Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2019 Jan;21(1):61-65. 10.14253/acn.2019.21.1.61.
Motor dominant polyradiculopathy with Primary Sjögren's syndrome mimicking motor neuron disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nrybn1230@gmail.com
- KMID: 2434190
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2019.21.1.61
Abstract
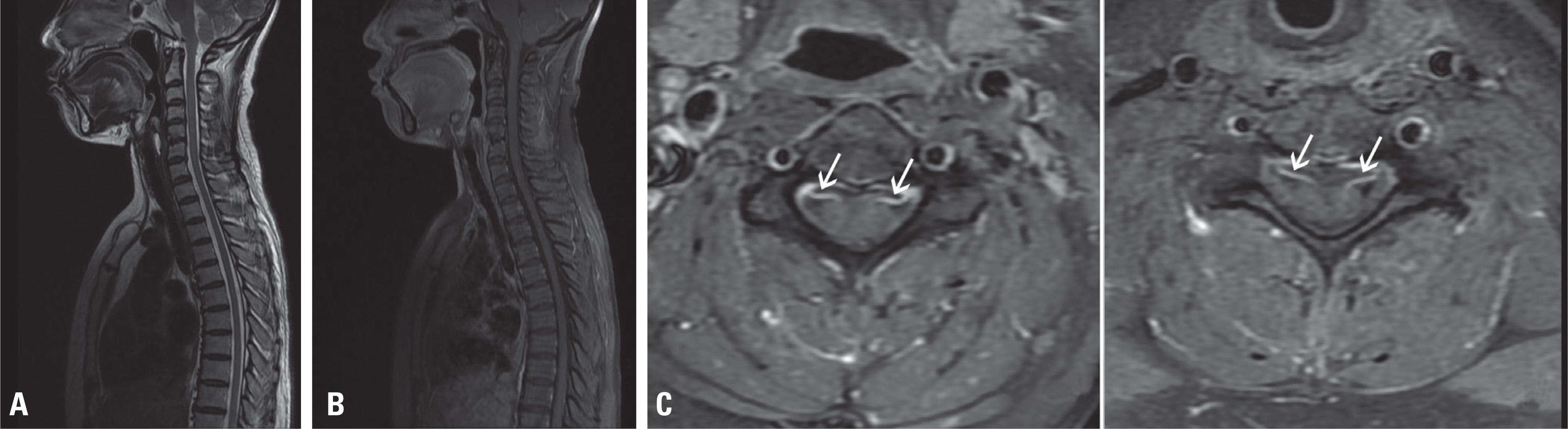
- Sjögren's syndrome (SS)-associated polyradiculopathy is rarely reported. A 51-year-old woman presented with a history of gradual weakness in all four extremities for several months. Based on electrophysiological studies, spinal magnetic resonance imaging and cerebrospinal fluid examination, inflammatory polyradiculopathy was confirmed. During a search for the aetiology, the patient was ultimately diagnosed with SS. This study introduces SS-associated polyradiculopathy that primarily presented with motor symptoms, thus mimicking motor neuron disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Venables P. Sjögren's syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2004; 18:313–329.
Article2. Asmussen K, Andersen V, Bendixen G, Schi⊘dt M, Oxholm P. A new model for classification of disease manifestations in primary Sjögren's syndrome: evaluation in a retrospective longterm study. J Intern Med. 1996; 239:475–482.3. Pavlakis PP, Alexopoulos H, Kosmidis ML, Mamali I, Moutsopoulos HM, Tzioufas AG, et al. Peripheral neuropathies in Sjögren's syndrome: a critical update on clinical features and pathogenetic mechanisms. J Autoimmun. 2012; 39:27–33.
Article4. Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, et al. Classification criteria for Sjögren's syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the Amer-ican-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002; 61:554–558.5. Lafitte C. Neurological manifestations in Sjögren's syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2000; 57:411–413.6. Delalande S, de Seze J, Fauchais AL, Hachulla E, Stojkovic T, Ferriby D, et al. Neurologic manifestations in primary Sjögren syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore). 2004; 83:280–291.
Article7. Mori K, Iijima M, Koike H, Hattori N, Tanaka F, Watanabe H, et al. The wide spectrum of clinical manifestations in Sjögren's syndrome-as-sociated neuropathy. Brain. 2005; 128(Pt 11):2518–2534.
Article8. Grant IA, Hunder GG, Homburger HA, Dyck PJ. Peripheral neuropathy associated with sicca complex. Neurology. 1997; 48:855–862.
Article9. Rigamonti A, Lauria G, Balgera R, Agostoni E. Subacute inflammatory polyradiculopathy associated with Sjögren's syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2009; 39:855–857.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Treatment with Steroid and Hydrochloroquine of Thrombocytopenia in Primary Sjögren's Syndrome
- A Case of Sjögren-Larsson Syndrome
- Longitudinal Changes of the European League Against Rheumatism Sjögren's Syndrome Patient Reported Index in Korean Patients with Primary Sjögren's Syndrome
- A Case of Lacrimal Gland MALT Lymphoma in a Patient with Primary Sjögren's Syndrome
- Rehabilitation using twin-stage method for a Sjögren's syndrome patient with severe discoloration and attrition on upper and lower anterior teeth