J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs.
2018 Dec;27(4):355-369. 10.12934/jkpmhn.2018.27.4.355.
An Integrative Review of Intervention for School-bullying Perpetrators
- Affiliations
-
- 1Doctoral Student, College of Nursing, Yonsei University, National Center for Mental Health, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Doctoral Student, College of Nursing, Korea University, National Center for Mental Health, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Professor, College of Nursing · Mo-Im Kim Nursing Research Institute, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. PSY0962@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2430261
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12934/jkpmhn.2018.27.4.355
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was intended to integrate the evidence of intervention for child and adolescent perpetrators of school violence through an integrative literature review.
METHODS
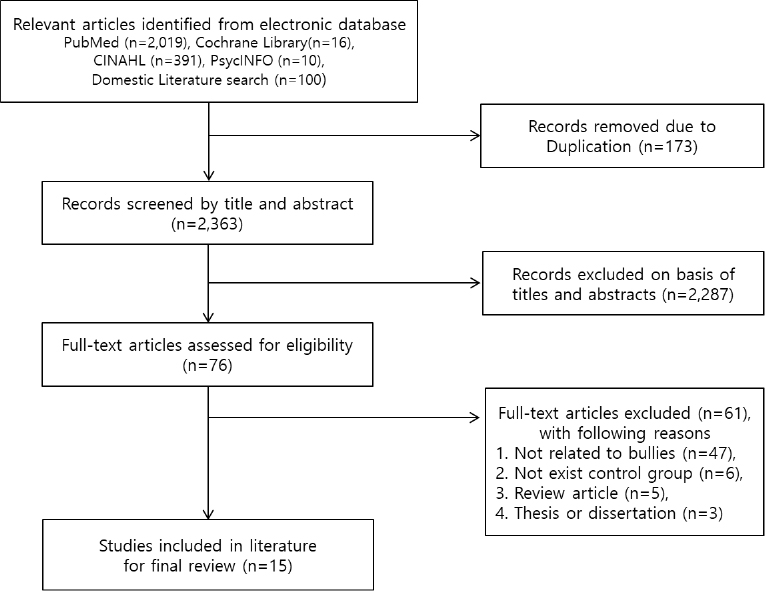
Using combinations of the terms "˜bullying', "˜school violence', and "˜intervention' as key words, the researchers searched eight electronic databases for relevant studies. Fifteen studies were selected through full-text screening of related research published in academic journals before June 2018. The framework was used to identify the selected studies' intervention patterns and classify the various intervention components. The extracted intervention components were grouped into potential themes to determine whether the researchers clearly showed the interventions in the studies.
RESULTS
The intervention components of 15 selected studies were categorized into five themes: 1) Utilizing intervention techniques for voluntary participation, 2) Enhancing self-awareness, 3) Strategies to improve emotional intelligence, 4) Promoting interpersonal skills, and 5) Emphasis on responsibility through future vision experience.
CONCLUSION
As a result of analyzing interventions for children and adolescent perpetrators of school violence, five components were derived. It is suggested that these components should be considered in the field, and intervention programs development and research using them are needed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hawker DS, Boulton MJ. Twenty years' research on peer victimization and psychosocial maladjustment: a meta-analytic review of cross-sectional studies. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 2000; 41(4):441–455. DOI: 10.1017/s0021963099005545.
Article2. Lee BC. Move the place and beat it overnight, school violence controversy in Jecheon. Newsis [Internet]. 2018. cited 2018 Oct 8. Available from: http://www.newsis.com/view/?id=NISX20181008_0000437040&cID=10806&pID=10800.3. Coloroso B. The bully, the bullied and the bystander. From preschool to high school: how parents and teachers can help break the cycle of violence. Updated ed. New York, NY: Collins Living;2010. p. 272.4. Wolke D, Copeland WE, Angold A, Costello EJ. Impact of bullying in childhood on adult health, wealth, crime, and social outcomes. Psychological Science. 2013; 24(10):1958–1970. DOI: 10.1177/0956797613481608.
Article5. Ttofi MM, Farrington DP. Effectiveness of school-based programs to reduce bullying: a systematic and meta-analytic review. Journal of Experimental Criminology. 2011; 7(1):27–56. DOI: 10.1007/s11292-010-9109-1.
Article6. Hess M, Wirtz S, Allroggen M, Scheithauer H. Intervention and therapy for perpetrators and victims of bullying: a systematic review. Praxis der Kinderpsychologie und Kinderpsychiatrie. 2017; 66(10):740–755. DOI: 10.13109/prkk.2017.66.10.740.
Article7. Olweus D. Bullying at school: basic facts and effects of a school based intervention program. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 1994; 35(7):1171–1190. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1994.tb01229.x.
Article8. Álvarez-García D, García T, Núñez JC. Predictors of school bullying perpetration in adolescence: a systematic review. Aggression and Violent Behavior. 2015; 23:126–136. DOI: 10.1016/j.avb.2015.05.007.
Article9. Haynie DL, Nansel T, Eitel P, Crump AD, Saylor K, Yu K, et al. Bullies, victims, and bully/victims: distinct groups of at-risk youth. The Journal of Early Adolescence. 2001; 21(1):29–49. DOI: 10.1177/0272431601021001002.10. Kwon SJ, Park TW, Park SH, Yang JC, Chung YC, Chung SK. Prevalence of school bullying and related psychopathology in children and adolescents. Journal of the Korean Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 2012; 23(3):143–153. DOI: 10.5765/jkacap.2012.23.3.143.
Article11. Song JI. A study on the effective preventive measures of recidivism for school violent offenders on juvenile probation. Korean Journal of Probation. 2012; 12(1):39–66.12. Yoon CH, Park SG, Shin IS. A meta-analysis of the effects of school violence prevention programs in Korea. Asian Journal of Education. 2014; 15(1):189–215.13. Whittemore R, Knafl K. The integrative review: updated methodology. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2005; 52(5):546–553. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2005.03621.x.
Article14. Kim SJ, Kim SH, Lee JE, Kim HY, Yoo SY, Oh J. An integrative review on nursing studies related to humor. Child Health Nursing Research. 2014; 20(1):58–66. DOI: 10.4094/chnr.2014.20.1.58.
Article15. Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration [Internet]. 2011. cited 2018 Oct 8. Available from: http://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org.16. Kim SY, Park JE, Seo HJ, Seo HS, Son HJ, Shin CM, et al. NECA's guidance for undertaking systematic reviews and meta-analyses for intervention. Seoul: National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency;2011. p. 271.17. Seo HJ, Kim SY, Lee YJ, Jang BH, Park JE, Sheen SS, et al. A newly developed tool for classifying study designs in systematic reviews of interventions and exposures showed substantial reliability and validity. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2016; 70:200–205. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2015.09.013.
Article18. Kim D, Lee I. An integrative review of home care service for pregnant women, mothers, infants, and toddlers in vulnerable group. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2017; 47(5):577–588. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.577.
Article19. Kim JE. The effects of positive psychology-based group counseling program on positivity and school adjustment resilience of school violence perpetrators. Journal of Social Science. 2016; 27(4):145–162. DOI: 10.16881/jss.2016.10.27.4.145.
Article20. Knowler C, Frederickson N. Effects of an emotional literacy intervention for students identified with bullying behaviour. Educational Psychology. 2013; 33(7):862–883. DOI: 10.1080/01443410.2013.785052.
Article21. Wong CS, Law KS. The effects of leader and follower emotional intelligence on performance and attitude: an exploratory study. The Leadership Quarterly. 2002; 13(3):243–274. DOI: 10.1016/s1048-9843(02)00099-1.
Article22. Lee GY, Choi JH, Song JY, Jeon JH. The effectiveness of prevention program of recidivism for school violence on juvenile probation <focusing on the empathy development training program>. Korean Journal of Probation. 2013; 13(2):249–274.23. Şahin M. An investigation into the efficiency of empathy training program on preventing bullying in primary schools. Children and Youth Services Review. 2012; 34(7):1325–1330. DOI: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2012.03.013.
Article24. Moon YL. Theory and practice of school violence crisis intervention. Seoul: Hakjisa;2008. p. 504.25. Perry DG, Kusel SJ, Perry LC. Victims of peer aggression. Developmental Psychology. 1988; 24(6):807–814. DOI: 10.1037/0012-1649.24.6.807.
Article26. Budman SH, Demby A, Redondo JP, Hannan M, Feldstein M, Ring J, et al. Comparative outcome in time-limited individual and group psychotherapy. International Journal of Group Psychotherapy. 1988; 38(1):63–86. DOI: 10.1080/00207284.1988.11491085.
Article27. Dishion TJ, McCord J, Poulin F. When interventions harm: peer groups and problem behavior. American Psychologist. 1999; 54(9):755–764. DOI: 10.1037//0003-066x.54.9.755.
Article28. Lee YS, Kwon JH, Lee SM. The effect of problem-solving group therapy for bullies and victims of bullying. Korean Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2006; 25(4):881–898.29. Yang JK, Kim CK. Relationships among delinquent risk factors, protective factors and recidivism of juvenile delinquency. The Korea Journal of Youth Counseling. 2002; 10(2):101–121.30. Kim SA, Kim JI, Choi JW, Lim J, Kim BN. Effects of cognitive behavioral therapy-based program for the adolescent perpetrators of school violence. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 2017; 56(3):118–126. DOI: 10.4306/jknpa.2017.56.3.118.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- School Bullying Among Korean Students-Current Status
- Development of Korean-Peer Nomination Inventory(K-PNI):An Inventory to Evaluate School Bullying
- The role of physicians in preventing school bullying
- School Bullying and Related Psychopathology in Elementary School Students
- The Relationship Between Bullying and Risk of Suicide Among Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia