J Clin Neurol.
2018 Oct;14(4):513-522. 10.3988/jcn.2018.14.4.513.
Association between Frontal-Executive Dysfunction and Speech-in-Noise Perception Deficits in Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Audiology and Speech-Language Pathology, Daegu Catholic University, Gyeongsan, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 4Graduate Program in Speech-Language Pathology and Department and Research Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. h.kim@yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 2424180
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2018.14.4.513
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Speech-in-noise perception deficits have been demonstrated in patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). However, it remains unclear whether the impairment of speech perception varies between MCI subtypes. The purpose of this study was twofold: 1) to compare speech perception performance among MCI subgroups, and 2) to identify the cognitive domains specifically related to speech-in-noise perception.
METHODS
We studied 46 patients with MCI and 39 hearing-threshold-matched cognitively normal elderly (CNE) subjects. Two different patient classifications were used: 1) patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) (n=21) or nonamnestic mild cognitive impairment (naMCI) (n=25), and 2) patients with frontal-executive dysfunction (FED) (n=16) or without FED (n=30). All of the subjects underwent audiometric, neuropsychological, and speech perception assessments. Speech-in-noise perception was measured using sentence recognition tests in the presence of two types of background noise at four levels.
RESULTS
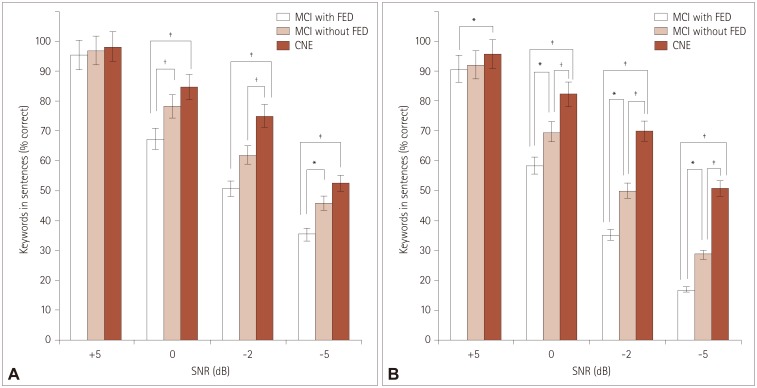
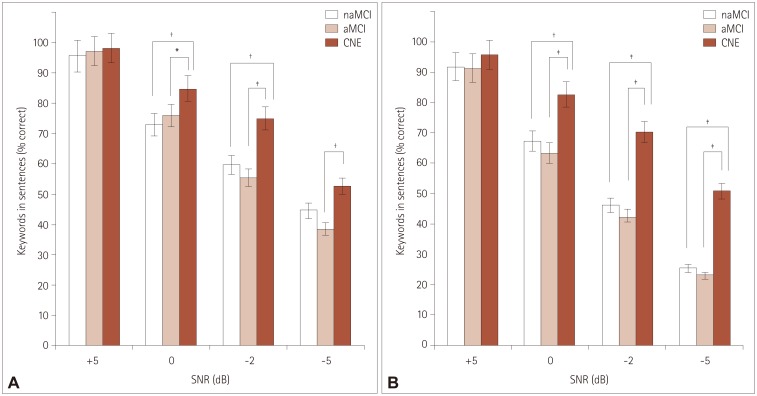
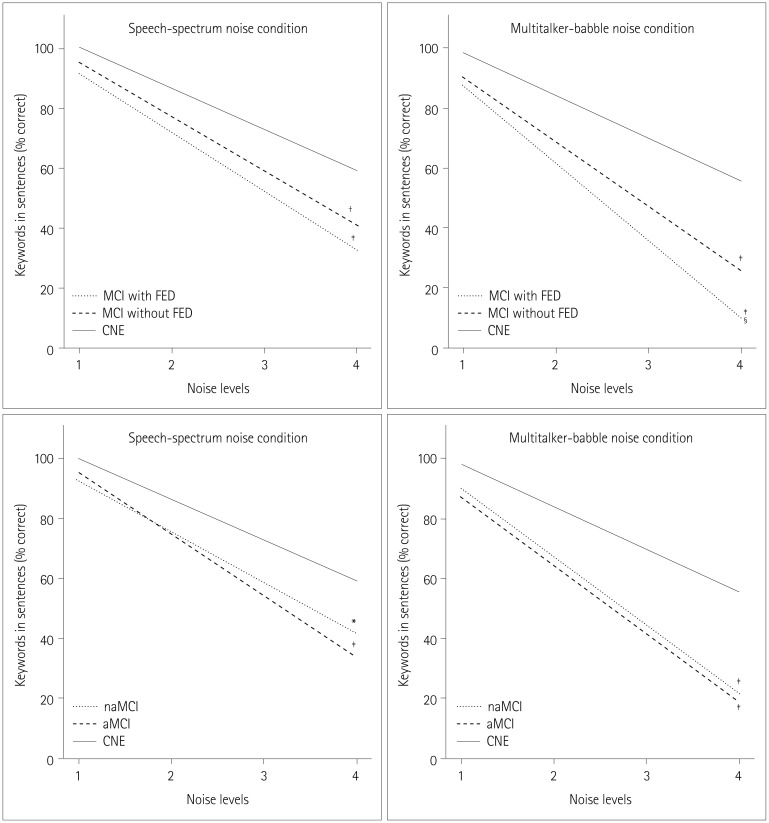
First, as the level of background noise increased, the MCI with FED group scored lower than both the MCI without FED and CNE groups under both types of noise. Second, both the naMCI and aMCI groups scored lower than the CNE group, but there were no differences between the naMCI and aMCI groups in sentence recognition under any noise conditions. Third, significant correlations were found between sentence recognition and executive function scores both in the MCI groups and in the CNE group.
CONCLUSIONS
Our findings suggest that frontal-executive function is strongly related to speech-in-noise perception and that MCI patients with FED have greater deficits in speech-in-noise perception compared to other subgroups of MCI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Panza F, Solfrizzi V, Logroscino G. Age-related hearing impairment-a risk factor and frailty marker for dementia and AD. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015; 11:166–175. PMID: 25686757.
Article2. Albers MW, Gilmore GC, Kaye J, Murphy C, Wingfield A, Bennett DA, et al. At the interface of sensory and motor dysfunctions and Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2015; 11:70–98. PMID: 25022540.
Article3. Gates GA, Gibbons LE, McCurry SM, Crane PK, Feeney MP, Larson EB. Executive dysfunction and presbycusis in older persons with and without memory loss and dementia. Cogn Behav Neurol. 2010; 23:218–223. PMID: 21150347.
Article4. Gates GA, Beiser A, Rees TS, D'Agostino RB, Wolf PA. Central auditory dysfunction may precede the onset of clinical dementia in people with probable Alzheimer's disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002; 50:482–488. PMID: 11943044.
Article5. Gates GA, Anderson ML, McCurry SM, Feeney MP, Larson EB. Central auditory dysfunction as a harbinger of Alzheimer dementia. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 137:390–395. PMID: 21502479.
Article6. Gates GA, Cobb JL, Linn RT, Rees T, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB. Central auditory dysfunction, cognitive dysfunction, and dementia in older people. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996; 122:161–167. PMID: 8630210.
Article7. Mattys SL, Davis MH, Bradlow AR, Scott SK. Speech recognition in adverse conditions: a review. Lang Cogn Process. 2012; 27:953–978.
Article8. Aimoni C, Prosser S, Ciorba A, Menozzi L, Soavi C, Zuliani G. Speech audiometry tests in noise are impaired in older patients with mild cognitive impairment: a pilot study. Int Adv Otol. 2014; 10:228–233.
Article9. Lee SJ, Park KW, Kim LS, Kim H. Effects of noise level and cognitive function on speech perception in normal elderly and elderly with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Cogn Behav Neurol. 2016; 29:68–77. PMID: 27336804.
Article10. Petersen RC. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med. 2004; 256:183–194. PMID: 15324362.
Article11. Kang YW, Jin JH, Na DL, Lee JH, Park JS. A normative study of the Korean version of Controlled Oral Word Association Test (COWAT) in the elderly. Korean J Clin Psychol. 2000; 19:385–392.12. Lee JH, Kang YW, Na DL. Efficiencies of stroop interference indexes in healthy older adults and dementia patients. Korean J Clin Psychol. 2000; 19:807–818.13. Kang YW. A normative study of the Korean-Mini Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in the elderly. Korean J Psychol Gen. 2006; 25:1–12.14. Kang YW, Chin JH, Na DL. A normative study of the digit span test for the elderly. Korean J Clin Psychol. 2002; 21:911–922.15. Kang YW, Na DL. Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery (SNSB). Seoul: Human Brain Research & Consulting Co.;2003.16. Kim H, Na DL. Normative data on the Korean version of the Boston Naming Test. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1999; 21:127–133. PMID: 10421007.17. Kang YW, Jang SM, Na DL. Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery (SNSB). 2nd ed. Seoul: Human Brain Research & Consulting Co.;2012.18. Lee JH, Jo SJ, Kim JS, Jang HS, Lim DH, Lee KW. Korean Speech Audiometry (KSA). Seoul: Hakjisa;2010.19. Koelewijn T, Zekveld AA, Festen JM, Rönnberg J, Kramer SE. Processing load induced by informational masking is related to linguistic abilities. Int J Otolaryngol. 2012; 2012:865731. PMID: 23091495.
Article20. Gordon-Salant S, Cole SS. Effects of age and working memory capacity on speech recognition performance in noise among listeners with normal hearing. Ear Hear. 2016; 37:593–602. PMID: 27232071.
Article21. Rönnberg J, Rudner M, Foo C, Lunner T. Cognition counts: a working memory system for ease of language understanding (ELU). Int J Audiol. 2008; 47(Suppl 2):S99–S105. PMID: 19012117.
Article22. Rönnberg J, Lunner T, Zekveld A, Sörqvist P, Danielsson H, Lyxell B, et al. The ease of language understanding (ELU) model: theoretical, empirical, and clinical advances. Front Syst Neurosci. 2013; 7:31. PMID: 23874273.
Article23. Rönnberg J, Rudner M, Lunner T, Zekveld AA. When cognition kicks in: working memory and speech understanding in noise. Noise Health. 2010; 12:263–269. PMID: 20871181.
Article24. Shao Z, Janse E, Visser K, Meyer AS. What do verbal fluency tasks measure? Predictors of verbal fluency performance in older adults. Front Psychol. 2014; 5:772. PMID: 25101034.
Article25. Wild CJ, Yusuf A, Wilson DE, Peelle JE, Davis MH, Johnsrude IS. Effortful listening: the processing of degraded speech depends critically on attention. J Neurosci. 2012; 32:14010–14021. PMID: 23035108.
Article26. D'Ausilio A, Craighero L, Fadiga L. The contribution of the frontal lobe to the perception of speech. J Neurolinguistics. 2012; 25:328–335.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Facial Emotion Recognition in Older Adults With Cognitive Complaints
- Cognitive Assessment in Traumatic Brain Injury
- Relation between Phonological Processing, Auditory Processing and Speech Perception among Bilingual Poor Readers
- Central Auditory Processing Tests as Diagnostic Tools for the Early Identification of Elderly Individuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Training Programs for Improving Speech Perception in Noise: A Review