Yonsei Med J.
2016 Nov;57(6):1482-1487. 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1482.
Temporal Lobe Retraction Provides Better Surgical Exposure of the Peri-Geniculate Ganglion for Facial Nerve Decompression via Transmastoid Approach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. jinsound@gmail.com
- KMID: 2427168
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1482
Abstract
- PURPOSE
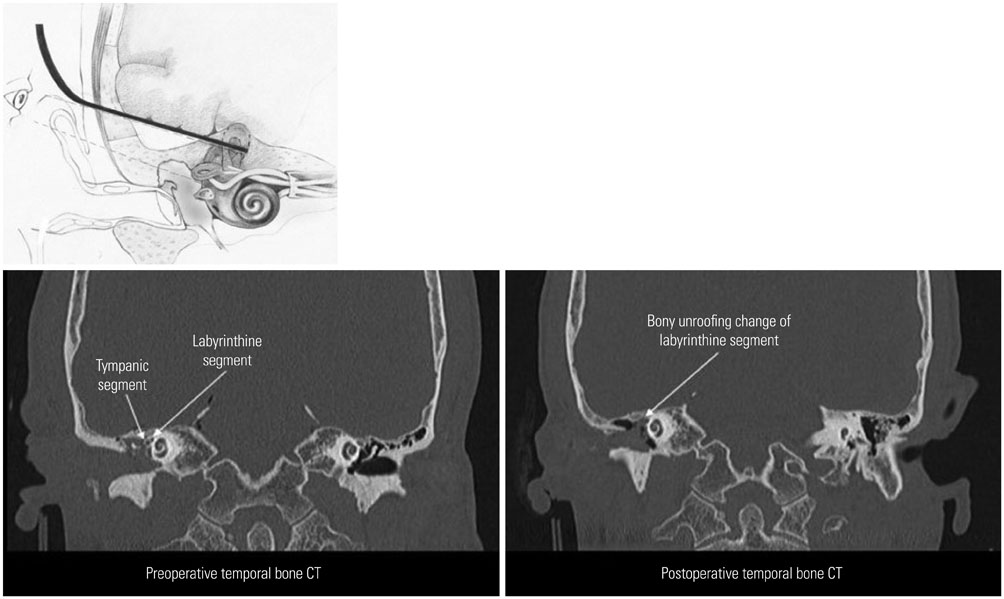
For the exposure of the labyrinthine segment of the facial nerve, transmastoid approach is not usually considered due to being situated behind the superior semicircular canal. To obtain a better view and bigger field for manipulation in the peri-geniculate area during facial nerve decompression, retraction of temporal lobe after bony removal of tegmen mastoideum was designed via transmastoid approach.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifteen patients with traumatic facial paralysis [House-Brackmann (HB) grade IV-VI], 3 patients with Bell's palsy (HB grade V-VI), and 2 patients with herpes zoster oticus (HB grade V-VI) underwent facial nerve decompression surgery between January 2008 and July 2014. In all patients, we performed temporal lobe retraction for facial nerve decompression via the transmastoid approach. Patients were examined using pre operative tests including high-resolution computed tomography, temporal magnetic resonance imaging, audiometry, and electroneurography (degenerative ratio >90%). Facial function was evaluated by HB grading scale before and 6 months after the surgery.
RESULTS
After the surgery, facial function recovered to HB grade I in 9 patients and to grade II in 11 patients. No problems due to surgical retraction of the temporal lobe were noted. Compared to the standard transmastoid approach, our method helped achieve a wider surgical view for improved manipulation in the peri-geniculate ganglion in all cases.
CONCLUSION
Facial nerve decompression via the transmastoid approach with temporal lobe retraction provides better exposure to the key areas around the geniculate ganglion without complications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Audiometry
Bell Palsy/etiology/surgery
Decompression, Surgical/*methods
Facial Nerve/diagnostic imaging/*surgery
Facial Paralysis/diagnostic imaging/etiology/*surgery
Female
Geniculate Ganglion/*diagnostic imaging/surgery
Herpes Zoster Oticus/surgery
Humans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Mastoid/surgery
Middle Aged
Neurosurgical Procedures/adverse effects
Temporal Bone/diagnostic imaging/surgery
Temporal Lobe
Tomography, X-Ray Computed/*methods
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Total Transcanal Endoscopic Facial Nerve Decompression for Traumatic Facial Nerve Palsy
Aveline Aloyce Kahinga, Ji Hyuk Han, In Seok Moon
Yonsei Med J. 2018;59(3):457-460. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.3.457.
Reference
-
1. Hadlock TA, Greenfield LJ, Wernick-Robinson M, Cheney ML. Multimodality approach to management of the paralyzed face. Laryngoscope. 2006; 116:1385–1389.
Article2. House WF. Middle cranial fossa approach to the petrous pyramid. Report of 50 cases. Arch Otolaryngol. 1963; 78:460–469.
Article3. Fisch U. Facial paralysis in fractures of the petrous bone. Laryngoscope. 1974; 84:2141–2154.
Article4. Yanagihara N, Hato N, Murakami S, Honda N. Transmastoid decompression as a treatment of Bell palsy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001; 124:282–286.
Article5. May M. Total facial nerve exploration: transmastoid, extralabyrinthine, and subtemporal indications and results. Laryngoscope. 1979; 89(6 Pt 1):906–917.6. Goin DW. Proximal intratemporal facial nerve in Bell’s palsy surgery. A study correlating anatomical and surgical findings. Laryngoscope. 1982; 92:263–272.
Article7. Yi H, Liu P, Yang S. Geniculate ganglion decompression of facial nerve by transmastoid-epitympanum approach. Acta Otolaryngol. 2013; 133:656–661.
Article8. Dimopoulos PA, Muren C, Smedby O, Wadin K. Anatomical variations of the tympanic and mastoid portions of the facial nerve canal. A radioanatomical investigation. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1996; 403:49–59.9. Ulug T. Zygomatic root approach. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009; 129:793–800.
Article10. Takeda T, Takebayashi S, Kakigi A, Nakatani H, Hamada M. Total decompression of the facial nerve - superior prelabyrinthine cell tracts approach. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2010; 71:Suppl 1. 112–115.
Article11. Proctor B, Nager GT. The facial canal: normal anatomy, variations and anomalies. I. Normal anatomy of the facial canal. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1982; 97:33–44.12. Nager GT, Proctor B. Anatomic variations and anomalies involving the facial canal. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1991; 24:531–553.13. Măru N, Cheiţă AC, Mogoantă CA, Prejoianu B. Intratemporal course of the facial nerve: morphological, topographic and morphometric features. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2010; 51:243–248.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Total Transcanal Endoscopic Facial Nerve Decompression for Traumatic Facial Nerve Palsy
- Microsurgical Anatomy of Perigeniculate Ganglion Area of the Facial Nerve
- Facial Nerve Decompression via Middle Fossa Approach: Report of Three Cases
- Outcomes and Prognosis of Patients Treated by Facial Nerve Decompression via Transmastoid Approach for Traumatic Facial Paralysis
- Facial Nerve Paralysis and Surgical Management