Korean Circ J.
2019 Jan;49(1):115-117. 10.4070/kcj.2018.0305.
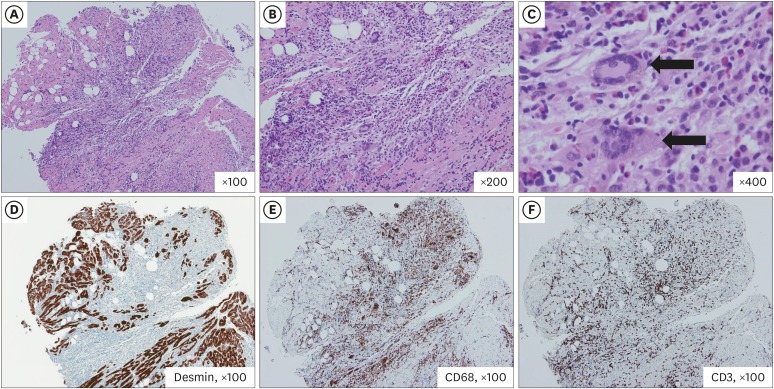
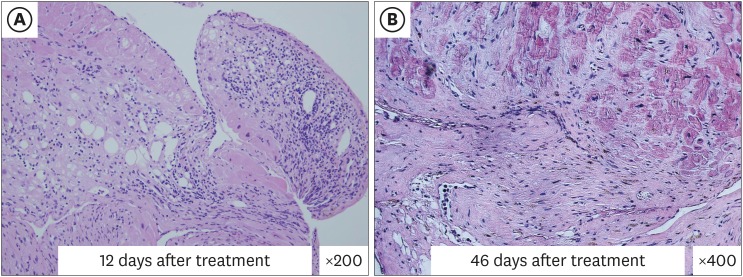
Clinical and Histological Response to Immunosuppressive Therapy in Giant Cell Myocarditis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. hyunjaicho@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2430756
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2018.0305
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fluschnik N, Escher F, Blankenberg S, Westermann D. Fatal recurrence of fulminant giant cell myocarditis and recovery after initialisation of an alternative immunosuppressive regime. BMJ Case Rep. 2014; 2014:bcr2014206386.2. Vaideeswar P, Cooper LT. Giant cell myocarditis: clinical and pathological features in an Indian population. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013; 22:70–74. PMID: 22863545.3. Kodama M, Matsumoto Y, Fujiwara M, Masani F, Izumi T, Shibata A. A novel experimental model of giant cell myocarditis induced in rats by immunization with cardiac myosin fraction. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990; 57:250–262. PMID: 2208806.4. Weimer R, Staak A, Süsal C, et al. ATG induction therapy: long-term effects on Th1 but not on Th2 responses. Transpl Int. 2005; 18:226–236. PMID: 15691277.