Cancer Res Treat.
2018 Oct;50(4):1084-1095. 10.4143/crt.2017.359.
Proposal of a Pretreatment Nomogram for Predicting Local Recurrence after Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy in T4 Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Retrospective Review of 415 Chinese Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangzhou, China. sunying@sysucc.org.cn, qizhy@sysucc.org.cn
- 2Department of Oncology, the First affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangdong, China.
- 3Department of Medical Statistics and Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
- KMID: 2424781
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2017.359
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Local relapse-free survival (LRFS) differs widely among patients with T4 category nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). We aimed to build a nomogram incorporating clinicopathological information to predict LRFS in T4 NPC after definitive intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Retrospective study of 415 Chinese patients with non-metastatic T4 NPC treated with definitive IMRT with or without chemotherapy at our cancer center between October 2009 and September 2013. The nomogram for LRFS at 3 and 5 years was generated based on multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression, and validated using bootstrap resampling, assessing discriminative performance using the concordance index (C-index) and determining calibration ability via calibration curves.
RESULTS
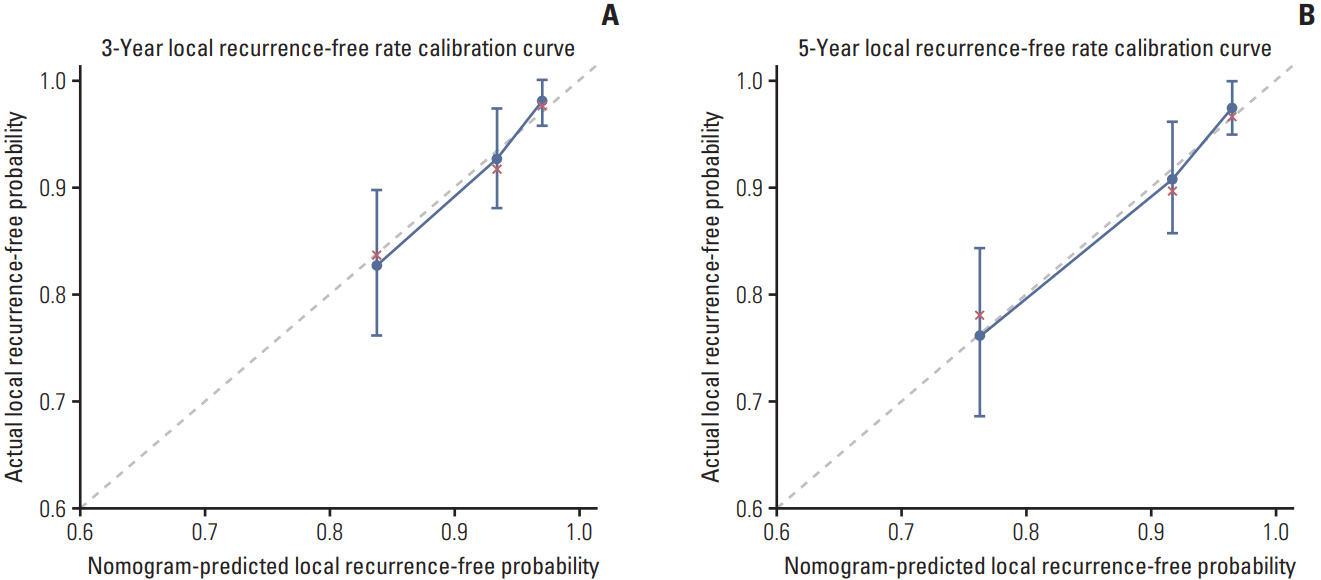
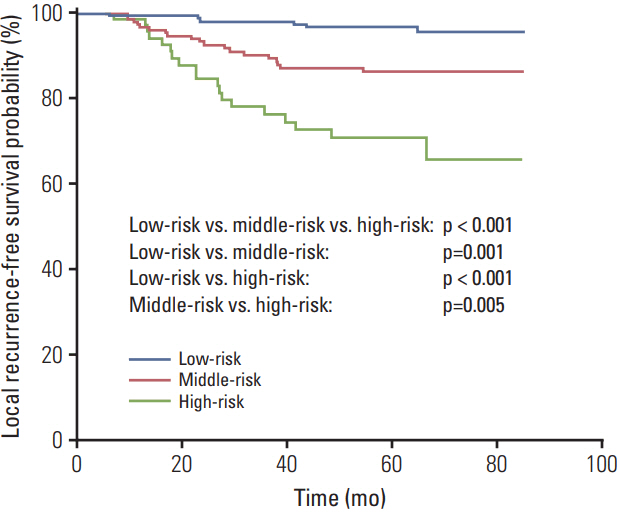
Five-year LRFS was 88.8%. We identified and incorporated four independent prognostic factors for LRFS: ethmoid sinus invasion, primary gross tumor volume, age, and pretreatment body mass index. The C-index of the nomogram for local recurrence was 0.732 (95% confidence interval, 0.726 to 0.738), indicating excellent predictive accuracy. The calibration curve revealed excellent agreement between nomogram-predicted and observed LRFS probabilities. Risk subgroups based on total point score cutoff values enabled effective discrimination of LRFS.
CONCLUSION
This pretreatment nomogram enables clinicians to accurately predict LRFS in T4 NPC after definitive IMRT, and could help to facilitate personalized patient counselling and treatment strategies.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Development and Validation of Web-Based Nomograms to Precisely Predict Survival Outcomes of Non-metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in an Endemic Area
Ji-Jin Yao, Li Lin, Tian-Sheng Gao, Wang-Jian Zhang, Wayne R. Lawrence, Jun Ma, Ying Sun
Cancer Res Treat. 2021;53(3):657-670. doi: 10.4143/crt.2020.899.
Reference
-
References
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90.
Article2. Chan AT. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2010; 21 Suppl 7:vii308–12.
Article3. Lee AW, Lin JC, Ng WT. Current management of nasopharyngeal cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2012; 22:233–44.
Article4. Lai SZ, Li WF, Chen L, Luo W, Chen YY, Liu LZ, et al. How does intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy influence the treatment results in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 80:661–8.5. Wu LR, Liu YT, Jiang N, Fan YX, Wen J, Huang SF, et al. Tenyear survival outcomes for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma receiving intensity-modulated radiotherapy: an analysis of 614 patients from a single center. Oral Oncol. 2017; 69:26–32.
Article6. Xu T, Tang J, Gu M, Liu L, Wei W, Yang H. Recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a clinical dilemma and challenge. Curr Oncol. 2013; 20:e406–19.
Article7. Li JX, Huang SM, Jiang XH, Ouyang B, Han F, Liu S, et al. Local failure patterns for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma after intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol. 2014; 9:87.
Article8. Wan XB, Wei L, Li H, Dong M, Lin Q, Ma XK, et al. High pretreatment serum lactate dehydrogenase level correlates with disease relapse and predicts an inferior outcome in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2013; 49:2356–64.
Article9. Cheng SH, Tsai SY, Horng CF, Yen KL, Jian JJ, Chan KY, et al. A prognostic scoring system for locoregional control in nasopharyngeal carcinoma following conformal radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 66:992–1003.
Article10. Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ, DeMatteo RP. Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:e173–80.
Article11. Iasonos A, Schrag D, Raj GV, Panageas KS. How to build and interpret a nomogram for cancer prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:1364–70.
Article12. Bendifallah S, Ballester M, Uzan C, Fauvet R, Morice P, Darai E. Nomogram to predict recurrence in patients with early- and advanced-stage mucinous and serous borderline ovarian tumors. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014; 211:637.
Article13. Li WF, Sun Y, Chen M, Tang LL, Liu LZ, Mao YP, et al. Locoregional extension patterns of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and suggestions for clinical target volume delineation. Chin J Cancer. 2012; 31:579–87.
Article14. Liang SB, Sun Y, Liu LZ, Chen Y, Chen L, Mao YP, et al. Extension of local disease in nasopharyngeal carcinoma detected by magnetic resonance imaging: improvement of clinical target volume delineation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009; 75:742–50.
Article15. Harrell FE Jr, Lee KL, Mark DB. Multivariable prognostic models: issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat Med. 1996; 15:361–87.
Article16. Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL. X-tile: a new bioinformatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res. 2004; 10:7252–9.17. Ng WT, Lee MC, Chang AT, Chan OS, Chan LL, Cheung FY, et al. The impact of dosimetric inadequacy on treatment outcome of nasopharyngeal carcinoma with IMRT. Oral Oncol. 2014; 50:506–12.
Article18. Tao CJ, Liu X, Tang LL, Mao YP, Chen L, Li WF, et al. Prognostic scoring system for locoregional control among the patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated by intensitymodulated radiotherapy. Chin J Cancer. 2013; 32:494–501.
Article19. Kong F, Ying H, Du C, Huang S, Zhou J, Chen J, et al. Patterns of local-regional failure after primary intensity modulated radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiat Oncol. 2014; 9:60.
Article20. Hong B, Lui VW, Hashiguchi M, Hui EP, Chan AT. Targeting tumor hypoxia in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck. 2013; 35:133–45.
Article21. Overgaard J. Hypoxic radiosensitization: adored and ignored. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:4066–74.
Article22. Cosse JP, Michiels C. Tumour hypoxia affects the responsiveness of cancer cells to chemotherapy and promotes cancer progression. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008; 8:790–7.
Article23. Sakata K, Hareyama M, Tamakawa M, Oouchi A, Sido M, Nagakura H, et al. Prognostic factors of nasopharynx tumors investigated by MR imaging and the value of MR imaging in the newly published TNM staging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 43:273–8.
Article24. Tang LQ, Li CF, Li J, Chen WH, Chen QY, Yuan LX, et al. Establishment and validation of prognostic nomograms for endemic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016; 108:djv291.
Article25. Chua DT, Sham JS, Choy D, Lorvidhaya V, Sumitsawan Y, Thongprasert S, et al. Preliminary report of the Asian-Oceanian Clinical Oncology Association randomized trial comparing cisplatin and epirubicin followed by radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in the treatment of patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Asian-Oceanian Clinical Oncology Association Nasopharynx Cancer Study Group. Cancer. 1998; 83:2270–83.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging–Detected Intracranial Extension in the T4 Classification Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma with Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy
- Review on the Pre-treatment Quality Assurance for Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy
- Intensity-modulated radiation therapy: a review with a physics perspective
- Re-irradiation with Moderate Hypo-fractionation Using Intensity Modulated Photon or Proton Radiation Therapy in Locally Recurrent Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Nasopharynx
- Radiotherapy for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma