NE, Webers CA, et al. Astigmatism management in cataract surgery with the AcrySof toric intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1483–1488.
Article6. De Silva DJ, Ramkissoon YD, Bloom PA. Evaluation of a toric intraocular lens with a Z-haptic. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1492–1498.
Article7. Entabi M, Harman F, Lee N, Bloom PA. Injectable 1-piece hydrophilic acrylic toric intraocular lens for cataract surgery: efficacy and stability. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:235–240.
Article8. Mendicute J, Irigoyen C, Aramberri J, et al. Foldable toric intraocular lens for astigmatism correction in cataract patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:601–607.
Article9. Poll JT, Wang L, Koch DD, Weikert MP. Correction of astigmatism during cataract surgery: toric intraocular lens compared to peripheral corneal relaxing incisions. J Refract Surg. 2011; 27:165–171.
Article10. Till JS, Yoder PR Jr, Wilcox TK, Spielman JL. Toric intraocular lens implantation: 100 consecutive cases. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:295–301.
Article11. Hill W. Expected effects of surgically induced astigmatism on AcrySof toric intraocular lens results. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:364–367.
Article12. Grosvenor T. Etiology of astigmatism. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1978; 55:214–218.
Article13. Saunders H. Age-dependence of human refractive errors. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1984; 4:107.
Article14. Howland HC, Sayles N. Photokeratometric and photorefractive measurements of astigmatism in infants and young children. Vision Res. 1985; 25:73–81.15. Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Hayashi F. Topographic analysis of the changes in corneal shape due to aging. Cornea. 1995; 14:527–532.
Article16. Hayashi K, Sato T, Yoshida M, Yoshimura K. Corneal shape changes of the total and posterior cornea after temporal versus nasal clear corneal incision cataract surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019; 103:181–185.
Article17. Kim YJ, Knorz MC, Auffarth GU, Choi CY. Change in anterior and posterior curvature after cataract surgery. J Refract Surg. 2016; 32:754–759.
Article18. Kohnen T, Dick B, Jacobi KW. Comparison of the induced astigmatism after temporal clear corneal tunnel incisions of different sizes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1995; 21:417–424.
Article19. Hirnschall N, Hoffmann PC, Draschl P, et al. Evaluation of factors influencing the remaining astigmatism after toric intraocular lens implantation. J Refract Surg. 2014; 30:394–400.
Article20. Cornut T, Touboul D, Rouglan S, et al. Refractive outcomes and precision in toric intraocular lens alignment using an automated alignment system. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2018; 41:291–301.21. Raucau M, El Chehab H, Agard E, et al. Toric lens implantation in cataract surgery: automatic versus manual horizontal axis marking, analysis of 50 cases. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2018; 41:136–144.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Efficacies in Treating Astigmatism between Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation and Limbal Relaxing Incision
- The Location of Scleral Incision for Decrease of corneal Astigmatism in Sutureless Cataract Surgery
- Correction of Internal Astigmatism Using Toric Scleral Contact Lens after Implantable Collamer Lens Surgery
- Comparison of the Astigmatic Power of Toric Intraocular Lenses Using Three Toric Calculators
- Improving the Toric Intraocular Lens Calculation by Considering Posterior Corneal Astigmatism and Surgically-induced Corneal Astigmatism