Ann Rehabil Med.
2018 Oct;42(5):722-729. 10.5535/arm.2018.42.5.722.
Cost of Rehabilitation Treatment of Patients With Cerebral Palsy in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Ilsan, Korea.
- 2Department of Statistics, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Ilsan, Korea. halwayskim@gmail.com
- KMID: 2429201
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2018.42.5.722
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate rehabilitation treatment cost of patients with cerebral palsy (CP) according to age.
METHODS
We analyzed the cost of rehabilitation treatment from 2007 to 2013 for patients diagnosed with CP by sourcing data from the National Health Information Database.
RESULTS
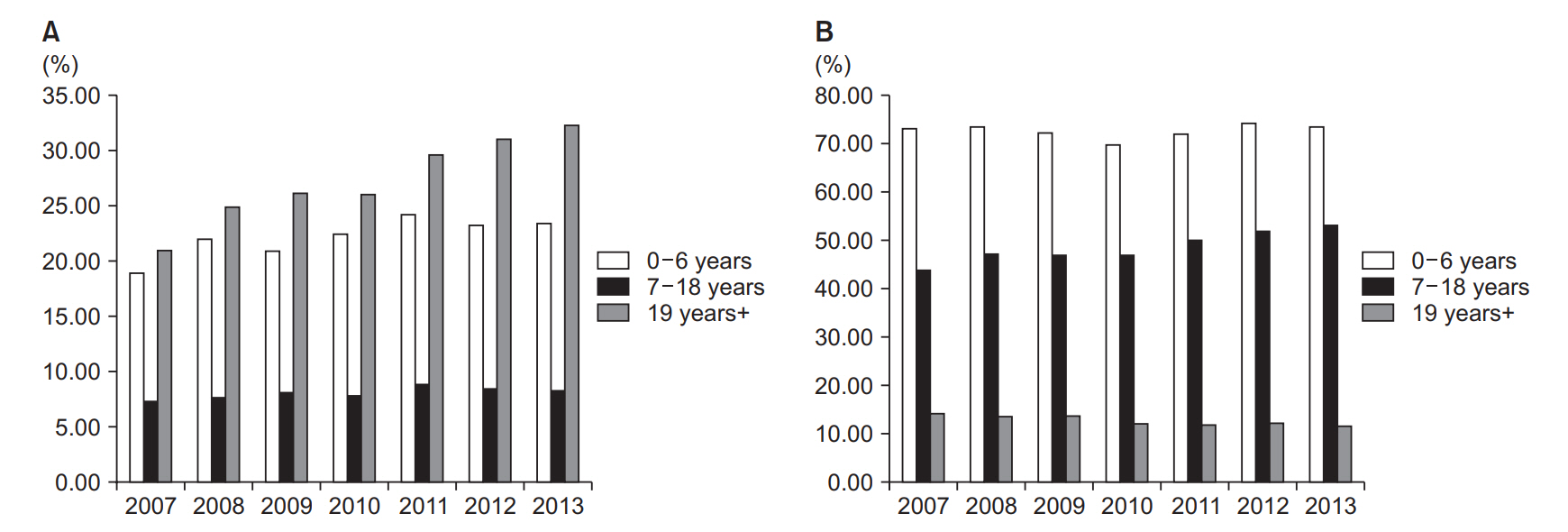
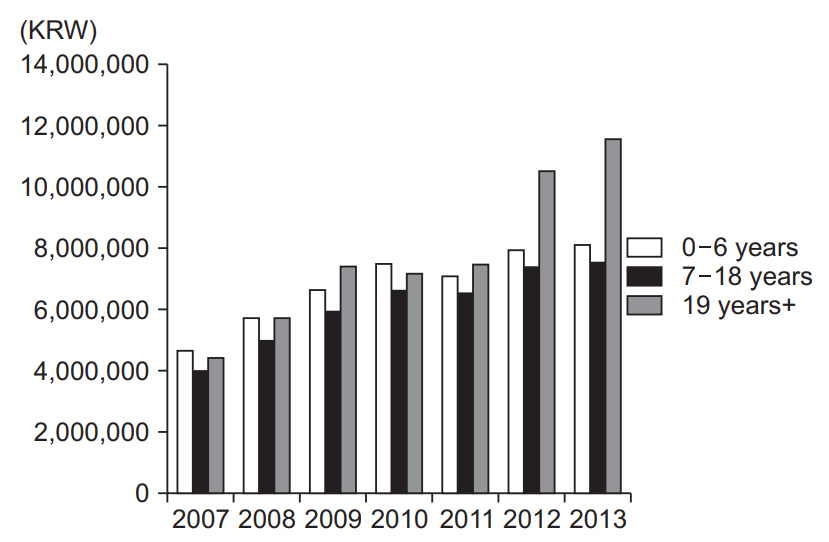
While the number of recently born children requiring rehabilitation treatment has decreased, the number of patients requiring this treatment in other age groups has gradually increased. In addition, annual physical therapy, occupational therapy, hydrotherapy, and botulinum toxin injection treatment costs per person have increased. On the other hand, the number of orthopedic surgeries and selective dorsal rhizotomy performed has decreased.
CONCLUSION
This study investigated trends in the cost of treatment for patients with CP. This study can be used as a basis to provide treatment support for patients with CP.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bax M, Goldstein M, Rosenbaum P, Leviton A, Paneth N, Dan B, et al. Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy, April 2005. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005; 47:571–6.
Article2. Voorman JM, Dallmeijer AJ, Van Eck M, Schuengel C, Becher JG. Social functioning and communication in children with cerebral palsy: association with disease characteristics and personal and environmental factors. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2010; 52:441–7.
Article3. Vos RC, Becher JG, Ketelaar M, Smits DW, Voorman JM, Tan SS, et al. Developmental trajectories of daily activities in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy. Pediatrics. 2013; 132:e915–23.
Article4. Novak I, McIntyre S, Morgan C, Campbell L, Dark L, Morton N, et al. A systematic review of interventions for children with cerebral palsy: state of the evidence. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2013; 55:885–910.
Article5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Economic costs associated with mental retardation, cerebral palsy, hearing loss, and vision impairment: United States, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2004; 53:57–9.6. Seong SC, Kim Y, Khang Y, Park JH, Kang H, Lee H, et al. Data resource profile: the national health information database of the National Health Insurance Service in South Korea. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 46:799–800.7. Doh S, Cole BR. Comparative analysis of health insurance systems in the United States and South Korea. World Med Health Policy. 2009; 1:85–116.
Article8. Steel D, Cylus J. United Kingdom (Scotland): health system review. Health Syst Transit. 2012; 14:1–150.9. Hutchison B, Levesque JF, Strumpf E, Coyle N. Primary health care in Canada: systems in motion. Milbank Q. 2011; 89:256–88.
Article10. Schoen C, Osborn R, Squires D, Doty MM, Pierson R, Applebaum S. How health insurance design affects access to care and costs, by income, in eleven countries. Health Aff (Millwood). 2010; 29:2323–34.
Article11. Schoen C, Doty MM. Inequities in access to medical care in five countries: findings from the 2001 Commonwealth Fund International Health Policy Survey. Health Policy. 2004; 67:309–22.
Article12. Japan Ministry of Health Labor and Welfare [Internet]. Tokyo: Ministry of Health Labor and Welfare;c2018. [cited 2018 Sep 15]. Available from: http://www.mhlw.go.jp.13. Andersson C, Mattsson E. Adults with cerebral palsy: a survey describing problems, needs, and resources, with special emphasis on locomotion. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2001; 43:76–82.
Article14. Young NL, Gilbert TK, McCormick A, Ayling-Campos A, Boydell K, Law M, et al. Youth and young adults with cerebral palsy: their use of physician and hospital services. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007; 88:696–702.
Article15. Gajdosik CG, Cicirello N. Secondary conditions of the musculoskeletal system in adolescents and adults with cerebral palsy. Phys Occup Ther Pediatr. 2001; 21:49–68.
Article16. Yim SY, Yang CY, Park JH, Kim MY, Shin YB, Kang EY, et al. Korean database of cerebral palsy: a report on characteristics of cerebral palsy in South Korea. Ann Rehabil Med. 2017; 41:638–49.
Article17. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Economic costs of birth defects and cerebral palsy: United States, 1992. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1995; 44:694–9.18. Kruse M, Michelsen SI, Flachs EM, Bronnum-Hansen H, Madsen M, Uldall P. Lifetime costs of cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2009; 51:622–8.
Article19. Chiarello LA, O’Neil M, Dichter CG, Westcott SL, Orlin M, Marchese VG, et al. Exploring physical therapy clinical decision making for children with spastic diplegia: survey of pediatric practice. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2005; 17:46–54.
Article20. Turk MA. Health, mortality, and wellness issues in adults with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2009; 51 Suppl 4:24–9.
Article21. McGinley JL, Dobson F, Ganeshalingam R, Shore BJ, Rutz E, Graham HK. Single-event multilevel surgery for children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2012; 54:117–28.
Article22. Thomason P, Selber P, Graham HK. Single Event Multilevel Surgery in children with bilateral spastic cerebral palsy: a 5 year prospective cohort study. Gait Posture. 2013; 37:23–8.
Article23. Aquilina K, Graham D, Wimalasundera N. Selective dorsal rhizotomy: an old treatment re-emerging. Arch Dis Child. 2015; 100:798–802.
Article24. Ingale H, Ughratdar I, Muquit S, Moussa AA, Vloeberghs MH. Selective dorsal rhizotomy as an alternative to intrathecal baclofen pump replacement in GMFCS grades 4 and 5 children. Childs Nerv Syst. 2016; 32:321–5.
Article25. Park MS, Kim SJ, Chung CY, Kwon DG, Choi IH, Lee KM. Prevalence and lifetime healthcare cost of cerebral palsy in South Korea. Health Policy. 2011; 100:234–8.
Article26. Kim DA, Hong HS, Lee HY, Lee HS, Kang MS. Age specificity in general and rehabilitation medical services in children with cerebral palsy. Ann Rehabil Med. 2014; 38:784–90.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Age Specificity in General and Rehabilitation Medical Services in Children With Cerebral Palsy
- Management of Cervical Myelopathy in Athetoid Cerebral Palsy: Case report
- A Survey of Drooling in Children with Cerebral Palsy
- Percutaneous Selective Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation in the Treatment of Spastic Cerebral Palsy: A case report
- Survey of the Demands of the Parents of Children with Cerebral Palsy