Korean Circ J.
2018 Dec;48(12):1081-1096. 10.4070/kcj.2018.0335.
Unsolved Questions on the Anatomy of the Ventricular Conduction System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Mediplex Sejong Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jwseo@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2424559
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2018.0335
Abstract
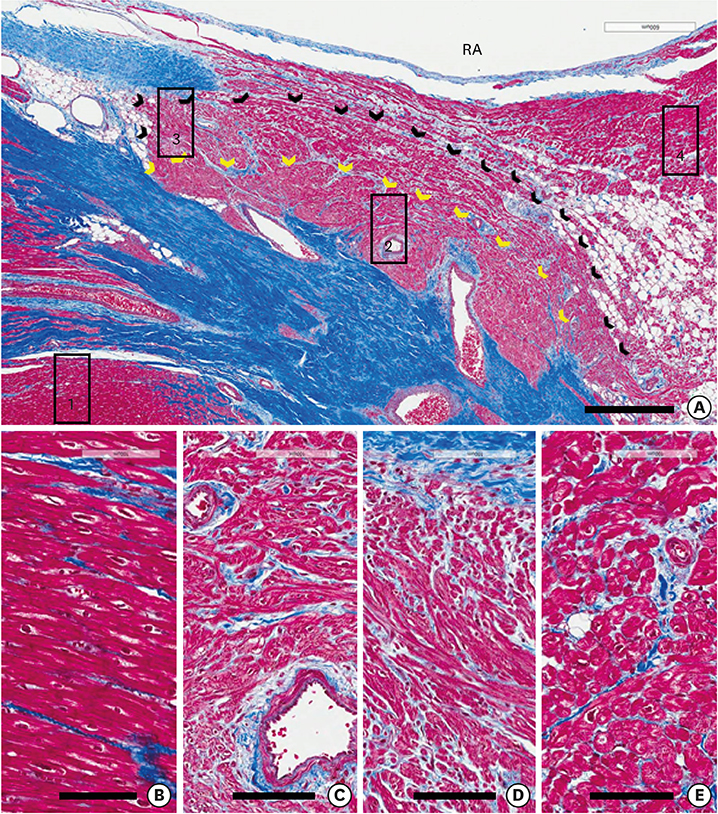
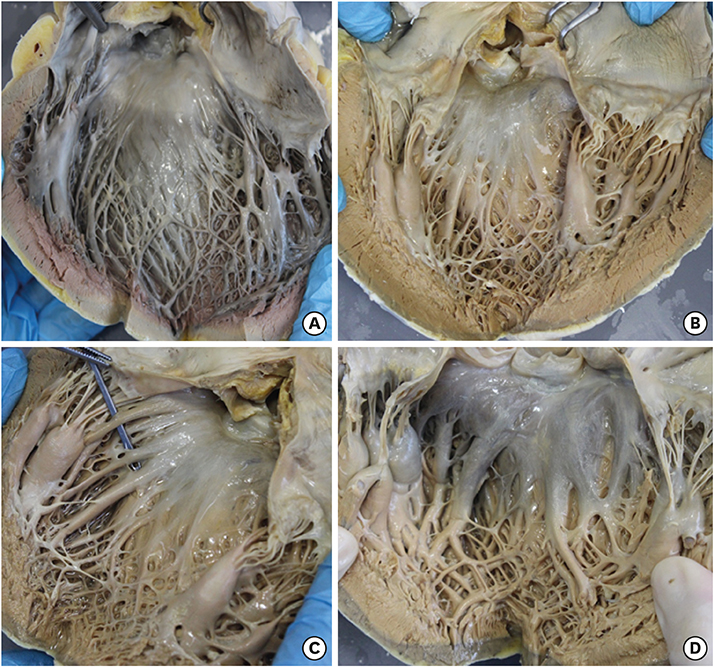
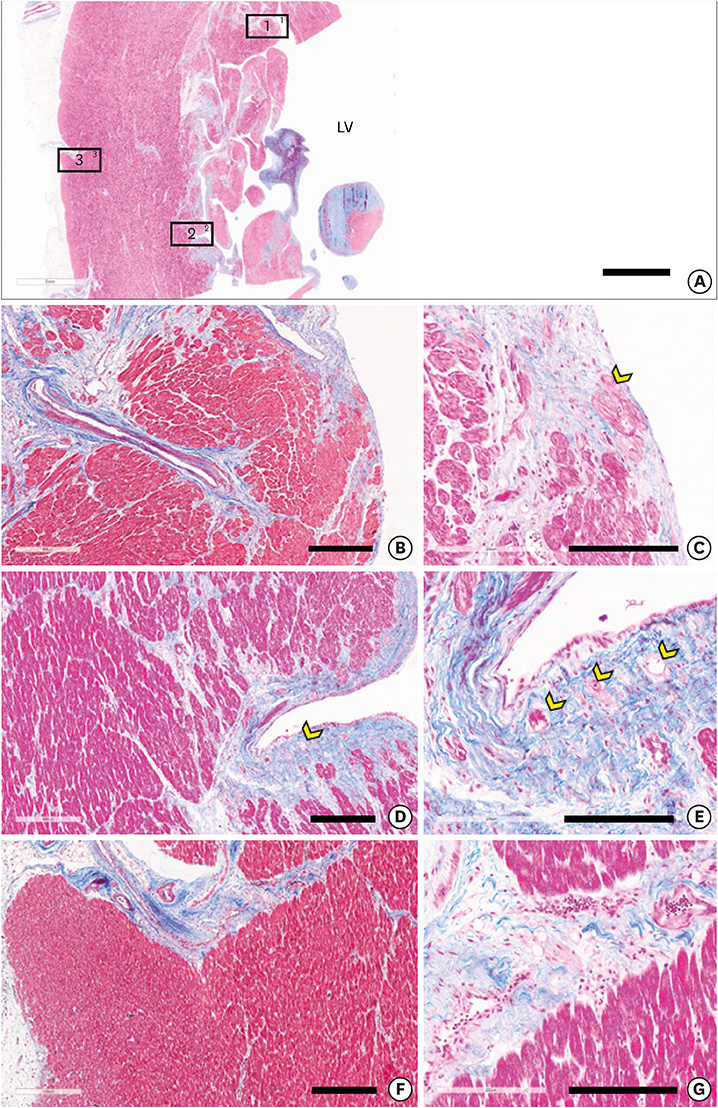
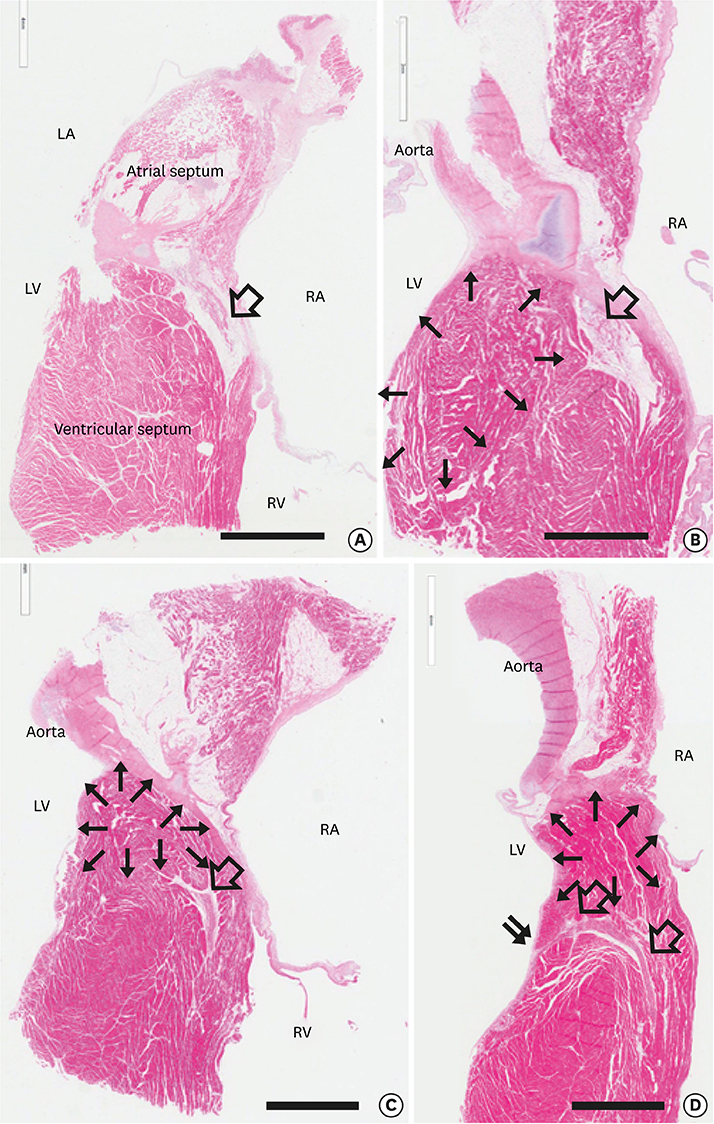
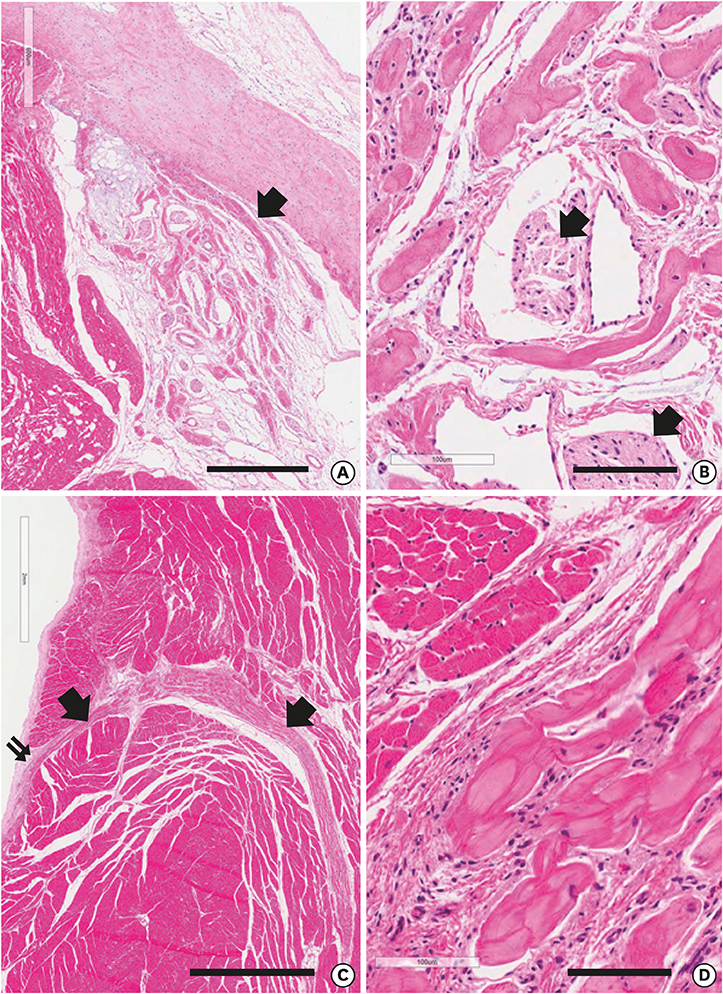
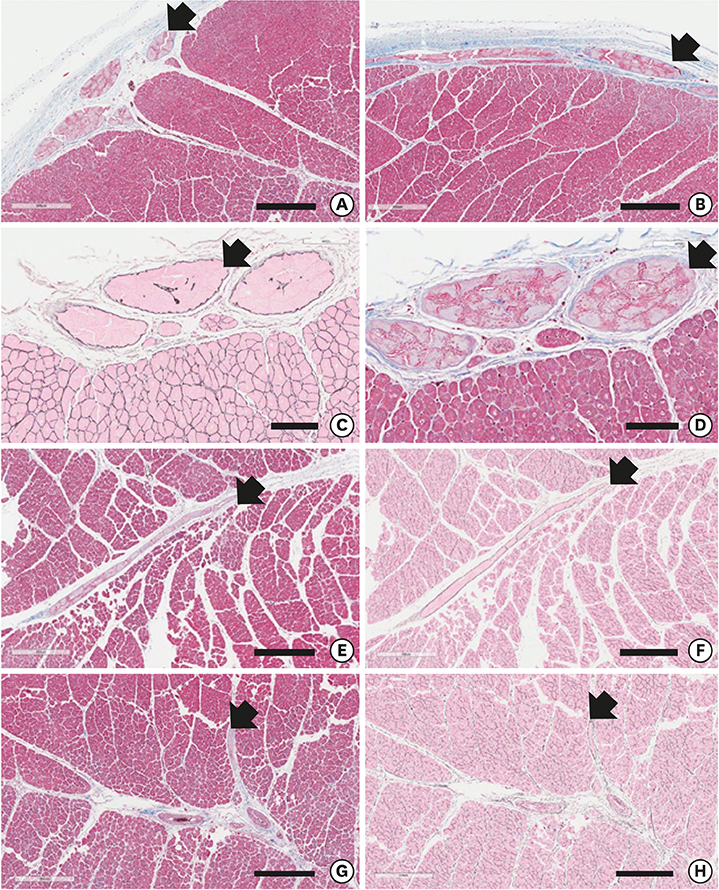
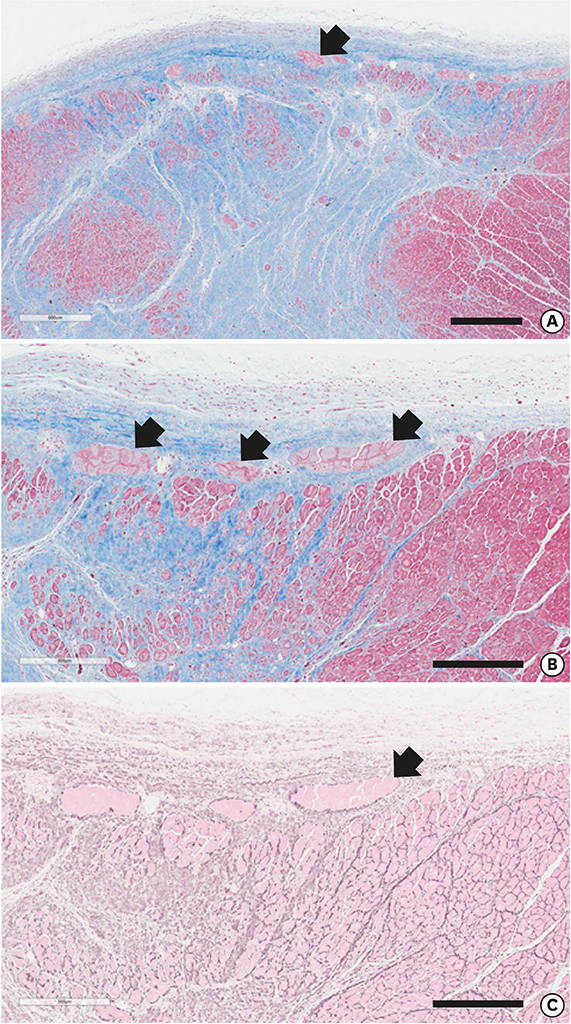
- We reviewed the anatomical characteristics of the conduction system in the ventricles of human and ungulate hearts and then raised some questions to be answered by clinical and anatomical studies in the future. The ventricular conduction system is a 3-dimensional structure as compared to the 2-dimensional character of the atrial conduction system. The proximal part consisting of the atrioventricular node, the bundle of His and fascicles are groups of conducting cells surrounded by fibrous connective tissue so as to insulate from the underlying myocardium. Their location and morphological characters are well established. The bundle of His is a cord like structure but the left and right fascicles are broad at the proximal and branching at the distal part. The more distal part of fascicles and Purkinje system are linear networks of conducting cells at the immediate subendocardium but the intra-mural network is detected at the inner half of the ventricular wall. The papillary muscle also harbors Purkinje system not in the deeper part. It is hard to recognize histologically in human hearts but conducting cells as well as Purkinje cells are easily recognized in ungulate hearts. Further observation on human and ungulate hearts with myocardial infarct, we could find preserved Purkinje system at the subendocardium in contrast to the damaged system at the deeper myocardium. Further studies are necessary on the anatomical characteristics of this peripheral conduction system so as to correlate the clinical data on hearts with ventricular arrhythmias.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Garcia-Bustos V, Sebastian R, Izquierdo M, Molina P, Chorro FJ, Ruiz-Sauri A. A quantitative structural and morphometric analysis of the Purkinje network and the Purkinje-myocardial junctions in pig hearts. J Anat. 2017; 230:664–678.
Article2. Davies MJ. Pathology of conducting tissue of the heart. London: Butterworths;1971.3. Seo JW, Chi JG, Lee SK. Cardiac conduction system-Morphological observations on the autopsy cases. Korean J Pathol. 1983; 17:127–137.4. Ansari A, Ho SY, Anderson RH. Distribution of the Purkinje fibres in the sheep heart. Anat Rec. 1999; 254:92–97.
Article5. Saffitz JE, Corradi D. The electrical heart: 25 years of discovery in cardiac electrophysiology, arrhythmias and sudden death. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2016; 25:149–157.
Article6. Silverman ME, Hollman A. Discovery of the sinus node by Keith and Flack: on the centennial of their 1907 publication. Heart. 2007; 93:1184–1187.
Article7. Silverman ME, Grove D, Upshaw CB Jr. Why does the heart beat? the discovery of the electrical system of the heart. Circulation. 2006; 113:2775–2781.8. Cho Y, Lee W, Park EA, et al. The anatomical characteristics of three different endocardial lines in the left atrium: evaluation by computed tomography prior to mitral isthmus block attempt. Europace. 2012; 14:1104–1111.
Article9. Dong J, Dickfeld T. Image integration in electroanatomic mapping. Herzschrittmacherther Elektrophysiol. 2007; 18:122–130.
Article10. Dukkipati SR, Koruth JS, Choudry S, Miller MA, Whang W, Reddy VY. Catheter ablation of ventricular tachycardia in structural heart disease: indications, strategies, and outcomes-part II. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017; 70:2924–2941.11. Muser D, Santangeli P, Liang JJ. Management of ventricular tachycardia storm in patients with structural heart disease. World J Cardiol. 2017; 9:521–530.
Article12. Tawara S. The conduction system of the Mammalian heart: an anatomico-histological study of the atrioventricular bundle and the Purkinje fibers. London: Imperial College Press;2000.13. De Almeida MC, Lopes F, Fontes P, Barra F, Guimaraes R, Vilhena V. Ungulates heart model: a study of the Purkinje network using India ink injection, transparent specimens and computer tomography. Anat Sci Int. 2015; 90:240–250.
Article14. Moorman AF, Christoffels VM, Anderson RH. Anatomic substrates for cardiac conduction. Heart Rhythm. 2005; 2:875–886.
Article15. Bharati S, Scheinman M, Lev M. Histologic findings of the heart and the conduction system in the first patient who underwent catheter ablation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1992; 15:1291–1299.
Article16. Jackman WM, Wang XZ, Friday KJ, et al. Catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways (Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome) by radiofrequency current. N Engl J Med. 1991; 324:1605–1611.
Article17. Seo JW. Ventricular anatomy for the electrophysiologist (part I). Int J Arrhythm. 2010; 11:6–11.18. Seo JW, Kim MY. Ventricular anatomy for the electrophysiologist (part II). Int J Arrhythm. 2010; 11:6–12.19. Assomull RG, Prasad SK, Lyne J, et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance, fibrosis, and prognosis in dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006; 48:1977–1985.
Article20. Massing GK, James TN. Anatomical configuration of the His bundle and bundle branches in the human heart. Circulation. 1976; 53:609–621.
Article21. Na CY, Hong JS, Park JJ, Kim WK, Kang MC, Seo JW. Establishment of the heart failure model by coronary artery ligation in sheep. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002; 35:1–10.22. Deo M, Boyle PM, Kim AM, Vigmond EJ. Arrhythmogenesis by single ectopic beats originating in the Purkinje system. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010; 299:H1002–H1011.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Role of Conduction System Pacing in Patients Requiring Permanent Pacing
- Anatomy of the septal perforating arteries of the heart
- Electrophysiologic Properties of Aberrant Ventricular Conduction Induced by Atrial Extrastimulation
- Cardiac Arrest induced by Epinephrine and Other Causes
- Survey Study on Practical Anatomy Education for Clinical Pathology Students