J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs.
2018 Dec;29(4):510-519. 10.12799/jkachn.2018.29.4.510.
Meta-Analysis of Social Psychological Factors related to Quality of Life in Stroke Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Associate Professor, Department of Nursing, Kaya University, Gimhae, Korea.
- 2Associate Professor, Department of Nursing, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea.
- 3Professor, Department of Nursing, Silla University, Busan, Korea. kypark@silla.ac.kr
- KMID: 2430184
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12799/jkachn.2018.29.4.510
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this meta-analysis isto identify social psychological factors related to quality of life and estimate the effect sizes of the factors among patients with strokes.
METHODS
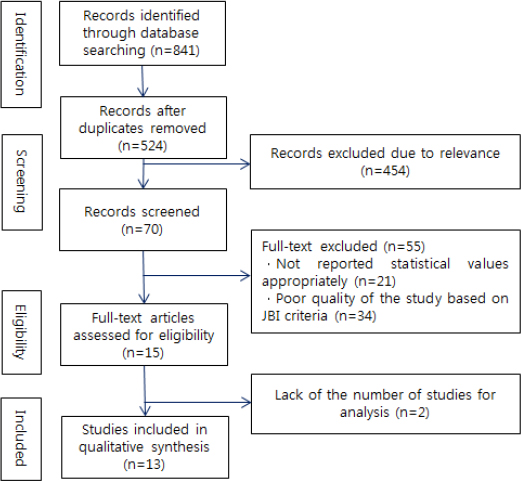
Thirteen studies with a total of 1,814 patients published from the earliest records to January 8, 2017 were selected through a systematic process of searching the literature, and evaluated against influencing factors of quality of life and their effect sizes. Pooled effect sizes were calculated using the random effect model. Meta-analysis was conducted by R software.
RESULTS
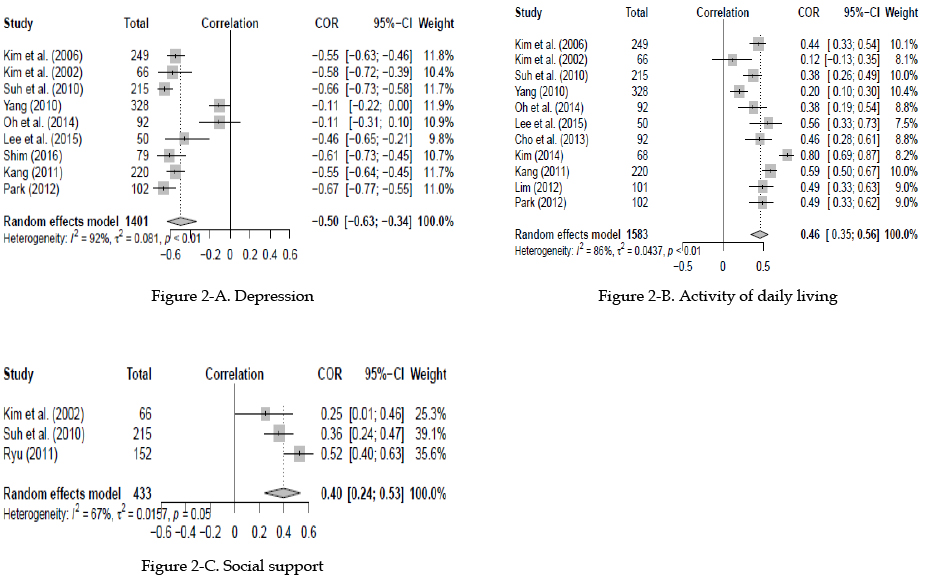
The following influencing factors had a strong association with quality of life with stroke: depression (r=−.50; 95% CI: −0.63~−0.46), activities of daily living (r=.46; 95% CI: 0.35~0.56), and social support (r=.40; 95% CI: 0.24~0.53).
CONCLUSION
The findings confirm that depression, activities of daily living and social support are associated with quality of life among patients with stroke survivors. We recommend that any intervention program to improve the quality of life with stroke patients consider addressing these modifiable influencing factors.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Takemasa S, Nakagoshi R, Murakami M, Uesugi M, Inoue Y, Gotou M, et al. Factors affecting quality of life of the home-bound elderly hemiparetic stroke patients. Journal of Physical Therapy Science. 2014; 26(2):301–303. DOI: 10.1589/jpts.26.301.2. Seok SJ, Lee JA. Comparison of stroke risk factors between middle-aged and elderly patients. Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing. 2017; 19(1):13–27. DOI: 10.17079/jkgn.2017.19.1.13.
Article3. Kim JH, Kang HS, Kim WO, Wang MJ, Chang CM. Factors affecting the quality of life in stroke patient at home. The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing. 2006; 9(1):49–55.4. Obembe AO, Eng JJ. Rehabilitation intervention for improvement social participation after stroke: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair. 2016; 30(4):384–392. DOI: 10.1177/1545968315597072.5. Suh MH, Choi-Kwon SM. Structural equation modeling on quality of life in stroke survivors. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2010; 40(4):533–541. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2010.40.4.533.
Article6. Buijck BI, Zuidema SU, Spruit-van Eijk M, Bor H, Gerritsen DL. Koopmans RTCM. Determinants of geriatric patients' quality of life after stroke rehabilitation. Aging & Mental Health. 2014; 18(8):980–985. DOI: 10.1080/13607863.2014.899969.
Article7. Kim K, Kim YM, Kim EK. Correlation between the activities of daily living of stroke patients in a community setting and their quality of life. Journal of Physical Therapy Science. 2014; 26(3):417–419. DOI: 10.1589/jpts.26.417.8. Yang JB. A study on the major factors affecting health-related quality of life of elderly stroke survivors. Journal of the Korean Geronological Society. 2010; 30(4):1239–1261.9. Tengs TO, Lin TH. A meta-analysis of quality-of-life estimates for stroke. PharmacoEconomics. 2003; 21(3):191–200. DOI: 10.2165/00019053-200321030-00004.
Article10. Chang WH, Sohn MK, Lee J, Kim DY, Lee SG, Shin YI, et al. Predictors of functional level and quality of life at 6 months after a first-ever stroke: The KOSCO study. Journal of Neurology. 2016; 263(6):1166–1177. DOI: 10.1007/s00415-016-8119-y.11. Cho OH, Choi SY, Song JH. The effect of functional dependency and stress on health-related quality of life in patients under rehabilitation after stroke. Journal of Muscle and Joint Health. 2013; 20(2):81–90. DOI: 10.5953/JMJH.2013.20.2.81.
Article12. Lim SO. A structural model for quality of life in stroke patients [dissertation]. [Seoul]: Kyung Hee University;2012.13. Oh EM, Son GR. Factors predicting quality of life among older adults in rehabilitation hospitals after stroke. Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing. 2014; 16(2):107–117. DOI: 10.17079/jkgn.2014.16.2.107.
Article14. Lee JM, Kim HM, Kim JH. The effect of depression, cognitive function, and activities of daily living on quality of life for patients with stroke. Journal of Korean Society of Community Based Occupational Therapy. 2015; 5(1):1–9.15. Kang JG. Factors related to stroke patients' quality of life, and moderating effect of rehabilitation motivation [dissertation]. [Cheong-Ju]: Chungbuk National University;2011. 116.16. Park EY, Shin IS, Kim JH. A meta-analysis of the variables related to depression in Korean patients with a stroke. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2014; 42(4):537–548. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2012.42.4.537.
Article17. Kim HC, Kim SJ, Choi NK, Kim YS, Lee BC, Lee BC, et al. Quality of life after stroke: A two-month follow-up. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 2002; 41(4):681–692.18. Min SK, Kim KI, Suh SY, Kim DK. Development of the Korean version of the world health organization quality of life scale (WHOQOL). Journal of the Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 2000; 39(1):78–88.19. Sturm JW, Dewey HM, Donnan GA, Macdonell RAL, McNeil JJ, Thrift AG. Handicap after stroke: How does it relate to disability, perception of recovery, and stroke subtype?: The North East Melbourne Stroke Incidence Study (NEMESIS). Stroke. 2002; 33(3):762–768. DOI: 10.1161/hs0302.103815.20. Shin SI, Kim YH. A meta-analysis on related variables of elders' quality of life. Korean Journal of Counseling. 2013; 14(6):3673–3690.21. Kruithof WJ, van Mierlo ML, Visser-Meily JMA, van Heugten CM, Post MWM. Associations between social support and stroke survivors' health-related quality of life-a systematic review. Patient Education & Counseling. 2013; 93(2):169–176. DOI: 10.1016/j.pec.2013.06.003.
Article22. The Joanna Briggs Institute. Checklist for analytical cross sectional studies [Internet]. Adelaide: The Joanna Briggs Institute;2017. cited 2017 December 25. Available http://joannabriggs.org/assets/docs/critical-appraisal-tools/JBI_Critical_Appraisal-Checklist_for_Analytical_Cross_Sectional_Studies2017.pdf.23. Schwarzer G. Meta: General package for meta-analysis. R package version 4.9-0 [Internet]. Berkeley, CA: The Comprehensive R Archive Network;2017. cited 2017 February 12. Available from: https://cran.r-project.org/.24. Hwang SD. Meta-analysis using R. Seoul: Hakjisa;2016. p. 236.25. Williams LS, Weinberger M, Harris LE, Clark DO, Biller J. Development of a stroke-specific quality of life scale. Stroke. 1999; 30(7):1362–1369. DOI: 10.1161/01.STR.30.7.1362.
Article26. Min SK, Lee CI, Kim KI, Suh SY. Kim DK. Development of Korean version of WHO quality of life scale abbreviated version (WHOQOL-BREF). Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 2000; 39(3):571–579.27. Lee H, Lee Y, Choi H, Pyun SB. Community intergration and quality of life in aphasia after stroke. Yonsei Medical Journal. 2015; 56(6):1694–1702. DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1694.28. Leach MJ, Gall SL, Dewey HM, Macdonell RA, Thrift AG. Factors associated with quality of life in 7-year survivors of stroke. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 2011; 82(12):1365–1371. DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1694.
Article29. Thilarajah S, Mentiplay BF, Bower KJ, Tan D, Pua YH, Williams G, et al. Factors associated with post-stroke physical activity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2018; 99(9):1876–1889. DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.2010.234765.
Article30. Davie-Smith F, Coulter E, Kennon B, Wyke S, Paul L. Factors influencing quality of life following lower limb amputation for peripheral arterial occlusive disease: A systematic review of the literature. Prosthetics & Orthotics International. 2017; 41(6):537–547. DOI: 10.1177/0309364617690394.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Related Factors of the Quality of Life in Stroke Patients
- A Meta-analysis of the Variables related to Depression in Korean Patients with a Stroke
- Developing a Prediction Model for Quality of Life in Patients with Schizophrenia
- Structural Equation Modeling on Quality of Life in Stroke Survivors
- The Association of Activity Limitation on Health-Related Quality of Life and Depression in Elderly Korean Stroke Patients