J Rhinol.
2018 Nov;25(2):108-113. 10.18787/jr.2018.25.2.108.
A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma of Maxillary Sinus Misdiagnosed as Odontogenic Cyst
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Inje University of College of Medicine, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Ilsan, Korea. leochoics@gmail.com
- KMID: 2431225
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2018.25.2.108
Abstract
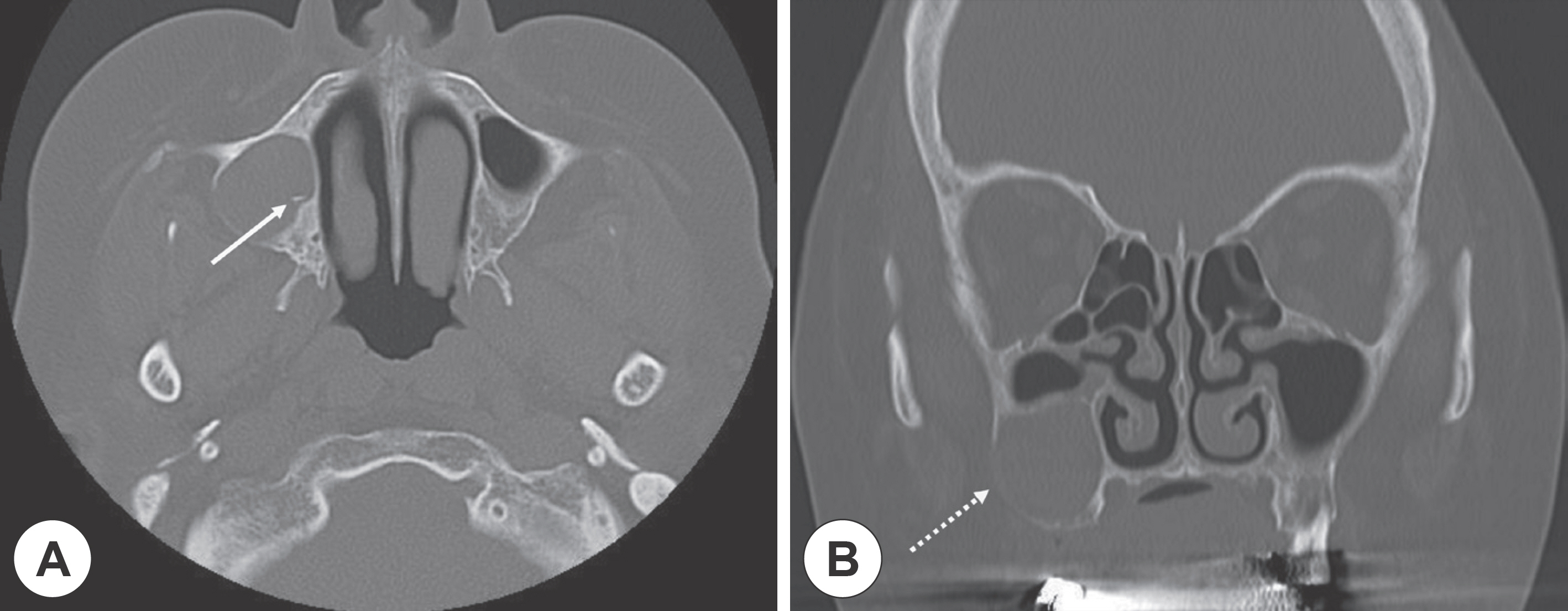
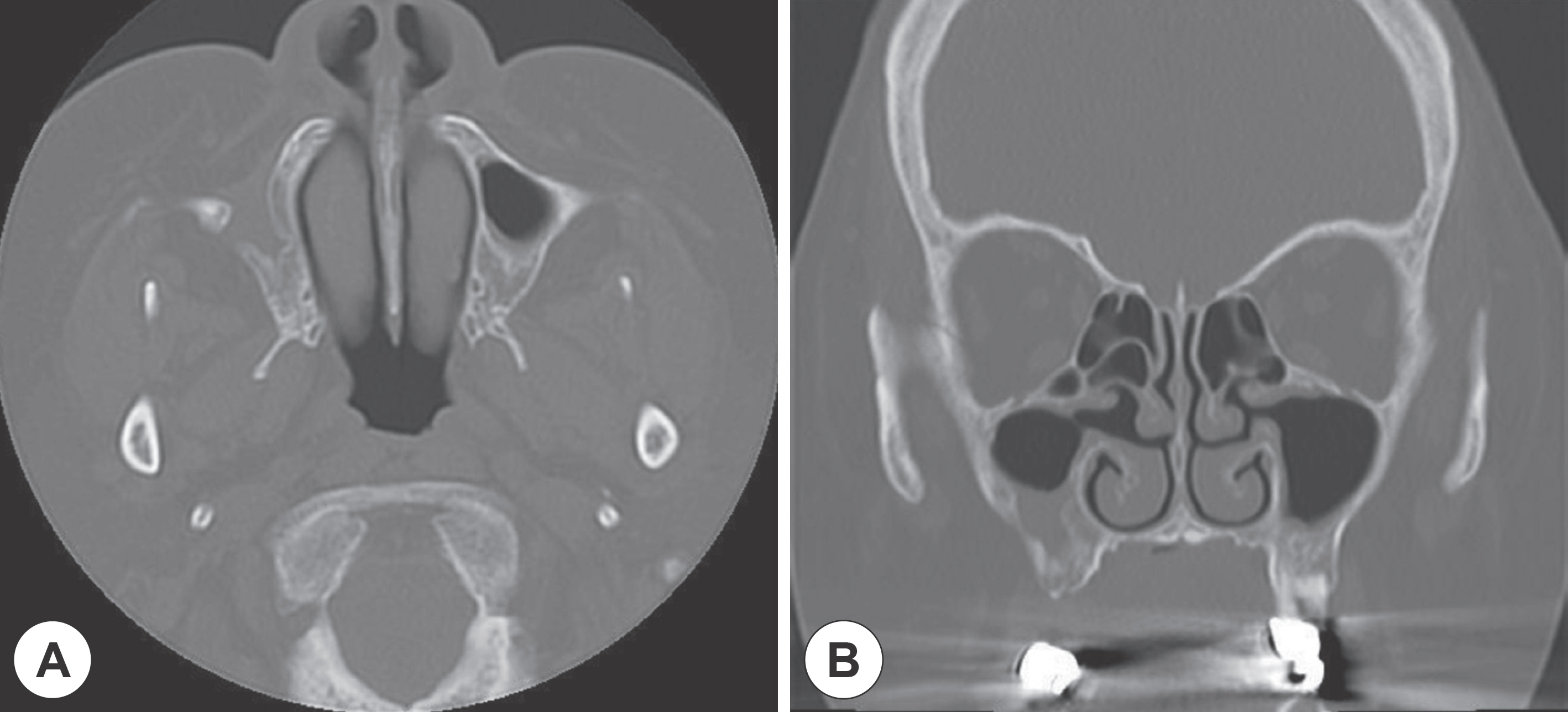
- Cholesterol granuloma is a disease in which cholesterol crystals act as a foreign substance in the surrounding tissues and cause granulomatous reaction and fibrosis within the chamber. It is found in various locations of the body, but the most common location is the temporal bone associated with middle ear disease. Because the disease is associated with breathing disturbance, it may also occur in the paranasal sinus. However, it has been rarely reported since its first report by Graham and Michaels in 1978. Recently, we experienced a case of cholesterol granuloma of the right maxillary sinus of a 63-year-old female patient without any nasal symptoms. We successfully managed this case with Caldwell-Luc operation. Also, we summarized the cases of cholesterol granuloma of the sinonasal region reported in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Nasopalatine Duct Cyst with Cholesterol Granuloma in Maxillary Sinus
Ju Chang Kang, Kyu Ha Shin, Eun Mee Han, Sang Hyeon Ahn
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2020;63(11):528-532. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2019.00661.
Reference
-
1). Eijpe AA., Koornneef L., Verbeeten B Jr., Peeters FLM., Zonneveld FW. Cholesterol granuloma of the frontal bone: CT diagnosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990. 14:914–7.2). Hellquist H., Lundgren I., Olofsson J. Cholesterol granuloma of the maxillary and frontal sinuses. ORL. 1978. 46:153–8.
Article3). McNab AA., Wright JE. Orbitofrontal cholesterol granuloma. Ophthalmology. 1990. 97:28–32.
Article4). Manasse P. Ueber Granulations geschwulste mit Fremdkoerrie-sen-zellen. Virchows Arch. 1894. 136:245.5). Kim JH., Kim MG., Yoo KS., Lee BJ. Cholesterol granuloma of the paranasal sinuses: Report of five cases. Korean J Otolaryngol. 2000. 43:234–8.6). Rath-Wolfson L., Talmi YP., Halpern M., Levit I., Zohar Y., Gal R. Cholesterol granulomas of the maxillary sinus presenting with nasal obstruction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993. 109:956–8.
Article7). Dinesh SF., Simon EP., John XO. Pathogenesis of orbital cholesterol granuloma. Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology. 2003. 31:78–82.8). Graham J., Michaels L. Cholesterol granuloma of the maxillary antrum. Clin Otolaryngol. 1978. 3:155–60.
Article9). Milton M., Bickerton RC. A review of maxillary sinus cholesterol granuloma. Brit J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1986. 24:293–9.
Article10). Butler S., Grossenbacher R. Cholesterol granuloma of the paranasal sinuses. J Laryngol Otol. 1989. 103:776–9.11). Choi YS., Lee HC., Joo M. Odontogenic keratocyst in the maxillary Sinus. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002. 24(1):61–64.12). Panders AK. Haddlers HN. Solitary keratocysts of the jaws. J Oral Surg. 1969. 27:931–8.13). Crowley TE., Kaugars GE., Gunsolley JC. Odontogenic keratocysts: a clinical and histologic comparison of the parakeratin and ortho-keratin variants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1992. 50:22–6.
Article14). Zachariades N., Papanicolaou S., Triantafyllou D. Odontogenic ker-atocysts: review of the literature and report of sixteen cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1985. 43:177–82.
Article15). Min YG., Jung HW., Yu WS., Kim IT. A case of cholesterol granuloma of the sphenoid sinus. Korean J Otolaryngol. 1991. 34:1237–41.16). Dilek FH., Kiriş M., Uğraş S. Cholesterol granuloma of the maxillary sinus. A case report. Rhinology. 1997. 35(3):140–1.17). Hartman JM., Stankiewicz JA., Maywood IL. Cholesteatoma of the paranasal sinuses: Case report and review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J. 1991. 70(10):719–25.18). Park KH., Koh JW., Kim SW. Clinical features of cholesterol granuloma in temporal bone. Korean J Otolatyngol. 1997. 40:513–9.19). Brackmann D E., Toh E H. Surgical management of petrous apex cholesterol granulomas. Otol Neurotol. 2002. 23(4):529–33.20). Mosnier I., Cyna-Gorse F., Grayeli AB., Fraysse B., Martin C., Robier A, et al. Management of cholesterol granulomas of the petrous apex based on clinical and radiologic evaluation. Otol Neurotol. 2002. 23(4):522–8.
Article21). Georgalas C., Kania R., Guichard JP., Sauvaget E., Tran Ba Huy P., Herman P. Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery for cholesterol granulomas involving the petrous apex. Clin Otolaryngol. 2008. 33(1):38–42.
Article22). Lim GS., Kim SW., Kwon SH., Yoon YJ. A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma of the Ethmoid Sinus. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 1990. 33(3):628–32.23). Uhm CS., Jang BS., Shin SL., Yoon HY., Chun IG. A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma of the Maxillary Antrum. Korean J Otorhinolaryn-gol-Head Neck Surg. 1990. 33(5):1012–5.24). Kim YD., Lee JE., Kwak DS., Song SY. Transnasal Endoscopic Treatment of Cholesterol Granuloma of Bilateral Maxillary Sinuses after Facial Trauma. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2002. 45(4):408–11.25). Jun JH., Park JY., Yeo CK., Shon KR. A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma of the Sphenoid Sinus. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2002. 45(3):293–5.26). Cho CG., Cho JG., Jung JR., Park JY. A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma of the Frontal and Ethmoid Sinus. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2004. 47(5):483–5.27). Park SW., Min IK., Park CH., Rha KS. Two Cases of Cholesterol Granuloma in Ethmoid Sinuses. J Rhinol. 2003. 10(1,2):53–6.28). Baek HI., Kim WH., Park BC., Choi DJ. A Case of Management of Cholesterol Granuloma in Frontal Sinus by Endoscopic Marsupialization. J Clinical Otolaryngol. 2007. 18(1):92–5.
Article29). Kim SW., Kang JH., Kim YJ., Kim CD. Multiple Cholesterol Granuloma Involving the Paranasal Sinus: A Case Report. J Rhinol. 2008. 15(1):69–73.30). Kim DH., Lee SK., Kim CH., Cho HJ. Radiologically Unusual Presentation of Cholesterol Granuloma in the Sphenoid Sinus. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2015. 58(9):641–5.
Article31). Koo SK., Kim YJ., Jung SH., Son H. Cholesterol Granuloma of Nasal Septum. J Rhinol. 2015. 22(1):44–6.
Article32). Lee IH., Nam IC., Jeong JW., Kim DH. A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma in the Nasal Septum. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2016. 59(1):49–52.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Nasopalatine Duct Cyst with Cholesterol Granuloma in Maxillary Sinus
- Transnasal Endoscopic Treatment of Cholesterol Granuloma of Bilateral Maxillary Sinuses after Facial Trauma
- Cholesterol granuloma of the paranasal sinuses: Report of five cases
- A Case of Cholesterol Granuloma in the Nasal Septum
- Endonasal Removal of Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxillary Sinus