J Vet Sci.
2018 Nov;19(6):782-787. 10.4142/jvs.2018.19.6.782.
Genomic analysis of Sheldrake origin goose hemorrhagic polyomavirus, China
- Affiliations
-
- 1Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory for Avian Diseases Control and Prevention, Fujian Animal Diseases Control Technology Development Center, Institute of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine of Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Fuzhou 350013, China. chunhewan@126.com
- KMID: 2427026
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2018.19.6.782
Abstract
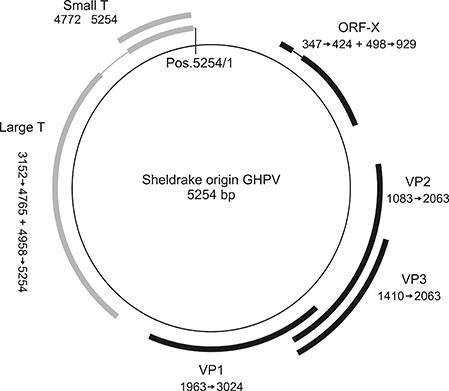
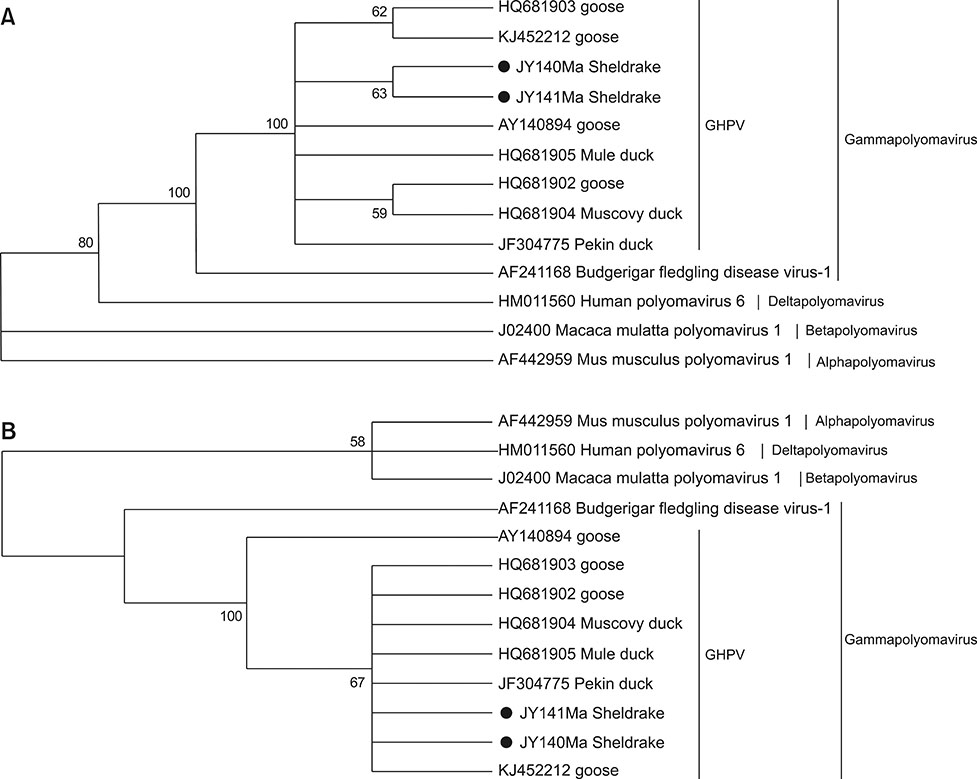
- Goose hemorrhagic polyomavirus (GHPV) is not a naturally occurring infection in geese in China; however, GHPV infection has been identified in Pekin ducks, a domestic duck species. Herein, we investigated the prevalence of GHPV in five domestic duck species (Liancheng white ducks, Putian black ducks, Shan Sheldrake, Shaoxing duck, and Jinyun Sheldrake) in China. We determined that the Jinyun Sheldrake duck species could be infected by GHPV with no clinical signs, whereas no infection was identified in the other four duck species. We sequenced the complete genome of the Jinyun Sheldrake origin GHPV. Genomic data comparison suggested that GHPVs share a conserved genomic structure, regardless of the host (duck or geese) or region (Asia or Europe). Jinyun Sheldrake origin GHPV genomic characterization and epidemiological studies will increase our understanding of potential heterologous reservoirs of GHPV.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bernáth S, Farsang A, Kovács A, Nagy E, Dobos-Kovács M. Pathology of goose haemorrhagic polyomavirus infection in goose embryos. Avian Pathol. 2006; 35:49–52.
Article2. Bernath S, Szalai F. [Investigation for clearing the etiology of the disease appeared among goslings in 1969]. Magy Allatorvosok Lapja. 1970; 25:531–536. Hungarian.3. Corrand L, Gelfi J, Albaric O, Etievant M, Pingret JL, Guerin JL. Pathological and epidemiological significance of Goose haemorrhagic polyomavirus infection in ducks. Avian Pathol. 2011; 40:355–360.
Article4. Dobos-Kovács M, Horváth E, Farsang A, Nagy E, Kovács A, Szalai F, Bernáth S. Haemorrhagic nephritis and enteritis of geese: pathomorphological investigations and proposed pathogenesis. Acta Vet Hung. 2005; 53:213–223.
Article5. Fehér E, Lengyel G, Dán A, Farkas SL, Bányai K. Whole genome sequence of a goose haemorrhagic polyomavirus detected in Hungary. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2014; 61:221–227.
Article6. Gaweł A, Woźniakowski G, Samorek-Salamonowicz E, Kozdruń W, Bobrek K, Bobusia K, Nowak M. Hemorrhagic nephritis and enteritis in a goose flock in Poland--disease course analysis and characterization of etiologic agent. Avian Dis. 2014; 58:518–522.
Article7. Guerin JL, Gelfi J, Dubois L, Vuillaume A, Boucraut-Baralon C, Pingret JL. A novel polyomavirus (goose hemorrhagic polyomavirus) is the agent of hemorrhagic nephritis enteritis of geese. J Virol. 2000; 74:4523–4529.
Article8. Jiang T, Zhang D. Molecular detection of goose hemorrhagic polyomavirus in Pekin ducks. China J Vet Med. 2012; 48:3–6.9. Johne R, Müller H. The genome of goose hemorrhagic polyomavirus, a new member of the proposed subgenus Avipolyomavirus. Virology. 2003; 308:291–302.
Article10. Lacroux C, Andreoletti O, Payre B, Pingret JL, Dissais A, Guerin JL. Pathology of spontaneous and experimental infections by Goose haemorrhagic polyomavirus. Avian Pathol. 2004; 33:351–358.
Article11. Moens U, Krumbholz A, Ehlers B, Zell R, Johne R, Calvignac-Spencer S, Lauber C. Biology, evolution, and medical importance of polyomaviruses: an update. Infect Genet Evol. 2017; 54:18–38.
Article12. Palya V, Ivanics E, Glávits R, Dán A, Mató T, Zarka P. Epizootic occurrence of haemorrhagic nephritis enteritis virus infection of geese. Avian Pathol. 2004; 33:244–250.
Article13. Pingret JL, Boucraut-Baralon C, Guérin JL. Goose haemorrhagic polyomavirus infection in ducks. Vet Rec. 2008; 162:164.
Article14. Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013; 30:2725–2729.
Article15. Wan C, Huang Y, Cheng L, Fu G, Shi SH, Chen H, Peng C, Lin F, Lin J. The development of a rapid SYBR Green I-based quantitative PCR for detection of Duck circovirus. Virol J. 2011; 8:465.
Article16. Woźniakowski G, Tarasiuk K. Visual detection of goose haemorrhagic polyomavirus in geese and ducks by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Avian Pathol. 2015; 44:311–318.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Simultaneous Detection of BK Virus and Adenovirus in a Case of Hemorrhagic Cystitis after Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Cytologic Findings of Polyomavirus Infection in the Urine: A Case Report
- Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome: Historical Aspects
- BK polyomavirus-associated nephropathy
- Polyomavirus Induced Interstital Nephritis in Renal Allograft Recipient