Clin Endosc.
2021 Jan;54(1):25-31. 10.5946/ce.2021.021.
Various Novel and Emerging Technologies in Endoscopic Bariatric and Metabolic Treatments
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
- KMID: 2512306
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.021
Abstract
- Obesity, along with its comorbidities, has become a significant public health concern worldwide. Bariatric surgery is considered the most effective treatment modality; however, only 2% of patients with obesity undergo bariatric surgery. Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies (EBMTs) are emerging alternatives to traditional bariatric surgery for patients who are not eligible for or do not prefer surgical treatment. EBMTs are generally categorized as space-occupying, gastric restrictive, aspiration, and small bowel therapies. We aimed to review various non-balloon and non-gastroplasty devices with available clinical data and discuss the possible mechanisms of action, efficacy, and safety profile of these EMBTs.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Role of endoscopic duodenojejunal bypass liner in obesity management and glycemic control
Willian Ferreira Igi, Victor Lira de Oliveira, Ayah Matar, Diogo Turiani Hourneaux de Moura
Clin Endosc. 2024;57(3):309-316. doi: 10.5946/ce.2023.217.
Reference
-
1. Bray GA, Frühbeck G, Ryan DH, Wilding JP. Management of obesity. Lancet. 2016; 387:1947–1956.
Article2. Prospective Studies Collaboration, Whitlock G, Lewington S, et al. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults: collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet. 2009; 373:1083–1096.3. ASGE/ASMBS Task Force on Endoscopic Bariatric Therapy, Ginsberg GG, Chand B, et al. A pathway to endoscopic bariatric therapies. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:943–953.
Article4. Gastrointestinal surgery for severe obesity. Consens Statement 1991;9:1-20.5. Arterburn DE, Telem DA, Kushner RF, Courcoulas AP. Benefits and risks of bariatric surgery in adults: a review. JAMA. 2020; 324:879–887.6. de Moura DTH, de Moura EGH, Thompson CC. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty: from whence we came and where we are going. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 11:322–328.7. Cho JH, Bilal M, Kim MC, Cohen J. The clinical and metabolic effects of intragastric balloon on morbid obesity and its related comorbidities. Clin Endosc. 2021; 54:9–16.
Article8. Yoon JY, Arau RT. The efficacy and safety of endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty as an alternative to laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Clin Endosc. 2021; 54:17–24.
Article9. US Food and Drug Administration. Summary of safety and effectiveness data (SSED) [Internet]. Silver Spring (MD): FDA; c2016 [updated 2016 Jun 14]. Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf15/p150024b.pdf.10. Sullivan S, Edmundowicz SA, Thompson CC. Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies: new and emerging technologies. Gastroenterology. 2017; 152:1791–1801.
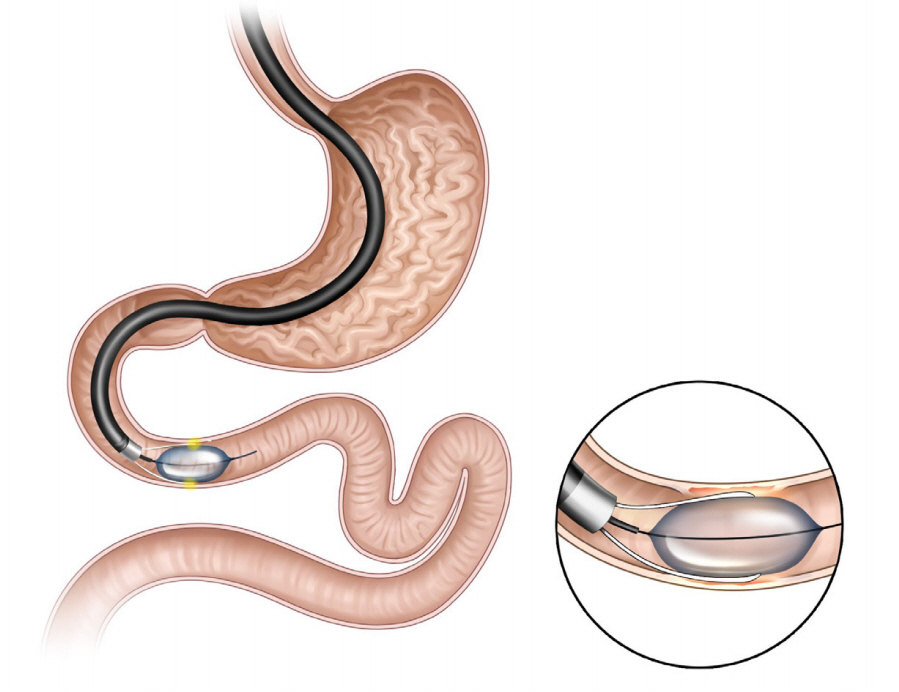
Article11. Swei EC, Sullivan SA. Aspiration therapy. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2020; 23:100659.
Article12. Sullivan S, Stein R, Jonnalagadda S, Mullady D, Edmundowicz S. Aspiration therapy leads to weight loss in obese subjects: a pilot study. Gastroenterology. 2013; 145:1245–1252.e1-e5.
Article13. Thompson CC, Abu Dayyeh BK, Kushner R, et al. Percutaneous gastrostomy device for the treatment of class II and class III obesity: results of a randomized controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017; 112:447–457.
Article14. Nyström M, Machytka E, Norén E, et al. Aspiration therapy as a tool to treat obesity: 1- to 4-year results in a 201-patient multi-center post-market European registry study. Obes Surg. 2018; 28:1860–1868.
Article15. Jirapinyo P, de Moura DTH, Horton LC, Thompson CC. Effect of aspiration therapy on obesity-related comorbidities: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Endosc. 2020; 53:686–697.
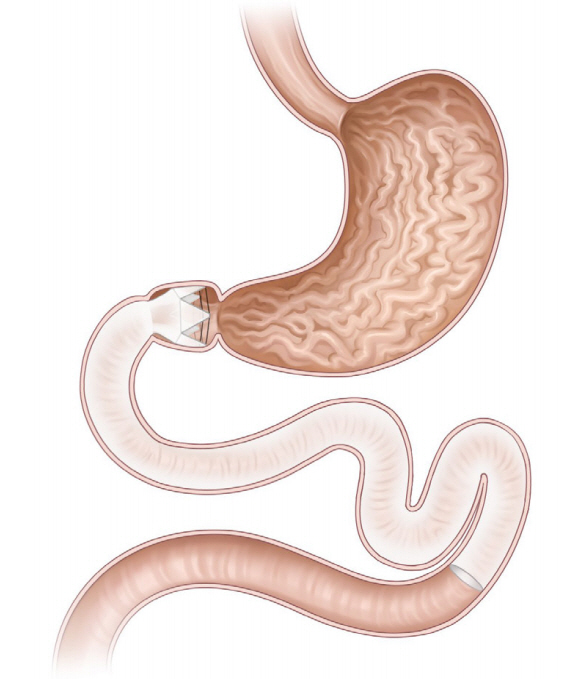
Article16. Ruban A, Ashrafian H, Teare JP. The EndoBarrier: duodenal-jejunal bypass liner for diabetes and weight loss. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018; 2018:7823182.
Article17. de Moura EG, Lopes GS, Martins BC, et al. Effects of duodenal-jejunal bypass liner (EndoBarrier®) on gastric emptying in obese and type 2 diabetic patients. Obes Surg. 2015; 25:1618–1625.
Article18. Gersin KS, Rothstein RI, Rosenthal RJ, et al. Open-label, sham-controlled trial of an endoscopic duodenojejunal bypass liner for preoperative weight loss in bariatric surgery candidates. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:976–982.
Article19. Rodriguez L, Reyes E, Fagalde P, et al. Pilot clinical study of an endoscopic, removable duodenal-jejunal bypass liner for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2009; 11:725–732.
Article20. Tarnoff M, Rodriguez L, Escalona A, et al. Open label, prospective, randomized controlled trial of an endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass sleeve versus low calorie diet for pre-operative weight loss in bariatric surgery. Surg Endosc. 2009; 23:650–656.
Article21. Glaysher MA, Mohanaruban A, Prechtl CG, et al. A randomised controlled trial of a duodenal-jejunal bypass sleeve device (EndoBarrier) compared with standard medical therapy for the management of obese subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open. 2017; 7:e018598.22. Koehestanie P, de Jonge C, Berends FJ, Janssen IM, Bouvy ND, Greve JW. The effect of the endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass liner on obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus, a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2014; 260:984–992.
Article23. Schouten R, Rijs CS, Bouvy ND, et al. A multicenter, randomized efficacy study of the EndoBarrier Gastrointestinal Liner for presurgical weight loss prior to bariatric surgery. Ann Surg. 2010; 251:236–243.
Article24. Rohde U, Hedbäck N, Gluud LL, Vilsbøll T, Knop FK. Effect of the EndoBarrier Gastrointestinal Liner on obesity and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016; 18:300–305.
Article25. ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force and ASGE Technology Committee, Abu Dayyeh BK, Kumar N, et al. ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting endoscopic bariatric therapies. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:425–438.e5.
Article26. van Rijn S, Roebroek YGM, de Jonge C, Greve JWM, Bouvy ND. Effect of the EndoBarrier device: a 4-year follow-up of a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Obes Surg. 2019; 29:1117–1121.
Article27. Quezada N, Muñoz R, Morelli C, et al. Safety and efficacy of the endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass liner prototype in severe or morbidly obese subjects implanted for up to 3 years. Surg Endosc. 2018; 32:260–267.
Article28. Jirapinyo P, Haas AV, Thompson CC. Effect of the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes with obesity: a meta-analysis with secondary analysis on weight loss and hormonal changes. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:1106–1115.
Article29. Roehlen N, Laubner K, Bettinger D, et al. Duodenal-jejunal bypass liner (DJBL) improves cardiovascular risk biomarkers and predicted 4-year risk of major CV events in patients with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Obes Surg. 2020; 30:1200–1210.
Article30. Betzel B, Drenth JPH, Siersema PD. Adverse events of the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner: a systematic review. Obes Surg. 2018; 28:3669–3677.
Article31. Betzel B, Homan J, Aarts EO, et al. Weight reduction and improvement in diabetes by the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner: a 198 patient cohort study. Surg Endosc. 2017; 31:2881–2891.
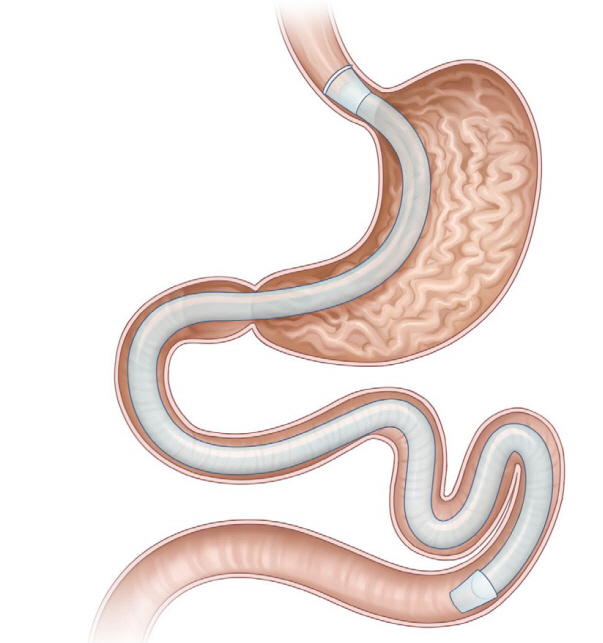
Article32. Sandler BJ, Rumbaut R, Swain CP, et al. Human experience with an endoluminal, endoscopic, gastrojejunal bypass sleeve. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:3028–3033.
Article33. Sandler BJ, Rumbaut R, Swain CP, et al. One-year human experience with a novel endoluminal, endoscopic gastric bypass sleeve for morbid obesity. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:3298–3303.
Article34. Cherrington AD, Rajagopalan H, Maggs D, Devière J. Hydrothermal duodenal mucosal resurfacing: role in the treatment of metabolic disease. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2017; 27:299–311.35. Rajagopalan H, Cherrington AD, Thompson CC, et al. Endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: 6-month interim analysis from the first-in-human proof-of-concept study. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:2254–2261.
Article36. van Baar ACG, Holleman F, Crenier L, et al. Endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: one year results from the first international, open-label, prospective, multicentre study. Gut. 2020; 69:295–303.
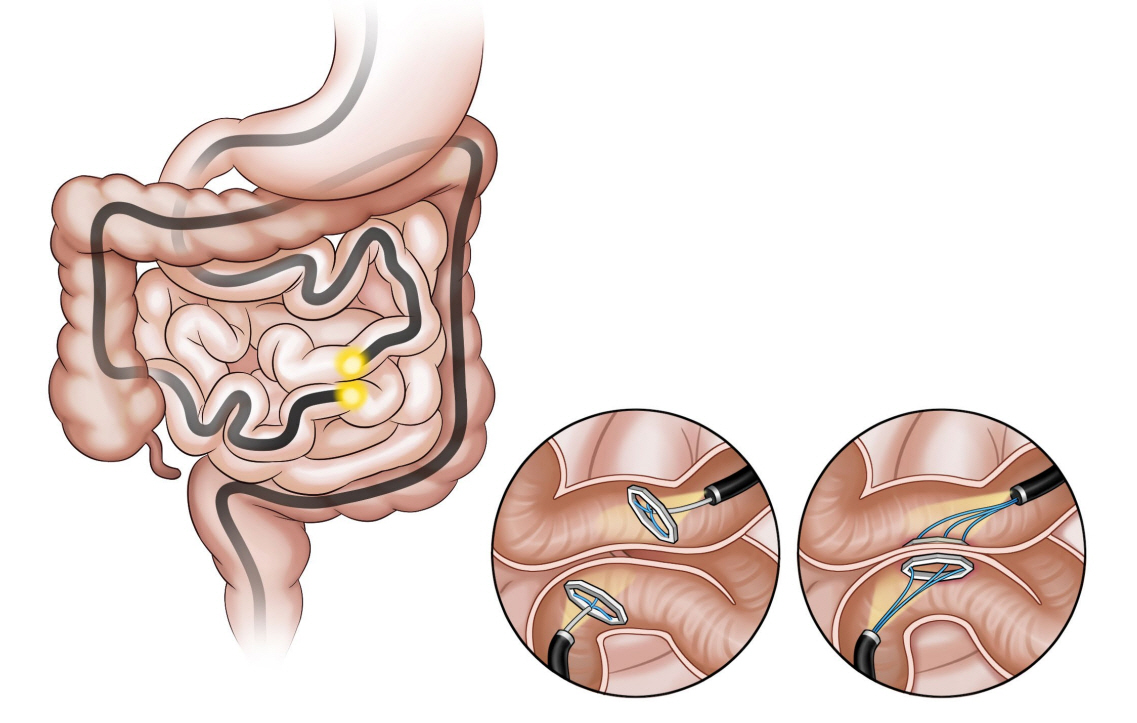
Article37. Aithal G, Sakai N, Chouhan M, et al. Endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing improves hepatic fat fraction, glycemic and lipid profiles in type 2 diabetes. J Hepatol. 2019; 70(1 Suppl):e70–e71.38. Ryou M, Aihara H, Thompson CC. Minimally invasive entero-enteral dual-path bypass using self-assembling magnets. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:4533–4538.
Article39. Machytka E, Bužga M, Zonca P, et al. Partial jejunal diversion using an incisionless magnetic anastomosis system: 1-year interim results in patients with obesity and diabetes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 86:904–912.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Training in Bariatric and Metabolic Endoscopic Therapies
- Role of Endoscopy in the Treatment of Bariatric and Metabolic Disease
- Endoscopic Bariatric Therapy for Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Bariatric endoscopy: from managing complications to primary metabolic procedures
- Endoluminal Gastroplasty for Obesity Treatment: Emerging Technology and Obstacles