Anesth Pain Med.
2018 Jan;13(1):34-39. 10.17085/apm.2018.13.1.34.
The effects of a loading dose of phenylephrine for the prevention of maternal hypotension under spinal anesthesia for Cesarean section
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea. kimst@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2436053
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2018.13.1.34
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Phenylephrine is frequently used for the prevention and treatment of maternal hypotension in patients undergoing Cesarean section. But there are limited studies about the prophylactic effect on maternal hypotension with a loading dose, followed by a continuous infusion of phenylephrine. Therefore, we investigated the additional effect of a loading dose infusion of phenylephrine on the prevention of maternal hypotension, and compared it to a continuous infusion of phenylephrine without a loading dose.
METHODS
Following spinal anesthesia, sixty-four patients were randomly assigned to one of two groups according to the phenylephrine administration regimen: group L (n = 32; loading dose [200 µg/min] just before continuous infusion [20 µg/min]) and group C (n = 32; continuous infusion [20 µg/min] without a loading dose). We measured the blood pressure and heart rate, and assessed the incidence of hypotension, nausea, vomiting, dosage of used rescue drugs and fetal parameters.
RESULTS
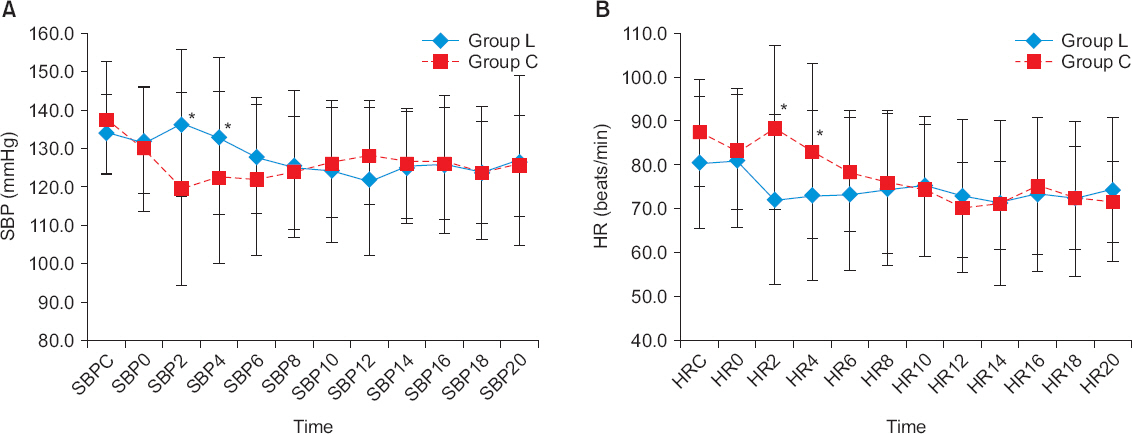
At 2, 4 minutes after administration of phenylephrine, group L showed a higher systolic blood pressure and lower heart rate than group C. However, there were no significant differences in the incidence of hypotension, nausea, vomiting and the dosage of used rescue drugs. There were no significant differences in the fetal parameters such as Apgar scores and umbilical pH.
CONCLUSIONS
The loading dose infusion of phenylephrine had no beneficial positive effect on the prevention of maternal hypotension.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jee YS. Management of hypotension after spinal anesthesia administered for caesarean section. Anesth Pain Med. 2017; 12:97–102. DOI: 10.17085/apm.2017.12.2.97.2. George RB, McKeen D, Columb MO, Habib AS. Up-down determination of the 90% effective dose of phenylephrine for the treatment of spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension in parturients undergoing cesarean delivery. Anesth Analg. 2010; 110:154–8. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181c30b72. PMID: 19910625.3. McKinlay J, Lyons G. Obstetric neuraxial anaesthesia: which pressor agents should we be using? Int J Obstet Anesth. 2002; 11:117–21. DOI: 10.1054/ijoa.2001.0926. PMID: 15321563.4. Tanaka M, Balki M, Parkes RK, Carvalho JC. ED95 of phenylephrine to prevent spinal-induced hypotension and/or nausea at elective cesarean delivery. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2009; 18:125–30. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2008.09.008. PMID: 19162468.5. Lee A, Ngan Kee WD, Gin T. A quantitative, systematic review of randomized controlled trials of ephedrine versus phenylephrine for the management of hypotension during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery. Anesth Analg. 2002; 94:920–6. DOI: 10.1097/00000539-200204000-00028. PMID: 11916798.6. Loubert C. Fluid and vasopressor management for Cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia: continuing professional development. Can J Anaesth. 2012; 59:604–19. DOI: 10.1007/s12630-012-9705-9. PMID: 22528166.7. The Korean Society of Obstetric Anesthesiologists. Obstetric anesthesia. 2th ed. Paju: Koonja Publishing Inc;2016. p. 200.8. Nussmeier NA, Sarwar MF, Searles BE, Shore-lesserson L, Stone ME, Russell I. Anesthesia for cardiac surgical procedures. Miller’s anesthesia. 7th ed. Miller RD, Eriksson LI, Fleisher LA, Wiener-Kronish JP, Young WL, editors. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone;2009. p. 2207–10.9. Ngan Kee WD, Khaw KS, Ng FF, Lee BB. Prophylactic phenylephrine infusion for preventing hypotension during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery. Anesth Analg. 2004; 98:815–21. DOI: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000099782.78002.30. PMID: 14980943.10. das Neves JF, Monteiro GA, de Almeida JR, Sant’Anna RS, Bonin HB, Macedo CF. Phenylephrine for blood pressure control in elective cesarean section: therapeutic versus prophylactic doses. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2010; 60:391–8. DOI: 10.1016/S0034-7094(10)70048-9.11. Langesaeter E, Rosseland LA, Stubhaug A. Continuous invasive blood pressure and cardiac output monitoring during cesarean delivery: a randomized, double-blind comparison of low-dose versus high-dose spinal anesthesia with intravenous phenylephrine or placebo infusion. Anesthesiology. 2008; 109:856–63. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31818a401f. PMID: 18946298.12. Allen TK, George RB, White WD, Muir HA, Habib AS. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of four fixed rate infusion regimens of phenylephrine for hemodynamic support during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery. Anesth Analg. 2010; 111:1221–9. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181e1db21. PMID: 20495139.13. Doherty A, Ohashi Y, Downey K, Carvalho JC. Phenylephrine infusion versus bolus regimens during cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia: a double-blind randomized clinical trial to assess hemodynamic changes. Anesth Analg. 2012; 115:1343–50. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31826ac3db. PMID: 23011562.14. Loughrey JP, Yao N, Datta S, Segal S, Pian-Smith M, Tsen LC. Hemodynamic effects of spinal anesthesia and simultaneous intravenous bolus of combined phenylephrine and ephedrine versus ephedrine for cesarean delivery. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2005; 14:43–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2004.07.011. PMID: 15627538.15. Langesæter E, Dyer RA. Maternal haemodynamic changes during spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2011; 24:242–8. DOI: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e32834588c5. PMID: 21415724.16. Ngan Kee WD, Khaw KS, Tan PE, Ng FF, Karmakar MK. Placental transfer and fetal metabolic effects of phenylephrine and ephedrine during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery. Anesthesiology. 2009; 111:506–12. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181b160a3. PMID: 19672175.17. Liu H, Huang Y, Diao M, Li H, Ma Y, Lin X, et al. Determination of the 90% effective dose (ED90) of phenylephrine for hypotension during elective cesarean delivery using a continual reassessment method. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2015; 194:136–40. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2015.07.001. PMID: 26372882.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management of hypotension after spinal anesthesia administered for caesarean section
- Comparison of Maternal and Fetal Effects of Ephedrine and Phenylephrine Infusion during Spinal Anesthesia for Cesarean Section
- Effects of fetal position on maternal hemodynamics after spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery
- Comparison of maternal and fetal effects of ephedrine, phenylephrine, and combination infusion during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery
- Combined spinal-epidural anesthesia for cesarean section in a patient with Moyamoya disease: A case report