Clin Endosc.
2018 Sep;51(5):425-429. 10.5946/ce.2018.153.
Small Bowel Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, Gangneung, Korea.
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. dohoon.md@gmail.com
- KMID: 2427715
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2018.153
Abstract
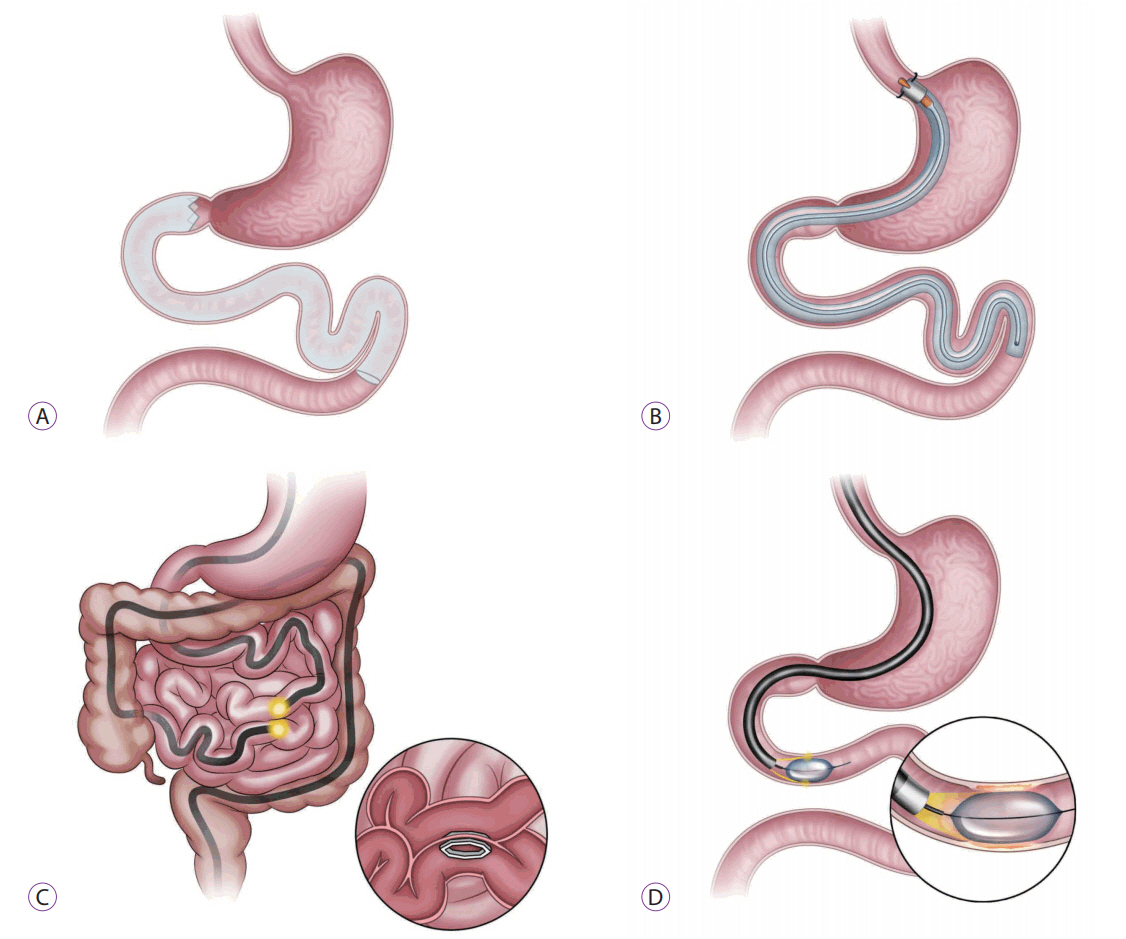
- Endoscopic bariatric therapies that emulate some of the principles of bariatric surgery have been developed as a less invasive option for the treatment of obesity and related comorbidities. Small bowel endoscopic bariatric therapies include bypass sleeves, incisionless anastomosis systems, and duodenal mucosal resurfacing. Clinical experience with small bowel devices suggests that endoscopic bariatric procedures can be safely implemented and that these devices are effective for both weight loss and metabolic improvement. Although the mechanisms behind these effects should be further elucidated, endoscopic bariatric therapies may be more effective and safer adjunctive interventions than lifestyle modifications and pharmacological regimens for patients with obesity or obesity-related comorbidities.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Adams KF, Schatzkin A, Harris TB, et al. Overweight, obesity, and mortality in a large prospective cohort of persons 50 to 71 years old. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:763–778.
Article2. Rubino F, Forgione A, Cummings DE, et al. The mechanism of diabetes control after gastrointestinal bypass surgery reveals a role of the proximal small intestine in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Ann Surg. 2006; 244:741–749.
Article3. Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes - 5-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:641–651.
Article4. Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, et al. Bariatric-metabolic surgery versus conventional medical treatment in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: 5 year follow-up of an open-label, single-centre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015; 386:964–973.
Article5. Sullivan S, Edmundowicz SA, Thompson CC. Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies: new and emerging technologies. Gastroenterology. 2017; 152:1791–1801.
Article6. Jirapinyo P, Thompson CC. Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies: surgical analogues and mechanisms of action. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 15:619–630.
Article7. Machytka E, Bužga M, Zonca P, et al. Partial jejunal diversion using an incisionless magnetic anastomosis system: 1-year interim results in patients with obesity and diabetes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 86:904–912.
Article8. Rubino F, Gagner M. Potential of surgery for curing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg. 2002; 236:554–559.
Article9. Pories WJ, Albrecht RJ. Etiology of type II diabetes mellitus: role of the foregut. World J Surg. 2001; 25:527–531.
Article10. Rubino F, Gagner M, Gentileschi P, et al. The early effect of the Rouxen-Y gastric bypass on hormones involved in body weight regulation and glucose metabolism. Ann Surg. 2004; 240:236–242.
Article11. Cummings DE, Overduin J, Foster-Schubert KE. Gastric bypass for obesity: mechanisms of weight loss and diabetes resolution. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:2608–2615.
Article12. Mason EE. The mechanisms of surgical treatment of type 2 diabetes. Obes Surg. 2005; 15:459–461.
Article13. Patriti A, Facchiano E, Sanna A, Gullà N, Donini A. The enteroinsular axis and the recovery from type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2004; 14:840–848.
Article14. Mason EE. Ileal [correction of ilial] transposition and enteroglucagon/GLP-1 in obesity (and diabetic?) surgery. Obes Surg. 1999; 9:223–228.15. Maljaars PW, Peters HP, Mela DJ, Masclee AA. Ileal brake: a sensible food target for appetite control. A review. Physiol Behav. 2008; 95:271–281.
Article16. Cohen R, le Roux CW, Papamargaritis D, et al. Role of proximal gut exclusion from food on glucose homeostasis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2013; 30:1482–1486.
Article17. Dixon JB, le Roux CW, Rubino F, Zimmet P. Bariatric surgery for type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2012; 379:2300–2311.
Article18. Meek CL, Lewis HB, Reimann F, Gribble FM, Park AJ. The effect of bariatric surgery on gastrointestinal and pancreatic peptide hormones. Peptides. 2016; 77:28–37.
Article19. Jirapinyo P, Haas AV, Thompson CC. Effect of the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes with obesity: a meta-analysis with secondary analysis on weight loss and hormonal changes. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:1106–1115.
Article20. Rodriguez L, Reyes E, Fagalde P, et al. Pilot clinical study of an endoscopic, removable duodenal-jejunal bypass liner for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2009; 11:725–732.
Article21. Tarnoff M, Rodriguez L, Escalona A, et al. Open label, prospective, randomized controlled trial of an endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass sleeve versus low calorie diet for pre-operative weight loss in bariatric surgery. Surg Endosc. 2009; 23:650–656.
Article22. Gersin KS, Rothstein RI, Rosenthal RJ, et al. Open-label, sham-controlled trial of an endoscopic duodenojejunal bypass liner for preoperative weight loss in bariatric surgery candidates. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:976–982.
Article23. Schouten R, Rijs CS, Bouvy ND, et al. A multicenter, randomized efficacy study of the EndoBarrier gastrointestinal liner for presurgical weight loss prior to bariatric surgery. Ann Surg. 2010; 251:236–243.
Article24. Koehestanie P, de Jonge C, Berends FJ, Janssen IM, Bouvy ND, Greve JW. The effect of the endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass liner on obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus, a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2014; 260:984–992.
Article25. ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force and ASGE Technology Committee, Abu Dayyeh BK, Kumar N, et al. ASGE bariatric endoscopy task force systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting endoscopic bariatric therapies. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:425–438. e5.
Article26. Rohde U, Hedbäck N, Gluud LL, Vilsbøll T, Knop FK. Effect of the EndoBarrier gastrointestinal liner on obesity and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016; 18:300–305.
Article27. Betzel B, Koehestanie P, Homan J, et al. Changes in glycemic control and body weight after explantation of the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:409–415.
Article28. Forner PM, Ramacciotti T, Farey JE, Lord RV. Safety and effectiveness of an endoscopically placed duodenal-jejunal bypass device (EndoBarrier®): outcomes in 114 patients. Obes Surg. 2017; 27:3306–3313.29. Betzel B, Koehestanie P, Aarts EO, et al. Safety experience with the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner: an endoscopic treatment for diabetes and obesity. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:845–852.
Article30. Quezada N, Muñoz R, Morelli C, et al. Safety and efficacy of the endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass liner prototype in severe or morbidly obese subjects implanted for up to 3 years. Surg Endosc. 2018; 32:260–267.
Article31. Sandler BJ, Rumbaut R, Swain CP, et al. Human experience with an endoluminal, endoscopic, gastrojejunal bypass sleeve. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:3028–3033.
Article32. Sandler BJ, Rumbaut R, Swain CP, et al. One-year human experience with a novel endoluminal, endoscopic gastric bypass sleeve for morbid obesity. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:3298–3303.
Article33. Ryou M, Aihara H, Thompson CC. Minimally invasive entero-enteral dual-path bypass using self-assembling magnets. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:4533–4538.
Article34. Machytka E, Buzga M, Ryou M, Lautz DB, Thompson CC. Endoscopic dual-path enteral anastomosis using self-assembling magnets: first-inhuman clinical feasibility. Gastroenterology. 2016; 150(4 Suppl 1):S232.35. Rajagopalan H, Cherrington AD, Thompson CC, et al. Endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: 6-month interim analysis from the first-in-human proof-of-concept study. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:2254–2261.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Training in Bariatric and Metabolic Endoscopic Therapies
- Various Novel and Emerging Technologies in Endoscopic Bariatric and Metabolic Treatments
- Bariatric endoscopy: from managing complications to primary metabolic procedures
- Role of Endoscopy in the Treatment of Bariatric and Metabolic Disease
- Recent Clinical Results of Endoscopic Bariatric Therapies as an Obesity Intervention