Korean J Ophthalmol.
2018 Dec;32(6):488-496. 10.3341/kjo.2017.0094.
Factors Influencing Visual Field Recovery after Transsphenoidal Resection of a Pituitary Adenoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. exo70@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2427964
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0094
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed to analyze the factors influencing visual field recovery after transsphenoidal approach-tumor resection (TSA-TR) in pituitary adenoma patients with visual field defects (VFDs).
METHODS
We retrospectively evaluated 102 eyes of 102 patients with VFDs induced by pituitary adenomas who underwent TSA-TR between January 2010 and December 2015. All patients had been observed for more than one year. The severity of the VFD in each patient was evaluated using the mean deviation (MD) and pattern standard deviation in the most-affected eye. Clinical and demographic data such as preoperative visual acuity and visual field, age, sex, tumor volume, neurological symptoms at diagnosis, duration of symptoms, patterns of the preoperative VFD, and preoperative central VFD were investigated and analyzed for association with recovery of the visual field.
RESULTS
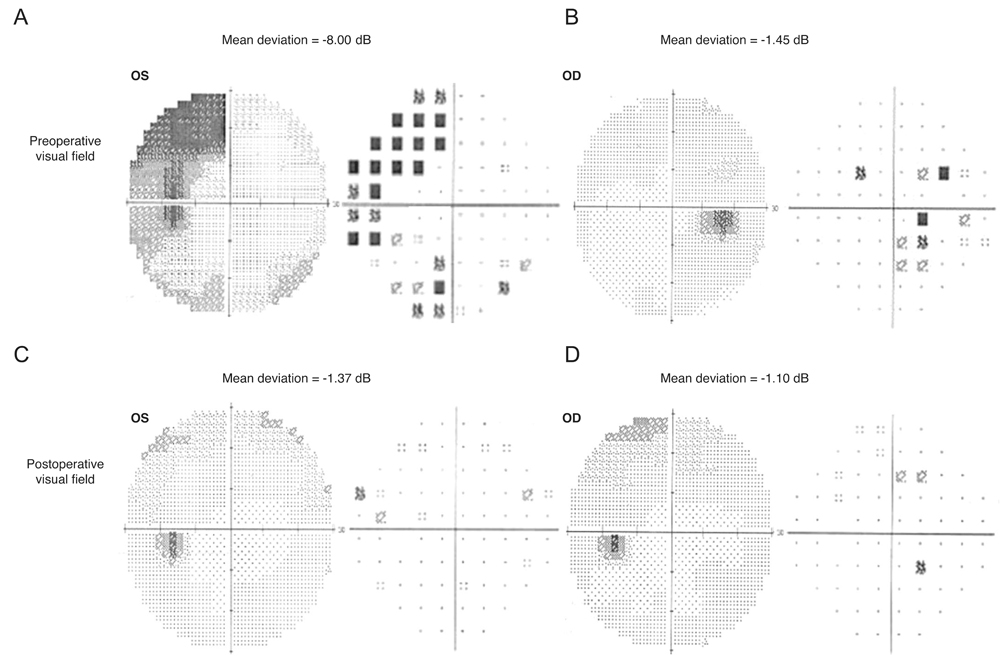
Recovery from VFDs occurred in 71 (69.6%) eyes after a mean period of 18.36 ± 5.21 months. The recovery group was younger (p = 0.003), had higher preoperative MD values (p = 0.016), and had better preoperative visual acuity (p = 0.03), compared with the non-recovery group. Preoperative central VFD (p = 0.006) and preoperative bilateral VFD (p = 0.016) were significantly less frequent in the recovery group. Multivariate logistic regression revealed that age at diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 0.962; p = 0.022), preoperative MD (OR, 1.069; p = 0.046), preoperative central VFD (OR, 0.212; p = 0.039), and preoperative bilateral VFD (OR, 0.212; p = 0.035) were associated with visual field recovery after TSA-TR.
CONCLUSIONS
Younger age, higher preoperative MD, and the preoperative abscence of central VFD or bilateral VFD were favorable factors influencing visual field recovery after TSA-TR in patients with pituitary adenomas. An understanding of the associated clinical factors may help predict visual outcomes after TSA-TR in pituitary adenoma patients with VFDs.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kerrison JB, Lynn MJ, Baer CA, et al. Stages of improvement in visual fields after pituitary tumor resection. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 130:813–820.
Article2. Dekkers OM, Hammer S, de Keizer RJ, et al. The natural course of non-functioning pituitary macroadenomas. Eur J Endocrinol. 2007; 156:217–224.
Article3. Anderson D, Faber P, Marcovitz S, et al. Pituitary tumors and the ophthalmologist. Ophthalmology. 1983; 90:1265–1270.
Article4. Hollenhorst RW, Younge BR. Ocular manifestations produced by adenomas of the pituitary gland: analysis of 1000 cases. In : Kohler PO, Ross GT, editors. Diagnosis and treatment of pituitary tumors. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica;1973. p. 53–64.5. Ebersold MJ, Quast LM, Laws ER Jr, et al. Long-term results in transsphenoidal removal of nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas. J Neurosurg. 1986; 64:713–719.
Article6. Mortini P, Losa M, Barzaghi R, et al. Results of transsphenoidal surgery in a large series of patients with pituitary adenoma. Neurosurgery. 2005; 56:1222–1233.
Article7. Yu FF, Chen LL, Su YH, et al. Factors influencing improvement of visual field after trans-sphenoidal resection of pituitary macroadenomas: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Ophthalmol. 2015; 8:1224–1228.8. Ho RW, Huang HM, Ho JT. The influence of pituitary adenoma size on vision and visual outcomes after trans-sphenoidal adenectomy: a report of 78 cases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015; 57:23–31.
Article9. Lee J, Kim SW, Kim DW, et al. Predictive model for recovery of visual field after surgery of pituitary adenoma. J Neurooncol. 2016; 130:155–164.
Article10. Peter M, De Tribolet N. Visual outcome after transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary adenomas. Br J Neurosurg. 1995; 9:151–157.
Article11. Ogra S, Nichols AD, Stylli S, et al. Visual acuity and pattern of visual field loss at presentation in pituitary adenoma. J Clin Neurosci. 2014; 21:735–740.
Article12. Sung MS, Heo H, Ji YS, Park SW. Predicting the risk of parafoveal scotoma in myopic normal tension glaucoma: role of optic disc tilt and rotation. Eye (Lond). 2017; 31:1051–1059.
Article13. Jesser J, Schlamp K, Bendszus M. Pituitary gland tumors. Radiologe. 2014; 54:981–988.14. Barzaghi LR, Medone M, Losa M, et al. Prognostic factors of visual field improvement after trans-sphenoidal approach for pituitary macroadenomas: review of the literature and analysis by quantitative method. Neurosurg Rev. 2012; 35:369–378.
Article15. Schmalisch K, Milian M, Schimitzek T, et al. Predictors for visual dysfunction in nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas: implications for neurosurgical management. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2012; 77:728–734.16. Eda M, Saeki N, Fujimoto N, Sunami K. Demonstration of the optic pathway in large pituitary adenoma on heavily T2 weighted MR images. Br J Neurosurg. 2002; 16:21–29.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Complete Visual Recovery From No Light Perception After Resection of Pituitary Adenoma
- Relationship between Location and Size of Pituitary Adenoma and Visual Field Change
- Surgical Experiences of Three Cases of Giant Pituitary Adenoma
- Postoperative Visual Field Outcomes in Patients Showing Visual Field Defects due to Pituitary Adenoma
- Visual Outcome after Transsphenoidal Surgery in Patients with Pituitary Apoplexy