Perinatology.
2018 Dec;29(4):153-158. 10.14734/PN.2018.29.4.153.
Efficacy of Serum Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio for Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. myojing@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2430217
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/PN.2018.29.4.153
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the relationship between serum neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and severity of meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS).
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed 197 neonates who admitted for MAS between 2008 and 2016 at the neonatal intensive care unit of Dong-A University Hospital. The serial changes of NLR were analyzed from 1st to 3rd day of life. The NLR was compared by disease severities (non-invasive respiratory care group vs. invasive respiratory care group and MAS with or without persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn [PPHN]).
RESULTS
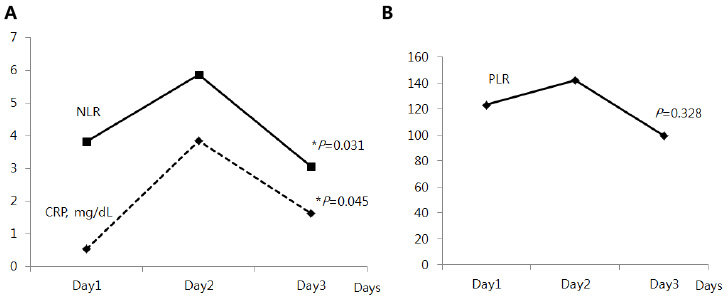
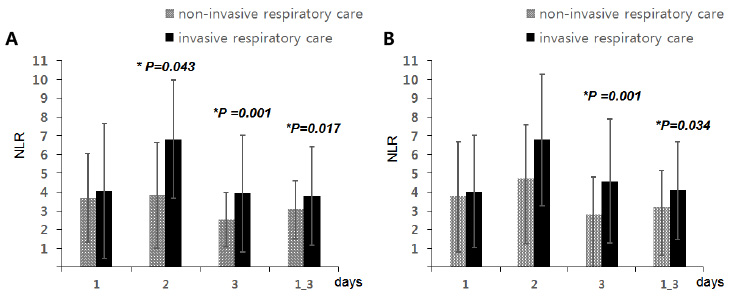
The NLR values from 1st to 3rd day of life significantly increased and then decreased (P=0.031). The NLR of invasive respiratory care group was significantly higher than non-invasive respiratory care group at 2nd, 3rd, and average of 1 to 3 days of life. The NLR of PPHN group was significantly higher than without PPHN group at 3rd, and average of 1 to 3 days of life.
CONCLUSION
The NLR was significantly increased and then decreased in early stage of MAS and associated with the severity of MAS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lindenskov PH, Castellheim A, Saugstad OD, Mollnes TE. Meconium aspiration syndrome: possible pathophysiological mechanisms and future potential therapies. Neonatology. 2015; 107:225–230.
Article2. Lee EC, Choi MG, Shim GH, Song YH, Chey MJ. Comorbid risk factors of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn in infants with meconium aspiration syndrome. Neonatal Med. 2014; 21:166–171.
Article3. Singh SN, Srivastava R, Singh A, Tahazzul M, Kumar M, Kanta C, et al. Respiratory distress including meconium aspiration syndrome in vigorous neonates born through meconium stained amniotic fluid: incidence, onset, severity and predictors at birth. Indian J Pediatr. 2013; 80:583–543.
Article4. Louis D, Sundaram V, Mukhopadhyay K, Dutta S, Kumar P. Predictors of mortality in neonates with meconium aspiration syndrome. Indian Pediatr. 2014; 51:637–640.
Article5. Wiswell TE. Handling the meconium-stained infant. Semin Neonatol. 2001; 6:225–231.
Article6. Vidyasagar D, Lukkarinen H, Kaapa P, Zagariya A. Inflammatory response and apoptosis in newborn lungs after meconium aspiration. Biotechnol Prog. 2005; 21:192–197.
Article7. de Beaufort AJ, Bakker AC, van Tol MJ, Poorthuis BJ, Schrama AJ, Berger HM. Meconium is a source of pro-inflammatory substances and can induce cytokine production in cultured A549 epithelial cells. Pediatr Res. 2003; 54:491–495.
Article8. Mokra D, Mokry J. Glucocorticoids in the treatment of neonatal meconium aspiration syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 2011; 170:1495–1505.
Article9. Hofer N, Jank K, Strenger V, Pansy J, Resch B. Inflammatory indices in meconium aspiration syndrome. Pediatric Pulmonology. 2016; 51:601–606.
Article10. Dargaville PA. Respiratory support in meconium aspiration syndrome: a practical guide. Int J Pediatr. 2012; 2012:965159.
Article11. Castellheim A, Lindenskov PH, Pharo A, Aamodt G, Saugstad OD, Mollnes TE. Meconium aspiration syndrome induces complement-associated systemic inflammatory response in newborn piglets. Scand J Immunol. 2005; 61:217–225.
Article12. Gupta GK, Cole CH, Abbasi S, Demissie S, Njinimbam C, Nielsen HC, et al. Effects of early inhaled beclomethsone therapy on tracheal aspirate inflammatory mediators IL-8 and IL-1ra in ventilated preterm infants at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000; 30:275–281.13. Hofer N, Zacharias E, MüllerW , Resch B. An update on the use of C-reactive protein in early-onset neonatal sepsis: current insights and new tasks. Neonatology. 2012; 102:25–36.
Article14. Bhandari V. Effective biomarkers for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2014; 3:234–245.
Article15. Wu Y, Chen Y, Yang X, Chen L, Yang Y. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were associated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016; 36:94–99.
Article16. Guthrie GJ, Charles KA, Roxburgh CS, Horgan PG, McMillan DC, Clarke SJ. The systemic inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: experience in patients with cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013; 88:218–230.
Article17. Walsh SR, Cook EJ, Goulder F, Justin TA, Keeling NJ. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2005; 91:181–184.
Article18. Tamhane UU, Aneja S, Montgomery D, Rogers EK, Eagle KA, Gurm HS. Association between admission neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 2008; 102:653–657.
Article19. Templeton AJ, Ace O, McNamara MG, Al-Mubarak M, Vera-Badillo FE, Hermanns T, et al. Prognostic role of platelet to lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014; 23:1204–1212.
Article20. Lee JY, Park KH, Kim A, Yang HR, Jung EY, Cho SH. Maternal and placental risk factors for developing necrotizing enterocolitis in very preterm infants. Pediatr Neonatol. 2017; 58:57–62.
Article21. Akgun N, Namli Kalem M, Yuce E, Kalem Z, Aktas H. Correlations of maternal neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) with birth weight. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017; 30:2086–2091.
Article22. Kurtul BE, Kabatas EU, Zenciroglu A, Ozer PA, Ertugrul GT, Beken S, et al. Serum neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in retinopathy of prematurity. J AAPOS. 2015; 19:327–331.
Article23. Lee J, Dammann O. Perinatal infection, inflammation, and retinopathy of prematurity. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012; 17:26–29.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical observation of meconium aspiration syndrome: prognostic implication of early meconium suctioning
- A Study of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
- A clinical study on meconium-stained babies
- A Clinical Observation of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
- Diagnosis of Meconium Aspiration by Spectrophotometric Analysis of Urine