Perspect Nurs Sci.
2018 Oct;15(2):70-80. 10.16952/pns.2018.15.2.70.
An Integrative Review of Interventions for Internet/Smartphone Addiction among Adolescents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate Student, College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. scarlett798@naver.com
- KMID: 2424091
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16952/pns.2018.15.2.70
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to investigate the characteristics of intervention programs for internet/smartphone addiction among adolescents through an integrative literature review.
METHODS
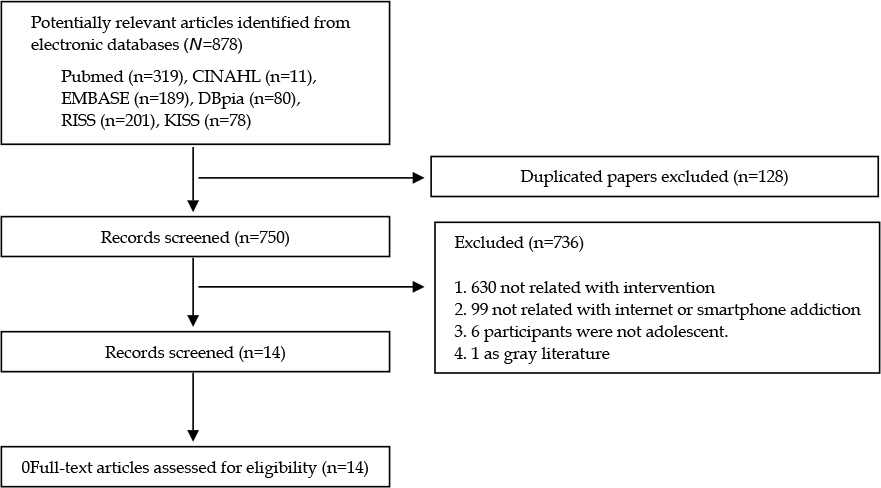
We searched MEDLINE(PubMed), CINAHL, Embase, DBpia, RISS, and KISS using a combination of "Internet or phone*,""addicti*,""adolescent," and "intervention or program or therapy." The searched studies were reviewed according to the criteria and an integrative literature review was conducted on the 14 selected papers published from January 1, 2013 to November 14, 2017.
RESULTS
Through the integrative review and analysis, a total of four attributes of interventions and their effects were derived. First, the number of group-focused interventions was significantly higher than that of individual-focused ones. Second, the interventions addressed various aspects of adolescents' problems while considering the complex nature of addiction problems. Third, there was a bias for region and sexual ratio. Lastly, most studies were actively conducted in community-based counseling or psychology settings.
CONCLUSION
It is necessary to find more effective methods for addressing internet/smartphone addiction among adolescents through multidisciplinary approaches, including the consideration of various cultural and gender characteristics. This study provides a basis for developing future programs addressing addiction problems among adolescents.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Information Society Agency (KR). [The direction of legal arrangement for the prevention and relief of internet addiction]. Seoul: National Information Society Agency;2010. 06. p. 94. Korean. Available from: http://www.ndsl.kr/ndsl/commons/util/ndslOriginalView.do.2. Jung ES, Shim MS. Family function and internet addiction in lower grade elementary school students. J Korean Public Health Nurs. 2012; 08. 26(2):328–340. DOI: 10.5932/jkphn.2012.26.2.328.
Article3. National Information Society Agency. The survey on internet overdependence 2016. Final report. Gwacheon (KR): Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, National Information Society Agency;2016. 12. p. 287. Report No.: NIA V-RER-C-16026. Available from: http://www.nia.or.kr/common/board/Download.do?bcIdx=18390&cbIdx=65914&fileNo=2.4. Lee YS, Lee DH, Kim EY, Kang SY, Kim LS, Choi YH, et al. Development of the manual for smartphone addiction prevention program for adolescent. Seoul: Korea Youth Counseling & Welfare Institute;2013. 12. p. 202. Available from: https://www.kyci.or.kr/fileup/lib_pdf/2013-106%EC%8A%A4%EB%A7%88%ED%8A%B8%ED%8F%B0%EC%A4%91%EB%8F%85%EC%98%88%EB%B0%A9.pdf.5. Jo H. The effect of elementary school students' perceived parenting attitude and internet use motives on internet addiction: self-control as a mediator. J Adolesc Welf. 2011; 12. 13(4):269–287.6. Demetrovics Z, Szeredi B, Rozsa S. The three-factor model of internet addiction: the development of the problematic internet use questionnaire. Behav Res Methods. 2008; 05. 40(2):563–574. DOI: 10.3758/brm.40.2.563.
Article7. Park MH, Park EJ, Choi J, Chai S, Lee JH, Lee C, et al. Preliminary study of internet addiction and cognitive function in adolescents based on IQ tests. Psychiatry Res. 2011; 12. 30. 190(2-3):275–281. DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2011.08.006.
Article8. Kang H, Park C. Development and validation of the smartphone addiction inventory. Korean J Psychol Gen. 2012; 06. 31(2):563–580.9. Kim HY, Cho MK. Meta-analysis of internet addiction treatment programs for adolescents. Ment Health Soc Work. 2015; 06. 43(2):89–118.10. Nam YO. Comparison of internet addiction, internet game addiction and cybersex addiction among middle school students. Korean J Youth Stud. 2005; 09. 12(3):363–388.11. Ah YA, Jeong WC, Kim TJ. A study on the mediating effect of internet using time on the relationship between internet media traits and adolescents' internet addiction. J Sch Soc Work. 2010; 18:29–52.12. Jang JH, Sin HJ. The effect of a protection program for adolescent excessive use of internet. Korean J Couns Psychother. 2003; 11. 15(4):651–672.13. Mittal VA, Dean DJ, Pelletier A. Internet addiction, reality substitution and longitudinal changes in psychotic-like experiences in young adults. Early Interv Psychiatry. 2013; 08. 7(3):261–269. DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7893.2012.00390.x.
Article14. Kim JS. [The relationship between adolescent addictional internet use and adulthood heavy drinking · smoking]. Weekly DongA(Vol. 1108) [Internet]. 2017. 10. 04. cited 2017 Nov 14. 106–108. Korean. Available from: http://weekly.donga.com/Library/3/all/11/1078044/1.15. Park H. The relationship between internet use for non-academic purposes and happiness and stress in adolescents. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2015; 06. 26(2):169–177. DOI: 10.12799/jkachn.2015.26.2.169.
Article16. Korea Internet Security Agency [Internet]. 2015 Mobile internet usage statistics. Seoul: Korea Internet Security Agency;c2015. cited 2018 Aug 08. Available from: https://isis.kisa.or.kr/statistics/?pageId=020300.17. Saunders JB. Substance use and addictive disorders in DSM-5 and ICD 10 and the draft ICD 11. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2017; 07. 30(4):227–237. DOI: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000332.
Article18. Kwon EJ, Jang SO. A meta-analysis on the effects of internet addiction treatment program for adolescents on reducing addiction. Korean J Soc Welf Res. 2016; 03. 48:105–129.
Article19. Kwon EJ, Jang SO. A meta-analysis on the effects of promoting self-control group program for internet addiction youth. J Soc Sci. 2016; 06. 55(1):87–122. DOI: 10.22418/JSS.2016.06.55.1.87.
Article20. Lee JK, Kang GM. A Meta-analysis on the effect of youth internet addiction group counseling program. Korea J Couns. 2015; 16(3):101–120. DOI: 10.15703/kjc.16.3.201506.101.
Article21. Ha JY, Shin SM. A Meta-analysis on the effects of Internet addiction counseling program among youth group. In : [2015 Korean Psychological Assication Annual Conference]; 2015 Aug 20-22; Seoul, Korean. Seoul: Korean Psychological Association;2005. p. 441. Korean.22. Ha JY, Shin SM. The effectiveness of youth internet addiction group counseling programs: a meta-analysis. Korean J Psychol Gen. 016; 03. 35(1):191–216. DOI: 10.22257/kjp.2016.03.35.1.191.
Article23. Whittemore R, Knafl K. The integrative review: updated methodology. J Adv Nurs. 2005; 12. 52(5):546–553. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2005.03621.x.
Article24. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edition: DSM-5. Arlington (VA): American Psychiatric Publishing;c2013. p. 947.25. Garrard J. Health sciences literature review made easy: the matrix method. 5th ed. Burlintong (MA): Jones & Bartlett Publishers;2016. p. 240.26. Yoon JS. Narrative therapy approach to adolescents internet game addiction: focused on externalization method. Yonsei J Couns Coach. 2017; 09. 8:51–70.27. Chang HR. A qualitative study of intervention for adolescents with severe internet addiction. Korean J Local Gov Adm Stud. 2016; 03. 30(1):231–251. DOI: 10.18398/kjlgas.2016.30.1.231.
Article28. Shin AR, Shin JH, Lim JH. A case study of art therapy for the improvement of interpersonal relation and internet addiction of youth with internet addiction: focused on the object relations theory of Winnicott. Korean Art Ther Assoc. 2015; 22(4):1161–1188.
Article29. Kim KH, Jang JH. Effects of internet game overuse group counseling for adolescent on internet game addiction, stress perception and stress coping strategy. Korean J Couns Psychother. 2010; 02. 22(1):213–232.30. Oh I, Kim C. Meta-analysis on the effects of the prevention and intervention programs for internet addiction. J Korean Assoc Inf Educ. 2009; 13(4):529–537.31. Muller KW, Janikian M, Dreier M, Wolfling K, Beutel ME, Tzavara C, et al. Regular gaming behavior and internet gaming disorder in European adolescents: results from a cross-national representative survey of prevalence, predictors, and psychopathological correlates. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2015; 05. 24(5):565–574. DOI: 10.1007/s00787-014-0611-2.
Article32. Feng W, Ramo DE, Chan SR, Bourgeois JA. Internet gaming disorder: trends in prevalence 1998–2016. Addict behav. 2017; 12. 75:17–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2017.06.010.
Article33. Shin , SM , Ra YA, Park MJ, Song Y, Yun J. [Evaluation and performance indicator development counseling program for youth internet smartphone overdependence counseling program]. Seoul: Ministry of Gender Equality and Family (KR);2017. 03. p. 134. Korean. Available from: http://www.ndsl.kr/ndsl/commons/util/ndslOriginalView.do?dbt=TRKO&cn=TRKO201700004480&rn=&url=&pageCode=PG18.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differences of Psychosocial Vulnerability Factors between Internet and Smartphone Addiction Groups Consisting of Children and Adolescents in a Small to Medium-Sized City
- Internet Addiction, Social Support and Psychological Factors in Adolescents
- A Preliminary Study on the Effectiveness of the Peer Relationship Enhancement Program in Adolescents at Risk for Internet and Smartphone Addiction
- Biological Model and Pharmacotherapy in Internet Addiction
- Smartphone Addiction