Healthc Inform Res.
2018 Oct;24(4):263-275. 10.4258/hir.2018.24.4.263.
Automated Audiometry: A Review of the Implementation and Evaluation Methods
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Health Information Management, School of Health Management and Information Sciences, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Ayatollahi.h@iums.ac.ir
- KMID: 2434541
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2018.24.4.263
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Automated audiometry provides an opportunity to do audiometry when there is no direct access to a clinical audiologist. This approach will help to use hearing services and resources efficiently. The purpose of this study was to review studies related to automated audiometry by focusing on the implementation of an audiometer, the use of transducers and evaluation methods.
METHODS
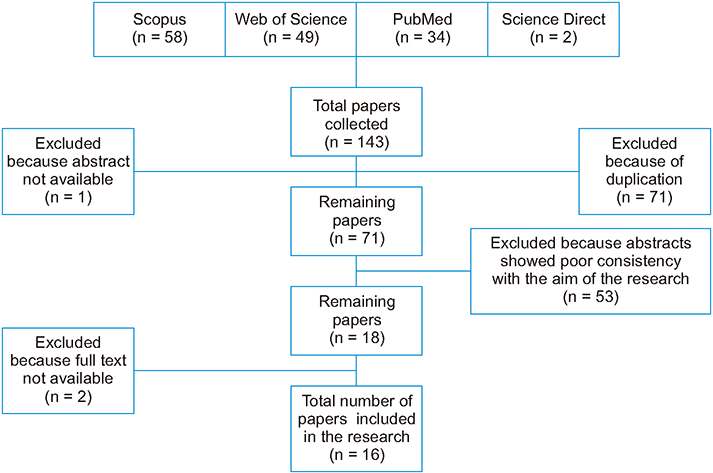
This review study was conducted in 2017. The papers related to the design and implementation of automated audiometry were searched in the following databases: Science Direct, Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus. The time frame for the papers was between January 1, 2010 and August 31, 2017. Initially, 143 papers were found, and after screening, the number of papers was reduced to 16.
RESULTS
The findings showed that the implementation methods were categorized into the use of software (7 papers), hardware (3 papers) and smartphones/tablets (6 papers). The used transducers were a variety of earphones and bone vibrators. Different evaluation methods were used to evaluate the accuracy and the reliability of the diagnoses. However, in most studies, no significant difference was found between automated and traditional audiometry.
CONCLUSIONS
It seems that automated audiometry produces the same results compared with traditional audiometry. However, the main advantages of this method; namely, saving costs and increased accessibility to hearing services, can lead to a faster diagnosis of hearing impairment, especially in poor areas.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mahomed F, Swanepoel de W, Eikelboom RH, Soer M. Validity of automated threshold audiometry: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ear Hear. 2013; 34(6):745–752.2. Eikelboom RH, Swanepoel de W, Motakef S, Upson GS. Clinical validation of the AMTAS automated audiometer. Int J Audiol. 2013; 52(5):342–349.
Article3. Sandstrom J, Swanepoel de W, Carel Myburgh H, Laurent C. Smartphone threshold audiometry in underserved primary health-care contexts. Int J Audiol. 2016; 55(4):232–238.
Article4. Margolis RH, Morgan DE. Automated pure-tone audiometry: an analysis of capacity, need, and benefit. Am J Audiol. 2008; 17(2):109–113.
Article5. Whitton JP, Hancock KE, Shannon JM, Polley DB. Validation of a self-administered audiometry application: an equivalence study. Laryngoscope. 2016; 126(10):2382–2388.
Article6. Munro KJ. Audiology [Internet]. London: Encyclopaedia Britannica;2016. cited at 2018 Oct 1. Available from: https://www.britannica.com/topic/audiology.7. Margolis RH, Moore BC. AMTAS: automated method for testing auditory sensitivity. III. Sensorineural hearing loss and air-bone gaps. Int J Audiol. 2011; 50(7):440–447.
Article8. Margolis RH, Glasberg BR, Creeke S, Moore BC. AMTAS: automated method for testing auditory sensitivity: validation studies. Int J Audiol. 2010; 49(3):185–194.
Article9. Margolis RH, Frisina R, Walton JP. AMTAS: automated method for testing auditory sensitivity. II. Air conduction audiograms in children and adults. Int J Audiol. 2011; 50(7):434–439.10. Margolis RH, Killion MC, Bratt GW, Saly GL. Validation of the Home Hearing Test. J Am Acad Audiol. 2016; 27(5):416–420.
Article11. Masalski M, Krecicki T. Self-test web-based pure-tone audiometry: validity evaluation and measurement error analysis. J Med Internet Res. 2013; 15(4):e71.
Article12. Yao J, Wan Y, Givens GD. Using web services to realize remote hearing assessment. J Clin Monit Comput. 2010; 24(1):41–50.
Article13. Swanepoel de W, Biagio L. Validity of diagnostic computer-based air and forehead bone conduction audiometry. J Occup Environ Hyg. 2011; 8(4):210–214.
Article14. Brennan-Jones CG, Eikelboom RH, Swanepoel de W, Friedland PL, Atlas MD. Clinical validation of automated audiometry with continuous noise-monitoring in a clinically heterogeneous population outside a sound-treated environment. Int J Audiol. 2016; 55(9):507–513.
Article15. Swanepoel de W, Mngemane S, Molemong S, Mkwanazi H, Tutshini S. Hearing assessment-reliability, accuracy, and efficiency of automated audiometry. Telemed J E Health. 2010; 16(5):557–563.
Article16. Meinke DK, Norris JA, Flynn BP, Clavier OH. Going wireless and booth-less for hearing testing in industry. Int J Audiol. 2017; 56(sup1):41–51.
Article17. van Tonder J, Swanepoel W, Mahomed-Asmail F, Myburgh H, Eikelboom RH. Automated smartphone threshold audiometry: validity and time efficiency. J Am Acad Audiol. 2017; 28(3):200–208.
Article18. Khoza-Shangase K, Kassner L. Automated screening audiometry in the digital age: exploring uHear and its use in a resource-stricken developing country. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2013; 29(1):42–47.
Article19. Foulad A, Bui P, Djalilian H. Automated audiometry using apple iOS-based application technology. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013; 149(5):700–706.
Article20. Voss SE, Herrmann BS. How does the sound pressure generated by circumaural, supra-aural, and insert earphones differ for adult and infant ears? Ear Hear. 2005; 26(6):636–650.
Article21. Tsai V, Ostroff J, Korman M, Chen JM. Bone-conduction hearing and the occlusion effect in otosclerosis and normal controls. Otol Neurotol. 2005; 26(6):1138–1142.
Article22. Margolis RH, Saly GL, Le C, Laurence J. Qualind: a method for assessing the accuracy of automated tests. J Am Acad Audiol. 2007; 18(1):78–89.
Article23. Brennan-Jones CG, Eikelboom RH, Swanepoel W. Diagnosis of hearing loss using automated audiometry in an asynchronous telehealth model: a pilot accuracy study. J Telemed Telecare. 2017; 23(2):256–262.
Article24. Xing Y, Fu Z, Wu X, Chen J. Evaluation of Apple iOS-based automated audiometry. In : Proceedings of the 22nd International Congress on Acoustics; 2016 Sep 5-9; Buenos Aires, Argentina.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Improvement of Night Pharmacy Service by Automated Dispensing Cabinet System Implementation in Emergency Medical Center
- The Feasibility of Using Automated Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emission (DPOAE) as a Screening Auditory Function Test of Workers in a Noisy Environment
- Auditory booster adaptor in scale-out cases on pure tone audiometry
- Evaluation of Recurrence of Otitis Media with Effusion Using Ultra High Frequency Audiometry
- Clinical application of 40Hz event related potential for audiometry