J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2018 Mar;20(1):35-39. 10.7461/jcen.2018.20.1.35.
Petrous Carotid Aneurysm Causing Pulsatile Tinnitus: Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. nslcy@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2422558
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2018.20.1.35
Abstract
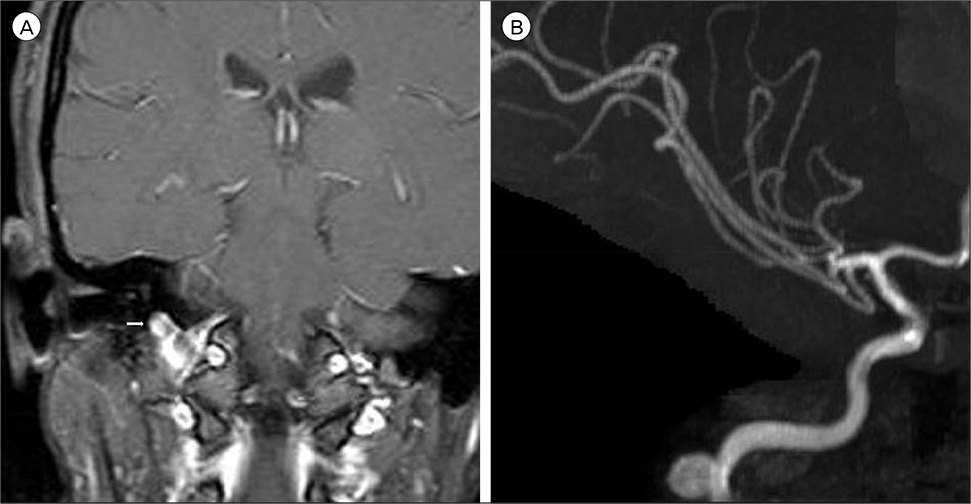
- We present the case of a patient who developed pulsatile tinnitus that was found to be associated with a petrous carotid aneurysm. The aneurysm was successfully obliterated using stent-assisted coiling, after which the patient was symptom-free. Although aneurysms arising from the petrous segment of the internal carotid artery are rare, this pathology must be considered as a causative factor in patients with pulsatile tinnitus. Endovascular treatment appears to have been successful in resolving the symptoms associated with this pathology.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Couldwell WT, Zuback J, Onios E, Ahluwalia BS, Tenner M, Moscatello A. Giant petrous carotid aneurysm treated by submandibular carotid-saphenous vein bypass. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2001; 05. 94(5):806–810.2. Debrun G, Lacour P, Caron JP, Hurth M, Comoy J, Keravel Y. Detachable balloon and calibrated-leak balloon techniques in the treatment of cerebral vascular lesions. J Neurosurg. 1978; 11. 49(5):635–649.
Article3. Ferroli P, Bisleri G, Miserocchi A, Albanese E, Polvani G, Broggi G. Endoscopic radial artery harvesting for U-clip high-flow EC-IC bypass: technical report. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009; 05. 151(5):529–535. discussion 535.4. Gross BA, Moon K, Ducruet AF, Albuquerque FC. A rare but morbid neurosurgical target: petrous aneurysms and their endovascular management in the stent/flow diverter era. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017; 04. 9(4):381–383.
Article5. Hofmann E, Behr R, Neumann-Haefelin T, Schwager K. Pulsatile tinnitus: imaging and differential diagnosis. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013; 06. 110(26):451–458.6. Holtzman RN, Parisier SC. Acute spontaneous otorrhagia resulting from a ruptured petrous carotid aneurysm. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1979; 08. 51(2):258–261.7. Houdart E, Chapot R, Merland JJ. Aneurysm of a dural sigmoid sinus: a novel vascular cause of pulsatile tinnitus. Ann Neurol. 2000; 10. 48(4):669–671.
Article8. Kawakami K, Kayama T, Kondo R, Kureyama H, Maruya J, Nakai O, et al. A case of mycotic ICA petrous portion aneurysm treated with endovascular surgery. No Shinkei Geka. 1996; 03. 24(3):253–257.9. Kim DK, Shin YS, Lee JH, Park SN. Pulsatile tinnitus as the sole manifestation of an internal carotid artery aneurysm successfully treated by coil embolization. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 09. 5(3):170–172.
Article10. Langguth B, Hund V, Busch V, Jurgens TP, Lainez JM, Landgrebe M, et al. Tinnitus and headache. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:797416.
Article11. Lee SH, Jang JH, Kim KH, Kim YZ. Stent-assisted coil embolization of petrous ICA in a teenager with neurofibromatosis. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2015; 09. 17(3):252–256.
Article12. Lempert TE, Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Dowd CF, Urwin RW, Balousek PA, et al. Endovascular treatment of pseudoaneurysms with electrolytically detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 05. 19(5):907–911.13. Liu JK, Gottfried ON, Amini A, Couldwell WT. Aneurysms of the petrous internal carotid artery: anatomy, origins, and treatment. Neurosurg Focus. 2004; 11. 17(5):E13.
Article14. Love MH, Bell KE. Case report: giant aneurysm of the intrapetrous carotid artery presenting as a cerebellopontine angle mass. Clin Radiol. 1996; 08. 51(8):587–588.
Article15. Marsot-Dupuch K. Pulsatile and nonpulsatile tinnitus: a systemic approach. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2001; 06. 22(3):250–270.
Article16. Mascitelli JR, De Leacy RA, Oermann EK, Skovrlj B, Smouha EE, Ellozy SH, et al. Cervical-petrous internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with otorrhagia treated with endovascular techniques. BMJ Case Rep. 2014; 06. 30. 2014:pii: bcr2014011286.
Article17. McGrail KM, Heros RC, Debrun G, Beyerl BD. Aneurysm of the ICA petrous segment treated by balloon entrapment after EC-IC bypass. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1986; 08. 65(2):249–252.18. Miller TR, Serulle Y, Gandhi D. Arterial abnormalities leading to tinnitus. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2016; 05. 26(2):227–236.
Article19. Moonis G, Hwang CJ, Ahmed T, Weigele JB, Hurst RW. Otologic manifestations of petrous carotid aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; Jun-Jul. 26(6):1324–1327.20. Park YH, Kwon HJ. Awake embolization of sigmoid sinus diverticulum causing pulsatile tinnitus: simultaneous confirmative diagnosis and treatment. Interv Neuroradiol. 2011; 09. 17(3):376–379.
Article21. Reardon MA, Raghavan P. Venous abnormalities leading to tinnitus: imaging evaluation. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2016; 05. 26(2):237–245.22. Signorelli F, Mahla K, Turjman F. Endovascular treatment of two concomitant causes of pulsatile tinnitus: sigmoid sinus stenosis and ipsilateral jugular bulb diverticulum. Case report and literature review. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012; 01. 154(1):89–92.
Article23. Sismanis A. Pulsatile tinnitus. A 15-year experience. Am J Otol. 1998; 07. 19(4):472–477.24. Sonmez G, Basekim CC, Ozturk E, Gungor A, Kizilkaya E. Imaging of pulsatile tinnitus: a review of 74 patients. Clin Imaging. 2007; Mar-Apr. 31(2):102–108.
Article25. Waldvogel D, Mattle HP, Sturzenegger M, Schroth G. Pulsatile tinnitus--a review of 84 patients. J Neurol. 1998; 03. 245(3):137–142.26. Willinsky R, Lasjaunias P, Pruvost P, Boucherat M. Petrous internal carotid aneurysm causing epistaxis: balloon embolization with preservation of the parent vessel. Neuroradiology. 1987; 29(6):570–572.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulsatile Tinnitus as the Sole Manifestation of an Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysm Successfully Treated by Coil Embolization
- A Case of Pulsatile Tinnitus from the Atherosclerosis and Atheroma in Superior Labial Artery and Facial Artery
- Stent-assisted Coil Embolization of Petrous ICA in a Teenager with Neurofibromatosis
- A Case of Jugular Bulb Diverticulum Accompanied with Pulsatile Tinnitus
- A Case of Pulsatile Tinnitus by Sigmoid Sinus Diverticulum