J Cardiovasc Imaging.
2018 Dec;26(4):217-225. 10.4250/jcvi.2018.26.e22.
Pseudonormal or Restrictive Filling Pattern of Left Ventricle Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease Presenting as Acute Heart Failure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. sejjoo@jejunu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2429996
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcvi.2018.26.e22
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
In patients with acute heart failure (AHF), diastolic dysfunction, especially pseudonormal (PN) or restrictive filling pattern (RFP) of left ventricle (LV), is considered to be implicated in a poor prognosis. However, prognostic significance of diastolic dysfunction in patients with ischemic heart disease (IHD) has been rarely investigated in Korea.
METHODS
We enrolled 138 patients with IHD presenting as AHF and sinus rhythm during echocardiographic study. Diastolic dysfunction of LV was graded as ≥ 2 (group 1) or 1 (group 2) according to usual algorithm using E/A ratio and deceleration time of mitral inflow, E"²/A"² ratio of tissue Doppler echocardiography and left atrial size.
RESULTS
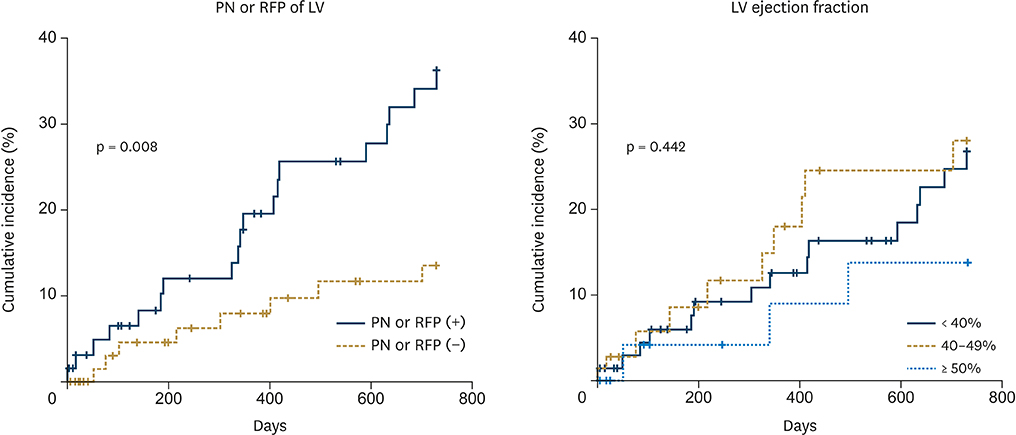
Patients in group 1 showed higher 2-year mortality rate (36.2% ± 6.7%) than those in group 2 (13.6% ± 4.5%; p = 0.008). Two-year mortality rate of patient with LV ejection fraction (LVEF) < 40% (26.8% ± 6.0%) was not different from those with LVEF 40%-49% (28.0% ± 8.0%) or ≥ 50% (13.7% ± 7.4%; p = 0.442). On univariate analysis, PN or RFP of LV, higher stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and higher New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class were poor prognostic factors, but LVEF or older age ≥ 75 years did not predict 2-year mortality. On multivariate analysis, PN or RFP of LV (hazard ratio [HR], 2.52; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.09-5.84; p = 0.031), higher stage of CKD (HR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.14-2.17; p = 0.006) and higher NYHA functional class (HR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.11-2.94; p = 0.017) were still significant prognostic factors for 2-year mortality.
CONCLUSIONS
PN or RFP of LV was a more useful prognostic factor for long-term mortality than LVEF in patients with IHD presenting as AHF.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Echocardiographic Hemodynamic Assessment in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease: the Impact of Diastolic Remodeling on Long-term Prognosis
Mi-Jeong Kim
J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;26(4):226-228. doi: 10.4250/jcvi.2018.26.e31.
Reference
-
1. Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2006 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2006; 113:e85–e151.2. DeFrances CJ, Podgornik MN. 2004 National Hospital Discharge Survey. Adv Data. 2006; 1–19.3. Hadjadj S, Coisne D, Mauco G, et al. Prognostic value of admission plasma glucose and HbA in acute myocardial infarction. Diabet Med. 2004; 21:305–310.4. Verma A, Pfeffer MA, Skali H, et al. Incremental value of echocardiographic assessment beyond clinical evaluation for prediction of death and development of heart failure after high-risk myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 2011; 161:1156–1162.
Article5. Kim SA, Rhee SJ, Shim CY, et al. Prognostic value of N-terminal probrain natriuretic peptide level on admission in patients with acute myocardial infarction and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. Coron Artery Dis. 2011; 22:153–157.
Article6. Lee SE, Cho HJ, Lee HY, et al. A multicentre cohort study of acute heart failure syndromes in Korea: rationale, design, and interim observations of the Korean Acute Heart Failure (KorAHF) registry. Eur J Heart Fail. 2014; 16:700–708.
Article7. Somaratne JB, Whalley GA, Gamble GD, Doughty RN. Restrictive filling pattern is a powerful predictor of heart failure events postacute myocardial infarction and in established heart failure: a literature-based meta-analysis. J Card Fail. 2007; 13:346–352.
Article8. Whalley GA, Gamble GD, Doughty RN. Restrictive diastolic filling predicts death after acute myocardial infarction: systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Heart. 2006; 92:1588–1594.
Article9. Whalley GA, Gamble GD, Doughty RN. The prognostic significance of restrictive diastolic filling associated with heart failure: a meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2007; 116:70–77.
Article10. Quinones MA, Waggoner AD, Reduto LA, et al. A new, simplified and accurate method for determining ejection fraction with two-dimensional echocardiography. Circulation. 1981; 64:744–753.
Article11. Nagueh SF, Smiseth OA, Appleton CP, et al. Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2016; 29:277–314.12. Mollema SA, Nucifora G, Bax JJ. Prognostic value of echocardiography after acute myocardial infarction. Heart. 2009; 95:1732–1745.
Article13. Otterstad JE, St John Sutton MG, Froeland GS, Holme I, Skjaerpe T, Hall C. Prognostic value of two-dimensional echocardiography and N-terminal proatrial natriuretic peptide following an acute myocardial infarction. Assessment of baseline values (2-7 days) and changes at 3 months in patients with a preserved systolic function. Eur Heart J. 2002; 23:1011–1020.
Article14. Whalley GA, Doughty RN, Gamble GD, et al. Pseudonormal mitral filling pattern predicts hospital re-admission in patients with congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002; 39:1787–1795.
Article15. Hellermann JP, Jacobsen SJ, Gersh BJ, Rodeheffer RJ, Reeder GS, Roger VL. Heart failure after myocardial infarction: a review. Am J Med. 2002; 113:324–330.
Article16. Ali AS, Rybicki BA, Alam M, et al. Clinical predictors of heart failure in patients with first acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 1999; 138:1133–1139.
Article17. Lewis EF, Moye LA, Rouleau JL, et al. Predictors of late development of heart failure in stable survivors of myocardial infarction: the CARE study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003; 42:1446–1453.
Article18. Dargie HJ. Effect of carvedilol on outcome after myocardial infarction in patients with left-ventricular dysfunction: the CAPRICORN randomised trial. Lancet. 2001; 357:1385–1390.19. Pitt B, Remme W, Zannad F, et al. Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:1309–1321.
Article20. Gaudron P, Eilles C, Kugler I, Ertl G. Progressive left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling after myocardial infarction. Potential mechanisms and early predictors. Circulation. 1993; 87:755–763.
Article21. Bolognese L, Cerisano G, Buonamici P, et al. Influence of infarct-zone viability on left ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1997; 96:3353–3359.
Article22. Køber L, Torp-Pedersen C, Carlsen JE, et al. A clinical trial of the angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor trandolapril in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Trandolapril Cardiac Evaluation (TRACE) Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:1670–1676.23. Møller JE, Whalley GA, Dini FL, et al. Independent prognostic importance of a restrictive left ventricular filling pattern after myocardial infarction: an individual patient meta-analysis: Meta-Analysis Research Group in Echocardiography acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2008; 117:2591–2598.24. Rigolli M, Rossi A, Quintana M, et al. The prognostic impact of diastolic dysfunction in patients with chronic heart failure and post-acute myocardial infarction: Can age-stratified E/A ratio alone predict survival? Int J Cardiol. 2015; 181:362–368.
Article25. Aljaroudi W, Alraies MC, Halley C, et al. Impact of progression of diastolic dysfunction on mortality in patients with normal ejection fraction. Circulation. 2012; 125:782–788.
Article26. Whalley GA, Wasywich CA, Walsh H, Doughty RN. Role of echocardiography in the contemporary management of chronic heart failure. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2005; 3:51–70.
Article27. Nishimura RA, Tajik AJ. Evaluation of diastolic filling of left ventricle in health and disease: Doppler echocardiography is the clinician's Rosetta Stone. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997; 30:8–18.
Article28. Xie GY, Berk MR, Smith MD, DeMaria AN. Relation of Doppler transmitral flow patterns to functional status in congestive heart failure. Am Heart J. 1996; 131:766–771.
Article29. de Lemos JA, Morrow DA, Bentley JH, et al. The prognostic value of B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:1014–1021.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Status in Patients Who Restrictive Pattern on Doppler Transmitral Flow Pattern
- Reversal of Dilated Cardiomyopathy with medical therapy in a case of Pheochromocytoma
- Correlation of the left ventricular diastolic function and the heart rate variability in patients with acute myocardial infarction
- Usefulness of Mitral Inflow Velocity and Mitral Annulus Velocity for Predicting Long-term Prognosis in Heart Failure with Restrictive Filling Pattern
- The Heart in Acute Glomerulonephritis: An Echocardiographic Study