Blood Res.
2018 Sep;53(3):227-232. 10.5045/br.2018.53.3.227.
The incidence of venous thromboembolism is not lowin Korean patients with advanced pancreatic cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology & Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, College of Medicine, Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea. jhwon@schmc.ac.kr
- 2Division of Hematology & Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, College of Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Division of Hematology & Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, College of Medicine, Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 2429323
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2018.53.3.227
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Pancreatic cancer is among the most common malignancies associated with venous thromboembolism (VTE). Asian patients are known to have a lower incidence of VTE compared to Caucasian patients. However, few studies have investigated the incidence of VTE in Asian patients with pancreatic cancer.
METHODS
This retrospective review of medical records was performed on 505 patients with histopathologically proven advanced stage pancreatic cancer, from January 2006 to December 2012, at Soonchunhyang University Hospitals.
RESULTS
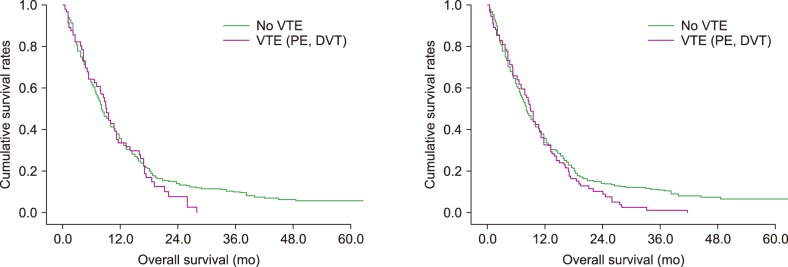
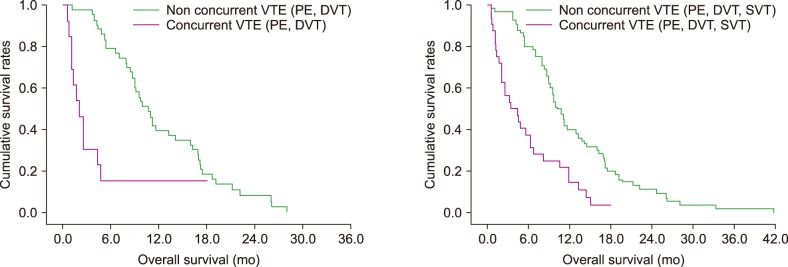
Ninety-four patients (18.6%) had at least one pulmonary embolism (PE), deep vein thrombosis (DVT), or splanchnic vein thrombosis (SVT); 38 patients had isolated SVT; and 56 patients (11.1%) had at least one classic VTE (PE and/or DVT of lower extremities). Patients with more advanced stages of pancreatic cancer (distant metastatic stage, recurrence) or who had received chemotherapy had a higher incidence of classic VTE. Patients who were simultaneously diagnosed with pancreatic cancer and classic VTE had a poorer prognosis than patients with subsequent VTEs. There was a significant difference in overall survival (OS) between the presence and absence of a concurrent classic VTE diagnosis (median: OS, 2.1 mo vs. 10.7 mo; P < 0.001). Even when VTE included SVT, the result was similar (P < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
In Korean patients with advanced pancreatic cancer, the incidence of VTEs is comparable to that of Caucasian patients. We also found that pancreatic cancer patients with concurrent VTEs had a poor prognosis compared to patients who developed VTEs later.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Current Management of Cancer-associated Venous Thromboembolism: Focus on Direct Oral Anticoagulants
Sang-A Kim, Ho-Young Yhim, Soo-Mee Bang
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(6):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e52.
Reference
-
1. Heit JA, Silverstein MD, Mohr DN, Petterson TM, O'Fallon WM, Melton LJ 3rd. Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a population-based case-control study. Arch Intern Med. 2000; 160:809–815. PMID: 10737280.2. Shaib W, Deng Y, Zilterman D, Lundberg B, Saif MW. Assessing risk and mortality of venous thromboembolism in pancreatic cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 2010; 30:4261–4264. PMID: 21036750.3. Blom JW, Osanto S, Rosendaal FR. High risk of venous thrombosis in patients with pancreatic cancer: a cohort study of 202 patients. Eur J Cancer. 2006; 42:410–414. PMID: 16321518.
Article4. Khorana AA, Fine RL. Pancreatic cancer and thromboembolic disease. Lancet Oncol. 2004; 5:655–663. PMID: 15522652.
Article5. Oh SY, Kim JH, Lee KW, et al. Venous thromboembolism in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma: lower incidence in Asian ethnicity. Thromb Res. 2008; 122:485–490. PMID: 18234292.
Article6. Mandalà M, Reni M, Cascinu S, et al. Venous thromboembolism predicts poor prognosis in irresectable pancreatic cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2007; 18:1660–1665. PMID: 17660490.
Article7. Epstein AS, Soff GA, Capanu M, et al. Analysis of incidence and clinical outcomes in patients with thromboembolic events and invasive exocrine pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 2012; 118:3053–3061. PMID: 21989534.
Article8. White RH, Zhou H, Romano PS. Incidence of idiopathic deep venous thrombosis and secondary thromboembolism among ethnic groups in California. Ann Intern Med. 1998; 128:737–740. PMID: 9556467.
Article9. Klatsky AL, Armstrong MA, Poggi J. Risk of pulmonary embolism and/or deep venous thrombosis in Asian-Americans. Am J Cardiol. 2000; 85:1334–1337. PMID: 10831950.
Article10. Stein PD, Kayali F, Olson RE, Milford CE. Pulmonary thromboembolism in Asians/Pacific Islanders in the United States: analysis of data from the National Hospital Discharge Survey and the United States Bureau of the Census. Am J Med. 2004; 116:435–442. PMID: 15047032.
Article11. Klatsky AL, Baer D. What protects Asians from venous thromboembolism? Am J Med. 2004; 116:493–495. PMID: 15047041.
Article12. Steffen LM, Folsom AR, Cushman M, Jacobs DR Jr, Rosamond WD. Greater fish, fruit, and vegetable intakes are related to lower incidence of venous thromboembolism: the Longitudinal Investigation of Thromboembolism Etiology. Circulation. 2007; 115:188–195. PMID: 17179018.13. Lee KW, Bang SM, Kim S, et al. The incidence, risk factors and prognostic implications of venous thromboembolism in patients with gastric cancer. J Thromb Haemost. 2010; 8:540–547. PMID: 20040044.
Article14. Chew HK, Wun T, Harvey D, Zhou H, White RH. Incidence of venous thromboembolism and its effect on survival among patients with common cancers. Arch Intern Med. 2006; 166:458–464. PMID: 16505267.
Article15. Tetzlaff ED, Correa AM, Baker J, Ensor J, Ajani JA. The impact on survival of thromboembolic phenomena occurring before and during protocol chemotherapy in patients with advanced gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 2007; 109:1989–1995. PMID: 17397035.
Article16. Khorana AA, Francis CW, Culakova E, Kuderer NM, Lyman GH. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J Thromb Haemost. 2007; 5:632–634. PMID: 17319909.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: The incidence of venous thromboembolism is not lowin Korean patients with advanced pancreatic cancer
- Prophylaxis of Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer
- Thromboembolic Events as Prognostic Clinical Markers in Advanced Pancreatic and Biliary Tract Cancer
- Clinical Year in Review of Venous Thromboembolism
- Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Receiving Palliative Chemotherapy: Incidence and Effect on Prognosis