J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2018 Dec;53(6):540-546. 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.6.540.
Multimodal Diagnostic Approach for Synovitis of the Wrist
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kjh12344@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2430061
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.6.540
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to suggest a multimodal diagnostic approach to determine the cause of the disease in patients diagnosed with synovitis of the wrist and who underwent synovectomy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
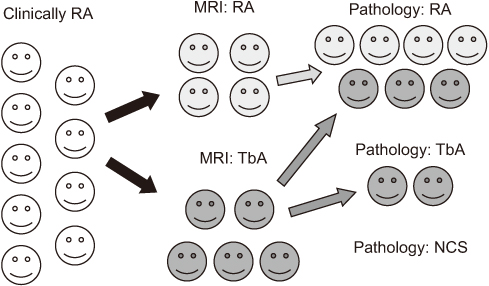
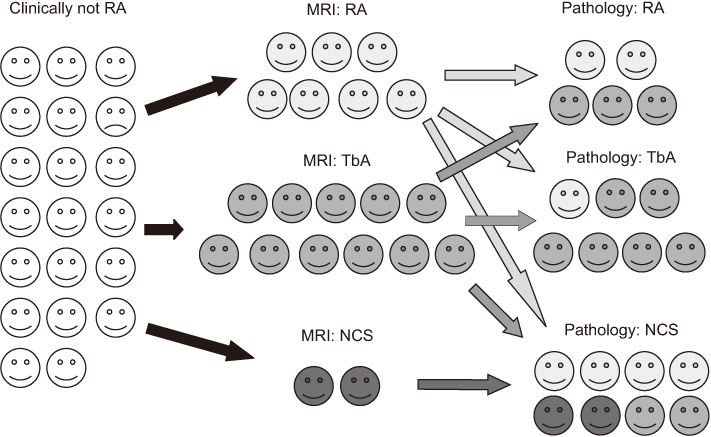
Twenty-nine patients, who underwent contrast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) preoperatively and synovectomy from January 2000 to December 2013, were reviewed retrospectively. Among them, 17 patients underwent a Tc99m white blood cell (WBC) scan preoperatively. In patients who met the diagnostic criteria of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the diagnosis was confirmed as RA if the MRI finding or histology was compatible with RA. If the MRI finding and histology were disparate, the final diagnosis was made based on the histologic finding.
RESULTS
Of the nine patients who met the diagnostic criteria of RA, seven patients were finally diagnosed as RA and two patients as tuberculous arthritis. Of the 20 patients who did not meet the diagnostic criteria of RA, the MRI findings and histology were consistent with the same disease in 12 patients. In the remaining eight patients, five were diagnosed with nonspecific chronic synovitis, one with RA, and two with tuberculous arthritis based on the clinical findings, MRI, and histology findings.
CONCLUSION
MRI and a WBC scan are very useful imaging modalities for diagnosing the causative condition of the wrist synovitis. A histology evaluation after synovectomy can also be useful in cases with a difficult diagnosis or are refractory to medications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Thirupathi RG, Ferlic DC, Clayton ML. Dorsal wrist synovectomy in rheumatoid arthritis: a long-term study. J Hand Surg Am. 1983; 8:848–856.2. Visuthikosol V, Kruavit A, Nitiyanant P, Siriwongpairat P. Tuberculous infection of the hand and wrist. Ann Plast Surg. 1996; 37:55–59.
Article3. Kim SM, Park MJ, Kang HJ, Choi YL, Lee JJ. The role of arthroscopic synovectomy in patients with undifferentiated chronic monoarthritis of the wrist. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012; 94:353–358.
Article4. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:2569–2581.5. Ilan DI, Rettig ME. Rheumatoid arthritis of the wrist. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2003; 61:179–185.6. Kim SJ, Jung KA. Arthroscopic synovectomy in rheumatoid arthritis of wrist. Clin Med Res. 2007; 5:244–250.
Article7. Uno K, Matsui N, Nohira K, et al. Indium-111 leukocyte imaging in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Nucl Med. 1986; 27:339–344.8. McCall IW, Sheppard H, Haddaway M, Park WM, Ward DJ. Gallium 67 scanning in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Radiol. 1983; 56:241–243.
Article9. Dhillon MS, Sharma S, Gill SS, Nagi ON. Tuberculosis of bones and joints of the foot: an analysis of 22 cases. Foot Ankle. 1993; 14:505–513.
Article10. Hodgson AR, Smith TK, Gabriel S. Tuberculosis of the wrist. With a note on chemotherapy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972; 83:73–83.11. Brashear HR, Winfield HG. Tuberculosis of the wrist: a report of ten cases. South Med J. 1975; 68:1345–1349.
Article12. Bush DC, Schneider LH. Tuberculosis of the hand and wrist. J Hand Surg Am. 1984; 9:391–398.
Article13. Choi JA, Koh SH, Hong SH, Koh YH, Choi JY, Kang HS. Rheumatoid arthritis and tuberculous arthritis: differentiating MRI features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:1347–1353.
Article14. Green M, Marzo-Ortega H, McGonagle D, et al. Persistence of mild, early inflammatory arthritis: the importance of disease duration, rheumatoid factor, and the shared epitope. Arthritis Rheum. 1999; 42:2184–2188.
Article15. Benton N, Stewart N, Crabbe J, Robinson E, Yeoman S, Mc-Queen FM. MRI of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis can be used to predict functional outcome at 6 years. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004; 63:555–561.
Article16. van Aken J, van Dongen H, le Cessie v, Allaart CF, Breedveld FC, Huizinga TW. Comparison of long term outcome of patients with rheumatoid arthritis presenting with undifferentiated arthritis or with rheumatoid arthritis: an observational cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006; 65:20–25.
Article17. Harrison BJ, Symmons DP, Barrett EM, Silman AJ. The performance of the 1987 ARA classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis in a population based cohort of patients with early inflammatory polyarthritis. American Rheumatism Association. J Rheumatol. 1998; 25:2324–2330.18. Savnik A, Malmskov H, Thomsen HS, et al. MRI of the arthritic small joints: comparison of extremity MRI (0.2 T) vs high-field MRI (1.5 T). Eur Radiol. 2001; 11:1030–1038.
Article19. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69:1580–1588.20. Kosta PE, Voulgari PV, Zikou AK, Drosos AA, Argyropoulou MI. The usefulness of magnetic resonance imaging of the hand and wrist in very early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011; 13:R84.
Article21. Martini M, Benkeddache Y, Medjani Y, Gottesman H. Tuberculosis of the upper limb joints. Int Orthop. 1986; 10:17–23.
Article22. Hoffman EB, Allin J, Campbell JA, Leisegang FM. Tuberculosis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; (398):100–106.
Article23. Iagnocco A, Coari G, Buzzi G, Guerrisi R, Valesini G. Magnetic resonance imaging of peripheral osteoarticular tuberculosis compared with sonography and standard radiographs. Rheumatol Int. 2003; 23:195–197.
Article24. Leigh Moore S, Rafii M. Advanced imaging of tuberculosis arthritis. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2003; 7:143–153.
Article25. Rydgren L, Wollmer P, Hultquist R, Gustafson T. 111Indium-labelled leukocytes for measurement of inflammatory activity in arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1991; 20:319–325.
Article26. Gaál J, Mézes A, Siró B, et al. 99m Tc-HMPAO labelled leukocyte scintigraphy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with disease activity. Nucl Med Commun. 2002; 23:39–46.27. Brumfield R Jr, Kuschner SH, Gellman H, Liles DN, Van Winckle G. Results of dorsal wrist synovectomies in the rheumatoid hand. J Hand Surg Am. 1990; 15:733–735.
Article28. Park MJ, Ahn JH, Kang JS. Arthroscopic synovectomy of the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003; 85:1011–1015.
Article29. Adolfsson L, Frisén M. Arthroscopic synovectomy of the rheumatoid wrist. A 3.8 year follow-up. J Hand Surg Br. 1997; 22:711–713.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Secondary to Tuberculous Tenosynovitis: A Case Report
- A case of remitting seronegative symmetrical synovitis with pitting edema
- A Case of Pedunculated Localized Nodular Synovitis of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings
- The Surgical Management of the Rheumatoid Wrist
- Arthroscopic Treatment of the Localized Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis of the Knee