J Korean Acad Nurs.
2016 Dec;46(6):813-823. 10.4040/jkan.2016.46.6.813.
Development of a Psychological Insulin Resistance Scale for Korean Patients with Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. yssong87@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2424653
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.6.813
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was done to develop and validate a measure to evaluate the Korean version of psychological insulin resistance (K-PIR) in patients with diabetes in Korea.
METHODS
Items were initially generated from literature reviews and interviews with 19 patients with diabetes. The content validity of the items was evaluated by experts. Participants were 424 patients with diabetes recruited through convenience sampling. A cross-sectional survey was designed for item-analysis, exploratory factor analysis with principal axis factoring, and confirmatory factor analysis. Cronbach's alpha was calculated to measure the internal consistency.
RESULTS
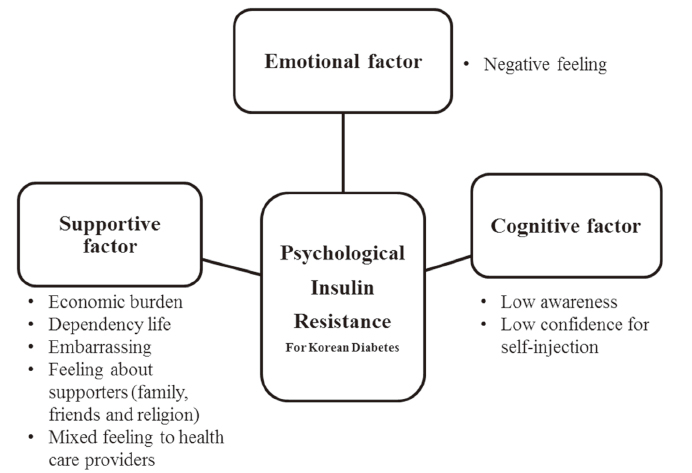
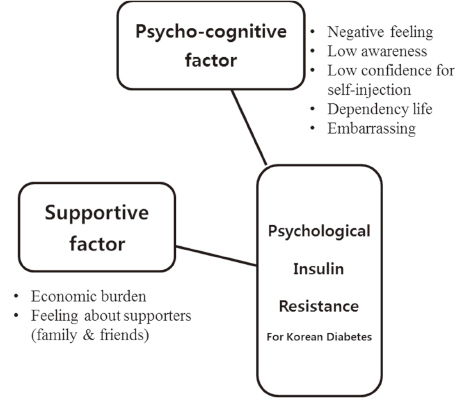
For the 24 items of the Korean version of psychological insulin resistance, six items were eliminated because of low correlation with the other items. Exploratory factor analysis with 18-item showed that two factors (psycho-cognitive factor and supportive factor) explained 41.8% of the variance, and the factor structure of K-PIR model had a good fit. Internal consistency of K-PIR with 18 items revealed good reliability.
CONCLUSION
The findings show that the K-PIR is reliable for measuring the psychological resistance to insulin therapy for Korean patients with diabetes. However, further study is needed to evaluate the validation because the proportion of variation of K-PIR was low in this study.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Cross-Sectional Studies
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/*psychology/therapy
Emotions
Female
Focus Groups
Humans
Insulin/therapeutic use
Insulin Resistance
Interviews as Topic
Male
Middle Aged
*Psychometrics
Republic of Korea
Social Support
Socioeconomic Factors
Surveys and Questionnaires
Insulin
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Psychological Insulin Resistance and Low Self-efficacy as Barriers to Diabetes Self-care Management in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Bohyun Kim, Youngshin Song, Jong Im Kim
Korean J Adult Nurs. 2019;31(1):61-67. doi: 10.7475/kjan.2019.31.1.61.Psychological Insulin Resistance: Key Factors and Intervention
Yeon Jeong Jang
J Korean Diabetes. 2021;22(3):192-196. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2021.22.3.192.
Reference
-
1. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2016: Summary of revisions. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:Suppl 1. S4–S5. DOI: 10.2337/dc16-S003.2. Gherman A, Veresiu IA, Sassu RA, Schnur JB, Scheckner BL, Montgomery GH. Psychological insulin resistance: A critical review of the literature. Practical Diabetes International. 2011; 28(3):125–128. DOI: 10.1002/pdi.1574.3. Abu Hassan H, Tohid H, Mohd Amin R, Long Bidin MB, Muthupalaniappen L, Omar K. Factors influencing insulin acceptance among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a primary care clinic: A qualitative exploration. BMC Fam Pract. 2013; 14:164. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2296-14-164.4. Karter AJ, Subramanian U, Saha C, Crosson JC, Parker MM, Swain BE, et al. Barriers to insulin initiation: the translating research into action for diabetes insulin starts project. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33(4):733–735. DOI: 10.2337/dc09-1184.5. Song Y, Song HJ, Han HR, Park SY, Nam S, Kim MT. Unmet needs for social support and effects on diabetes self-care activities in Korean Americans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Educ. 2012; 38(1):77–85. DOI: 10.1177/0145721711432456.6. Polonsky WH, Anderson BJ, Lohrer PA, Welch G, Jacobson AM, Aponte JE, et al. Assessment of diabetes-related distress. Diabetes Care. 1995; 18(6):754–760. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.18.6.754.7. Snoek FJ, Skovlund SE, Pouwer F. Development and validation of the insulin treatment appraisal scale (ITAS) in patients with type 2 diabetes. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2007; 5:69. DOI: 10.1186/1477-7525-5-69.8. Fu SN, Chin WY, Wong CK, Yeung VT, Yiu MP, Tsui HY, et al. Development and validation of the Chinese attitudes to starting insulin questionnaire (Ch-ASIQ) for primary care patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One. 2013; 8(11):e78933. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078933.9. Larkin ME, Capasso VA, Chen CL, Mahoney EK, Hazard B, Cagliero E, et al. Measuring psychological insulin resistance: Barriers to insulin use. Diabetes Educ. 2008; 34(3):511–517. DOI: 10.1177/0145721708317869.10. Petrak F, Stridde E, Leverkus F, Crispin AA, Forst T, Pfützner A. Development and validation of a new measure to evaluate psychological resistance to insulin treatment. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30(9):2199–2204. DOI: 10.2337/dc06-2042.11. Hong SH, Kim MJ, Noh SG, Suh DW, Youn SJ, Lee KW, et al. A study on resistance in type 2 diabetic patient against commencement of insulin treatment. Korean Diabetes J. 2008; 32(3):269–279. DOI: 10.4093/kdj.2008.32.3.269.12. Kang MR. Relationships among psychological insulin resistance, diabetes knowledge and self-efficacy in patients with type 2 diabetes[master's thesis]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2014. 1–71.13. Peyrot M, Rubin RR, Lauritzen T, Skovlund SE, Snoek FJ, Matthews DR, et al. Resistance to insulin therapy among patients and providers: results of the cross-national diabetes attitudes, wishes, and needs (DAWN) study. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28(11):2673–2679. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.28.11.2673.14. Costello AB, Osborne JW. Best Practices in exploratory factor analysis: Four recommendations for getting the most from your analysis. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation. 2005; 10(7):1–9.15. Myers ND, Ahn S, Jin Y. Sample size and power estimates for a confirmatory factor analytic model in exercise and sport: A Monte Carlo approach. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2011; 82(3):412–423. DOI: 10.1080/02701367.2011.10599773.16. Song Y, Son YJ, Oh D. Methodological issues in questionnaire design. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2015; 45(3):323–328. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2015.45.3.323.17. Waltz CF, Strickland OL, Lenz ER. Measurement in nursing and health research. 4th ed. New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company;2010. p. 1–504.18. Nunnally JC, Bernstein IH. Psychometric theory. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill;1994. p. 1–752.19. Hu LT, Bentler PM. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct Equ Modeling. 2009; 6(1):1–55. DOI: 10.1080/10705519909540118.20. Kim NH. A study on drug users'intention to use treatment services: Application of the behavioral model of health services use and the theory of planned behavior [dissertation]. Seoul: Seoul National University;2015. 1–171.21. Nam S, Chesla C, Stotts NA, Kroon L, Janson SL. Factors associated with psychological insulin resistance in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33(8):1747–1749. DOI: 10.2337/dc10-0099.22. Nam S, Song HJ, Park SY, Song Y. Challenges of diabetes management in immigrant Korean Americans. Diabetes Educ. 2013; 39(2):213–221. DOI: 10.1177/0145721713475846.23. Jenkins N, Hallowell N, Farmer AJ, Holman RR, Lawton J. Initiating insulin as part of the treating to target in type 2 diabetes (4-T) trial: An interview study of patients’ and health professionals' experiences. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33(10):2178–2180. DOI: 10.2337/dc10-0494.24. Nakar S, Yitzhaki G, Rosenberg R, Vinker S. Transition to insulin in type 2 diabetes: Family physicians' misconception of patients' fears contributes to existing barriers. J Diabetes Complications. 2007; 21(4):220–226. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2006.02.004.25. Song Y. Concept analysis for psychological insulin resistance in Korean People with Diabetes. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2016; 46(3):443–453. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.443.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Using Motivational Interviewing to Overcome Psychological Insulin Resistance
- Psychological Insulin Resistance: Key Factors and Intervention
- Effect of Psychological Insulin Resistance, Diabetes Distress, and Diabetes Self-Efficacy on the Insulin Therapy Adherence of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: An Analysis Based on the Actor-Partner Interdependence Model
- Psychological Insulin Resistance and Low Self-efficacy as Barriers to Diabetes Self-care Management in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Educational Strategies for Insulin Injection Therapy in Elderly Diabetic Patients