Ann Surg Treat Res.
2019 Feb;96(2):95-99. 10.4174/astr.2019.96.2.95.
Incidence and risk factors for herpes zoster after adult liver transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yjongman21@gmail.com
- KMID: 2433946
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2019.96.2.95
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Herpes zoster (HZ) is caused by reactivation of the varicella zoster virus, which occurs frequently in liver transplant recipients with impaired cellular immunity. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the incidence and risk factors for HZ after adult liver transplantation (LT).
METHODS
In our institution, 993 patients underwent adult LT from January 1997 to December 2013. We retrospectively analyzed the incidence rate of HZ and risk factors for HZ after LT.
RESULTS
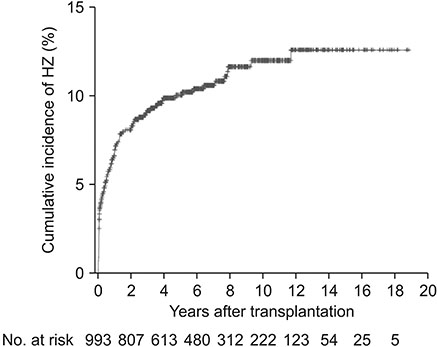
Of 993 LT recipients, 101 (10.2%) were diagnosed with HZ. The incidence of HZ at 1, 3, 5, and 10 years was 6.6%, 9.1%, 10.0%, and 11.9%, respectively. Therefore, we observed that the incidence of HZ after LT was 16.3 per 1,000 person-years. Older age (≥50 years) at LT and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) exposure were independent risk factors of HZ infection after adult LT.
CONCLUSION
Patients older than 50 years or with MMF exposure are considered to be at high risk for HZ. Therefore, adult liver recipients with such factors should not be given strong immunosuppression treatments.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Levitsky J, Kalil A, Meza JL, Hurst GE, Freifeld A. Herpes zoster infection after liver transplantation: a case-control study. Liver Transpl. 2005; 11:320–325.
Article2. Kim YJ, Lee CN, Lim CY, Jeon WS, Park YM. Population-based study of the epidemiology of herpes zoster in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:1706–1710.
Article3. Herrero JI, Quiroga J, Sangro B, Pardo F, Rotellar F, Alvarez-Cienfuegos J, et al. Herpes zoster after liver transplantation: incidence, risk factors, and complications. Liver Transpl. 2004; 10:1140–1143.
Article4. Hamaguchi Y, Mori A, Uemura T, Ogawa K, Fujimoto Y, Okajima H, et al. Incidence and risk factors for herpes zoster in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis. 2015; 17:671–678.
Article5. Fishman JA. Overview: cytomegalovirus and the herpesviruses in transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13:Suppl 3. 1–8.
Article6. Whitley RJ, Shukla S, Crooks RJ. The identification of risk factors associated with persistent pain following herpes zoster. J Infect Dis. 1998; 178:Suppl 1. S71–S75.
Article7. Manuel O, Kumar D, Singer LG, Cobos I, Humar A. Incidence and clinical characteristics of herpes zoster after lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2008; 27:11–16.
Article8. Pergam SA, Forsberg CW, Boeckh MJ, Maynard C, Limaye AP, Wald A, et al. Herpes zoster incidence in a multicenter cohort of solid organ transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis. 2011; 13:15–23.
Article9. Koo S, Gagne LS, Lee P, Pratibhu PP, James LM, Givertz MM, et al. Incidence and risk factors for herpes zoster following heart transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis. 2014; 16:17–25.
Article10. Miller GG, Dummer JS. Herpes simplex and varicella zoster viruses: forgotten but not gone. Am J Transplant. 2007; 7:741–747.
Article11. Gialloreti LE, Merito M, Pezzotti P, Naldi L, Gatti A, Beillat M, et al. Epidemiology and economic burden of herpes zoster and post-herpetic neuralgia in Italy: a retrospective, population-based study. BMC Infect Dis. 2010; 10:230.
Article12. Ko GB, Kim T, Kim SH, Choi SH, Kim YS, Woo JH, et al. Increased incidence of herpes zoster in the setting of cytomegalovirus preemptive therapy after kidney transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis. 2013; 15:416–423.
Article13. Klupp J, Pfitzmann R, Langrehr JM, Neuhaus P. Indications of mycophenolate mofetil in liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2005; 80:1 Suppl. S142–S146.
Article14. Brennan DC, Aguado JM, Potena L, Jardine AG, Legendre C, Saemann MD, et al. Effect of maintenance immunosuppressive drugs on virus pathobiology: evidence and potential mechanisms. Rev Med Virol. 2013; 23:97–125.
Article15. Levin MJ, Smith JG, Kaufhold RM, Barber D, Hayward AR, Chan CY, et al. Decline in varicella-zoster virus (VZV)-specific cell-mediated immunity with increasing age and boosting with a high-dose VZV vaccine. J Infect Dis. 2003; 188:1336–1344.
Article16. Yawn BP, Gilden D. The global epidemiology of herpes zoster. Neurology. 2013; 81:928–930.
Article17. Schlitt HJ, Barkmann A, Boker KH, Schmidt HH, Emmanouilidis N, Rosenau J, et al. Replacement of calcineurin inhibitors with mycophenolate mofetil in liver-transplant patients with renal dysfunction: a randomised controlled study. Lancet. 2001; 357:587–591.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Clinical Study of Motor Involvement by Herpes Zoster
- Epidemiological Study on the Incidence of Herpes Zoster in Nearby Cheonan
- Zoster-associated Pain
- Herpes Simplex Virus and Varicella Zoster Virus Infections in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients: Incidence and Risk Factor Analysis
- A Study of Cellular and Humoral Immunity in Patients with Herpes Zoster