J Korean Acad Nurs.
2016 Aug;46(4):475-489. 10.4040/jkan.2016.46.4.475.
Stimulation-Oriented Interventions for Behavioral Problems among People with Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychotherapy, College of Nursing and Public Health, Kyungil University, Kyungsan, Korea.
- 2Department of Social Welfare, College of Social Science, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Nursing, College of Health and Medical Science, Daejeon University, Daejeon, Korea. ejkim@dju.kr
- KMID: 2424545
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.4.475
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to investigate the effects of stimulation-oriented interventions for behavioral problems among people with dementia.
METHODS
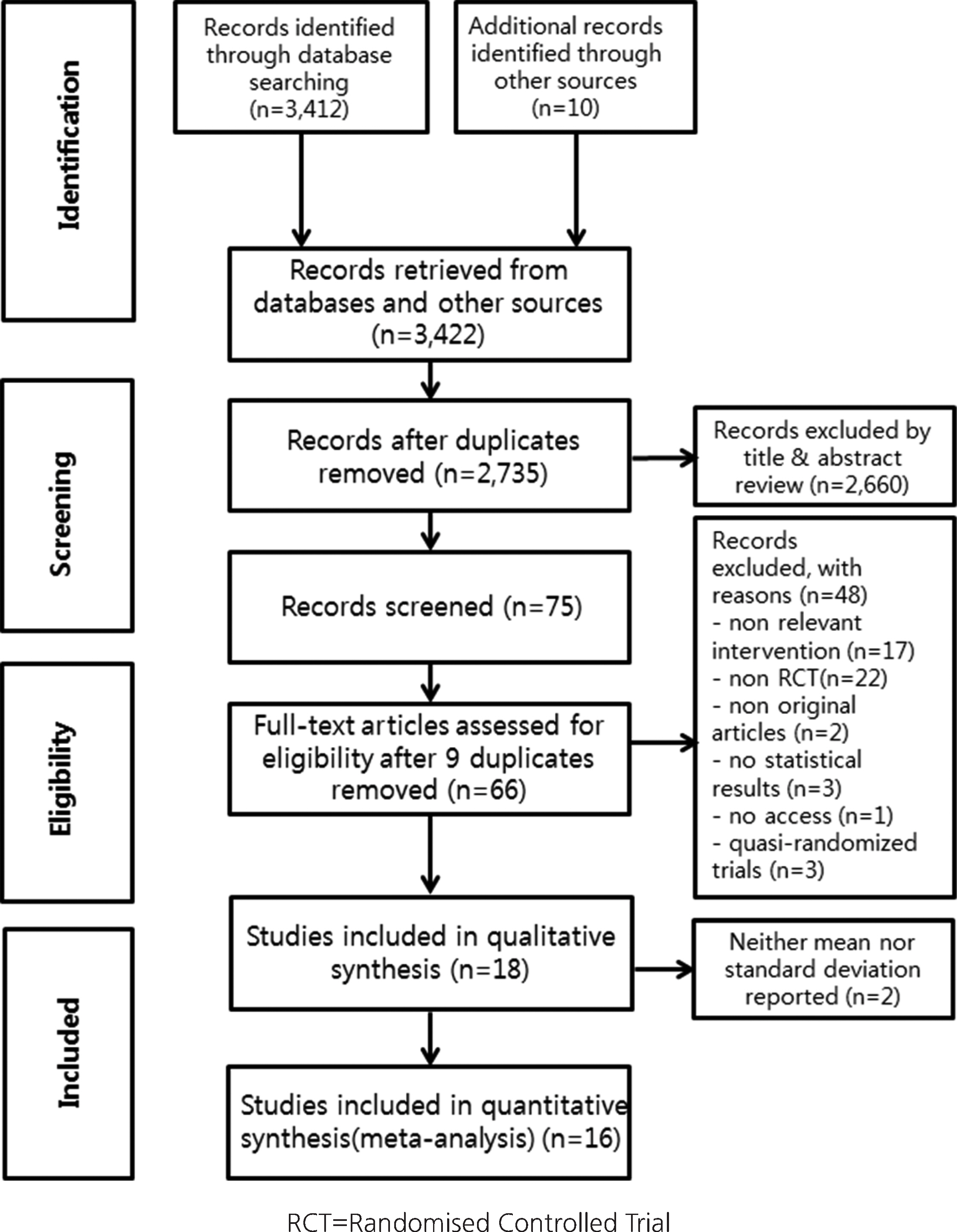
Based on the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA), a literature search was conducted using seven electronic databases, gray literature, and other sources. Methodological quality was assessed using the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) for randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Data were analyzed using R with the 'meta' package and the Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA 2.0) program.
RESULTS
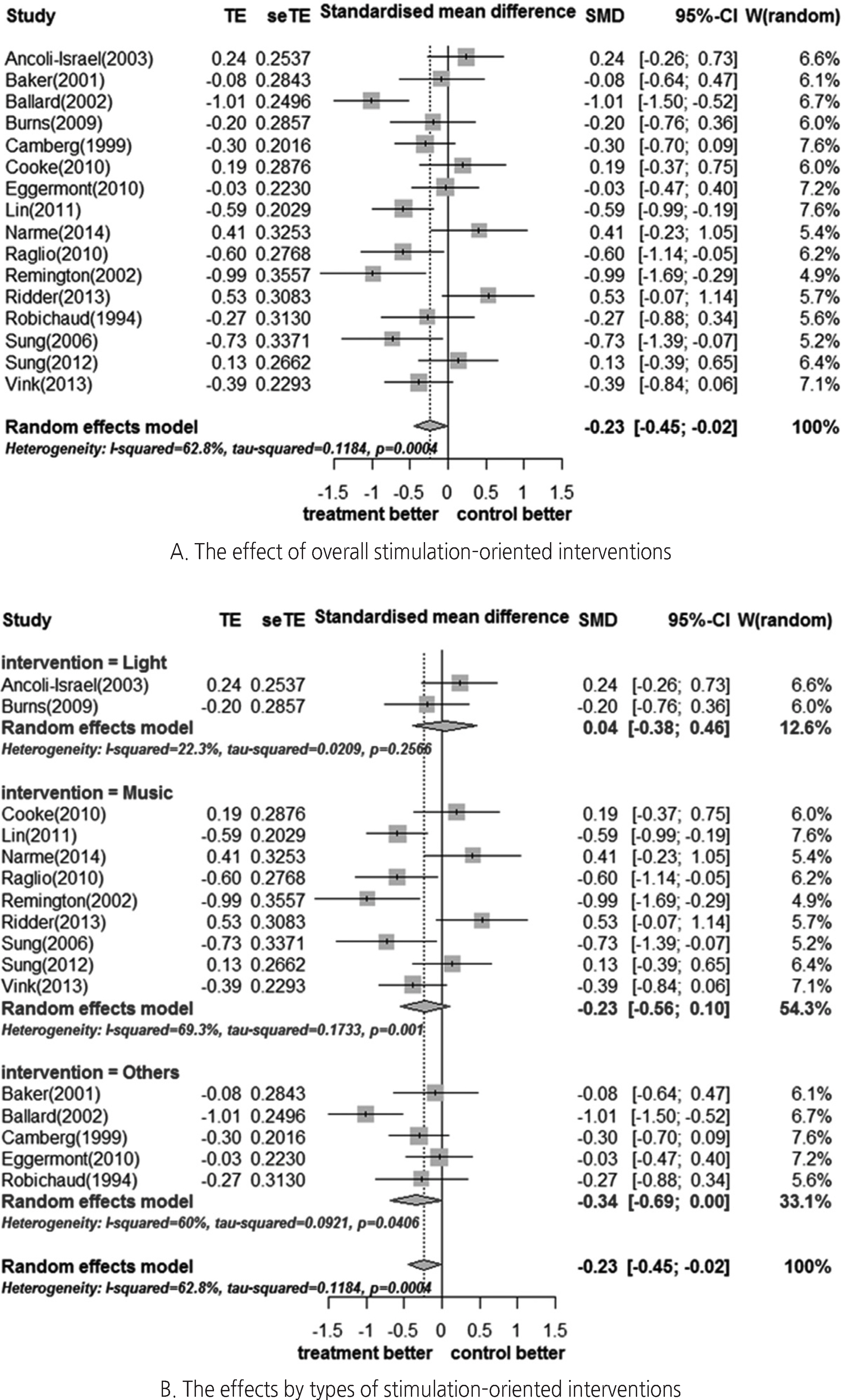
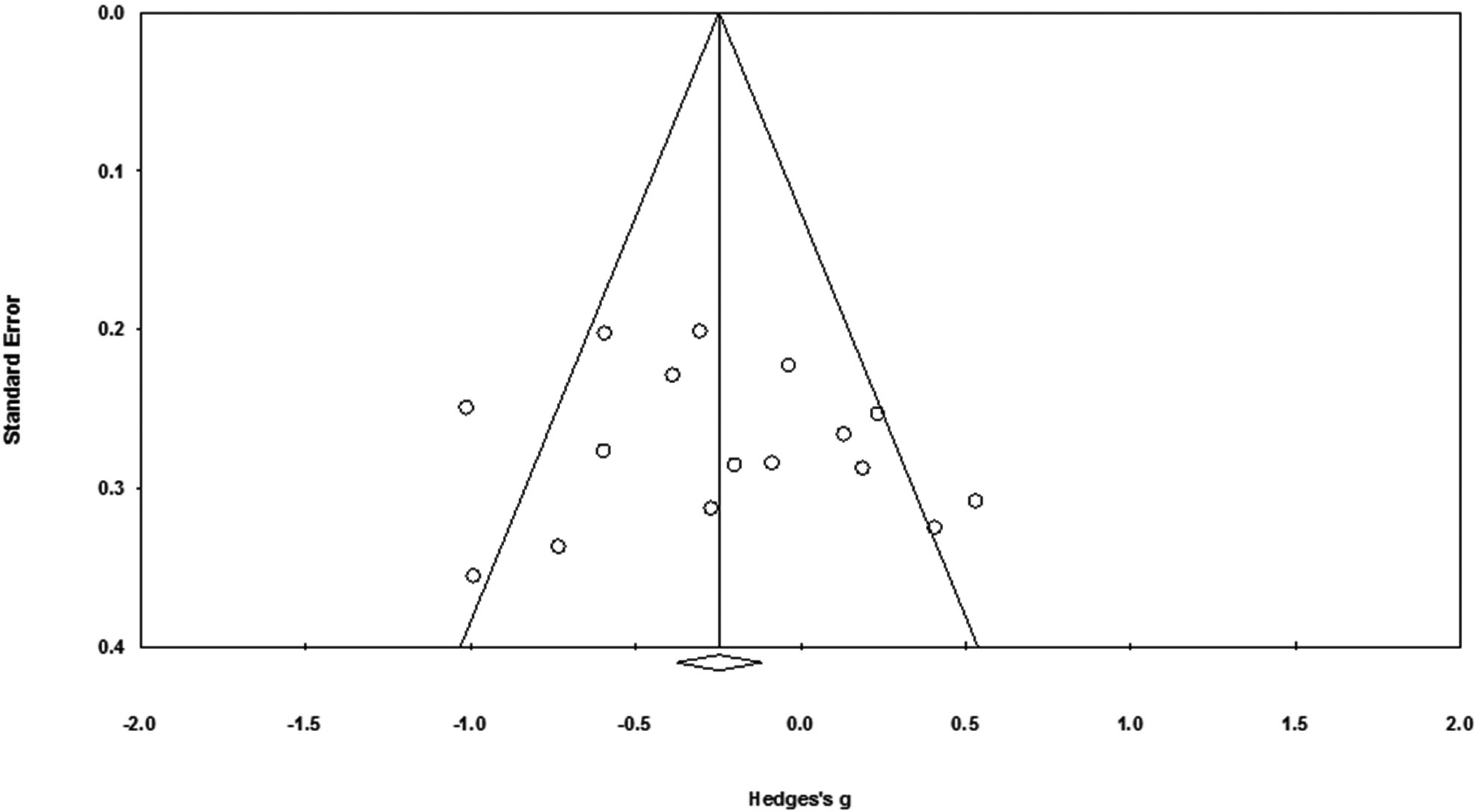
Sixteen studies were included for meta-analysis to investigate the effect of stimulation-oriented interventions. The quality of individual studies was rated as '++' for eight studies and '+' for the rest. The effect sizes were analyzed according to three subgroups of interventions (light, music, and others); Hedges' g=0.04 (95% CI: -0.38~0.46), -0.23 (95% CI: -0.56~0.10), -0.34 (95% CI: -0.34~0.00), respectively. To explore the possible causes of heterogeneity (I²=62.8%), meta-regression was conducted with covariates of sample size, number of sessions, and length of session (time). No moderating effects were found for sample size or number of sessions, but session time showed a significant effect (Z=1.96, 95% CI: 0.00~0.01). Finally, a funnel plot along with Egger's regression test was performed to check for publication bias, but no significant bias was detected.
CONCLUSION
Based on these findings, stimulation-oriented interventions seem to have a small effect for behavioral problems among people with dementia. Further research is needed to identify optimum time of the interventions for behavioral problems among dementia pateints.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ministry of Health & Welfare. National dementia strategy 2013-2015[Internet]. Seoul: Author;2012. [cited 2012 July 27]. Available from:. http://www.silverweb.or.kr/_data/board_list_file/1/2012/1207301339541.pdf.2. Kong EH, Evans LK, Guevara JP. Nonpharmacological intervention for agitation in dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging & Mental Health. 2009; 13(4):512–520. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/13607860902774394.
Article3. Slone DG, Gleason CE. Behavior management planning for problem behaviors in dementia: A practical model. Professional Psychology. 1999; 30(1):27–36. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0735-7028.30.1.27.
Article4. Medical World News. During past 5 years number of dementia patients increased 17% and missing rates increased 80%[Internet]. Seoul: Author;2013. [cited 2013 April 19]. Available from:. http://medicalworldnews.co.kr/news/view.php?newsid=1366370094.5. Schneider LS, Dagerman K, Insel PS. Efficacy and adverse effects of atypical antipsychotics for dementia: Meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2006; 14(3):191–210. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.JGP.0000200589.01396.6d.
Article6. Talerico KA, Evans LK, Strumpf NE. Mental health correlates of aggression in nursing home residents with dementia. The Gerontologist. 2002; 42(2):169–177. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/geront/42.2.169.
Article7. Cohen-Mansfield J, Billig N. Agitated behaviors in the elderly. I. A conceptual review. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 1986; 34(10):711–721. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.1986.tb04302.x.
Article8. Rabins PV, Rovner BW, Rummans T, Schneider LS, Tariot PN. Guideline watch (October 2014): Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association;2014. p. 1–26.9. Rabins PV, Blacker D, Rovner BW, Rummans T, Schneider LS, Tariot PN, et al. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with Alzheimer’ disease and other dementias. 2nd ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association;2007. p. 1–86.10. Harbour R, Miller J. A new system for grading recommendations in evidence based guidelines. BMJ: British Medical Journal.,. 2001; 323(7308):334–336. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.323.7308.334.
Article11. Hwang SD. Meta analysis. Seoul: Hakjisa Corp.;2014. p. 1–318.12. Kong EH, Park M. Effects of music therapy on agitation in dementia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 2015; 27(1):106–116. http://dx.doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2015.27.1.106.
Article13. Brodaty H, Arasaratnam C. Meta-analysis of nonpharmacological interventions for neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia. The American Journal of Psychiatry. 2012; 169(9):946–953. http://dx.doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.11101529.
Article14. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. SIGN 50: A guideline developer’ handbook[Internet]. Edinburgh, UK: Author;2011. [cited 2014 November 20]. Available from:. http://www.sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/50/index.html.15. Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein HR. Introduction to meta-analysis. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd;2009. p. 1–452.16. Schwarzer G. Meta: General package for meta-analysis. R package version 4.3-2[Internet]. Berkeley, CA: The Comprehensive R Archive Network;2015. [cited 2015 December 2]. Available from:. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/meta/index.html.17. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates;1988. p. 1–567.18. Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0[Internet]. London, UK: The Cochrane Collaboration;2011. [cited 2011 March 2]. Available from:. http://handbook.cochrane.org/.19. Littell JH, Corcoran J, Pillai V. Systematic reviews and meta-analysis. New York, NY: Oxford University Press;2008.20. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ: British Medical Journal. 1997; 315(7109):629–634. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629.
Article21. Baker R, Bell S, Baker E, Gibson S, Holloway J, Pearce R, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the effects of multi-sensory stimulation (MSS) for people with dementia. The British Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2001; 40(Pt 1):81–96. http://dx.doi.org/10.1348/014466501163508.
Article22. Cooke ML, Moyle W, Shum DH, Harrison SD, Murfield JE. A randomized controlled trial exploring the effect of music on agitated behaviours and anxiety in older people with dementia. Aging & Mental Health. 2010; 14(8):905–916. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/13607861003713190.
Article23. Raglio A, Bellelli G, Traficante D, Gianotti M, Ubezio MC, Gentile S, et al. Efficacy of music therapy treatment based on cycles of sessions: A randomised controlled trial. Aging & Mental Health. 2010; 14(8):900–904. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/13607861003713158.
Article24. Livingston G, Kelly L, Lewis-Holmes E, Baio G, Morris S, Patel N, et al. Non-pharmacological interventions for agitation in dementia: Systematic review of randomised controlled trials. The British Journal of Psychiatry. 2014; 205(6):436–442. http://dx.doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.113.141119.
Article25. Cabrera E, Sutcliffe C, Verbeek H, Saks K, Soto-Martin M, Meyer G, et al. Non-pharmacological interventions as a best practice strategy in people with dementia living in nursing homes. A systematic review. European Geriatric Medicine. 2015; 6(2):134–150. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eurger.2014.06.003.
Article26. Yury CA, Fisher JE. Meta-analysis of the effectiveness of atypical antipsychotics for the treatment of behavioural problems in persons with dementia. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics. 2007; 76(4):213–218. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000101499.
Article27. Ueda T, Suzukamo Y, Sato M, Izumi S. Effects of music therapy on behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Research Reviews. 2013; 12(2):628–641. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2013.02.003.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Systematic Review of Nonpharmacological Interventions for Moderate to Severe Dementia: A Study Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions to reduce internalized stigma in people with severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Non-pharmacological Intervention for Wandering Behavior in Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Effects of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Factors associated with Burden of Family Caregivers of Home-dwelling Elderly People with Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis