Anesth Pain Med.
2018 Jul;13(3):302-307. 10.17085/apm.2018.13.3.302.
Application of percutaneous foraminotomy with a specially designed drill tip for foraminal stenosis patient: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. euny62827@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2436039
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2018.13.3.302
Abstract
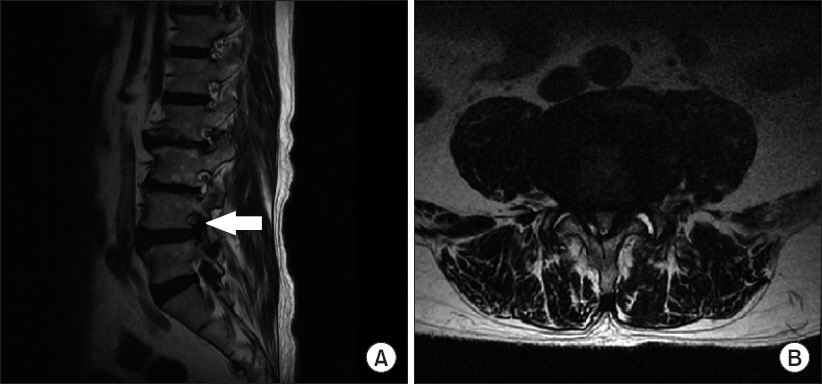
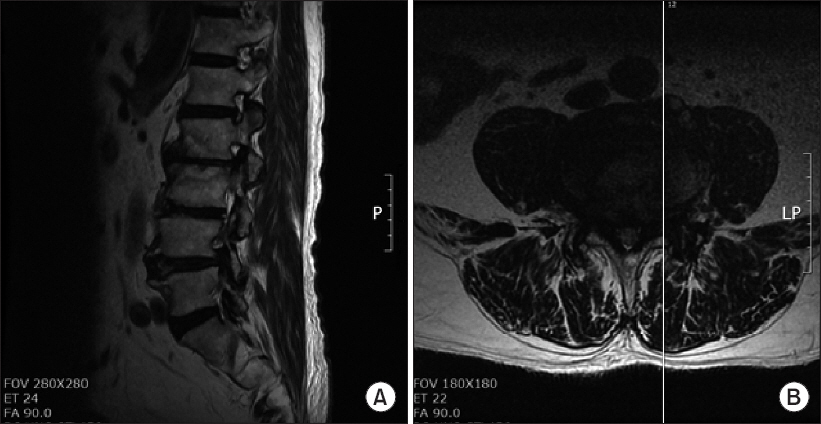
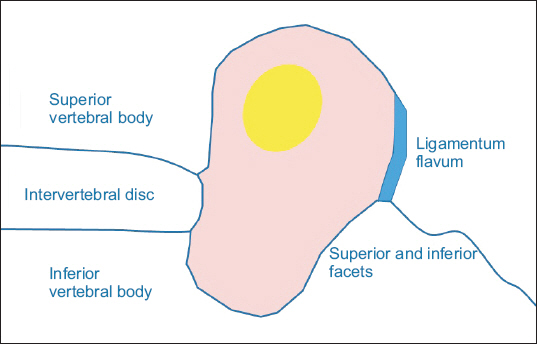
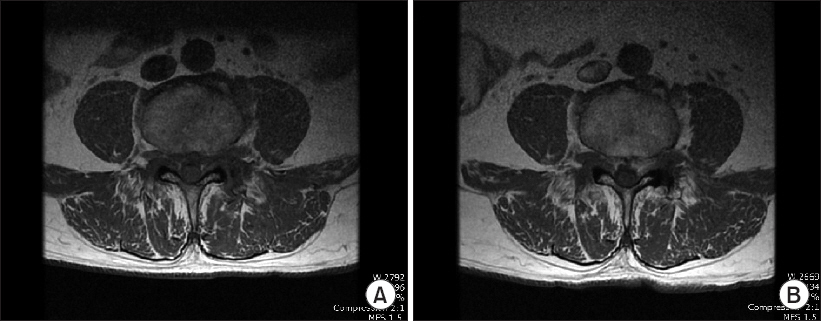
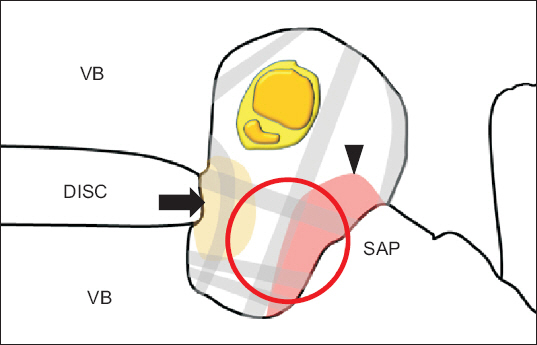
- This case report describes a new method of pain management intervention: percutaneous foraminotomy using the Claudicare system (Seawon Meditech, Korea). In this case, a 77-year-old Asian man visited the hospital with motor weakness in his left foot. He was diagnosed with L4-5 grade three foraminal stenosis using Magnetic Resonance Imaging on both sides. A left L4-5 foraminal decompression was performed using percutaneous foraminotomy. The patient revisited the hospital after 17 months because the same symptoms recurred in his right foot. We observed that the symptoms on the left foot had disappeared completely. We confirmed the lesion on the right side and the postoperative change on the left side on the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image. Both the pre- and postoperative MRI images were compared by measuring the dimensions of the foraminal area (28.12 mm² vs. 38.58 mm², repectively). T1W images showed signs of increased epidural soft tissue after percutaneous foraminotomy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Manchikanti L, Pampati V, Hirsch JA. Utilization of interventional techniques in managing chronic pain in medicare population from 2000 to 2014: an analysis of patterns of utilization. Pain Physician. 2016; 19:E531–46. PMID: 27228520.2. Rydevik B, Brown MD, Lundborg G. Pathoanatomy and pathophysiology of nerve root compression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1984; 9:7–15. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-198401000-00004.3. Lee S, Lee JW, Yeom JS, Kim KJ, Kim HJ, Chung SK, et al. A practical MRI grading system for lumbar foraminal stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:1095–8. DOI: 10.2214/AJR.09.2772. PMID: 20308517.4. Singh V, Montgomery SR, Aghdasi B, Inoue H, Wang JC, Daubs MD. Factors affecting dynamic foraminal stenosis in the lumbar spine. Spine J. 2013; 13:1080–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.03.041. PMID: 23669126.5. Ross JS, Masaryk TJ, Modic MT, Bohlman H, Delamater R, Wilber G. Lumbar spine: postoperative assessment with surface-coil MR imageing. Radiology. 1987; 164:851–60. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.164.3.3615887. PMID: 3615887.6. Wang YP, Zhang W, Li BL, Sun YP, Ding WY, Shen Y. Suprapedicular foraminal endoscopic approach to lumbar lateral recess decompression surgery to treat degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Med Sci Monit. 2016; 22:4604–11. DOI: 10.12659/MSM.901686. PMID: 27890911. PMCID: PMC5142585.7. Chang HS. Microsurgical posterolateral foraminotomy on patients with adult isthmic spondylolisthesis. World Neurosurg. 2017; 100:434–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.wneu.2017.01.040. PMID: 28109864.8. Gu YT, Cui Z, Shao HW, Ye Y, Gu AQ. Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic surgery (PTES) for symptomatic lumbar disc herniation: a surgical technique, outcome, and complications in 209 consecutive cases. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017; 12:25. DOI: 10.1186/s13018-017-0524-0. PMID: 28178992. PMCID: PMC5299691.9. Lee CW, Yoon KJ, Ha SS, Kang JK. Foraminoplastic superior vertebral notch approach with reamers in percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: technical note and clinical outcome in limited indications of percutaneous endoscopic Lumbar discectomy. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2016; 59:172–81. DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.2.172. PMID: 26962427. PMCID: PMC4783487.10. Li ZZ, Hou SX, Shang WL, Cao Z, Zhao HL. Percutaneous lumbar foraminoplasty and percutaneous endoscopic lumbar decompression for lateral recess stenosis through transforaminal approach: technique notes and 2 years follow-up. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016; 143:90–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2016.02.008. PMID: 26907998.11. Uniyal P, Choi G, Khedkkar B. Percutaneous transpedicular lumbar endoscopy: a case report. Int J Spine Surg. 2016; 10:31. DOI: 10.14444/3031. PMID: 27909652. PMCID: PMC5130320.12. Wen B, Zhang X, Zhang L, Huang P, Zheng G. Percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal lumbar spinal canal decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e5186. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005186. PMID: 27977571. PMCID: PMC5268017.13. Xin G, Shi-Sheng H, Hai-Long Z. Morphometric analysis of the YESS and TESSYS techniques of percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Clin Anat. 2013; 26:728–34. DOI: 10.1002/ca.22286. PMID: 23824995.14. Cramer GD, Skogsbergh DR, Bakkum BW, Winterstein JF, Yu S, Tuck NR Jr. Evaluation of transforaminal ligaments by magnetic resonance imaging. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2002; 25:199–208. DOI: 10.1067/mmt.2002.123174. PMID: 12021738.15. Chun EH, Park HS. A Modified approach of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy (PELD) for far lateral disc herniation at L5-S1 with foot drop. Korean J Pain. 2016; 29:57–61. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.1.57. PMID: 26839673. PMCID: PMC4731554.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Novel Foraminal Expansion Technique
- Change of the Intervertebral Foraminal Pressure after Removal of the Disc Material
- Comparison of the Morphometric Changes in the Cervical Foramen: Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion versus Posterior Foraminotomy
- Foraminal stenosis complicating retained broken epidural needle tip: A case report
- Biportal Endoscopic Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy for Adjacent 2-Level Foraminal Lesions Using a Single Approach (Sliding Technique)