Perinatology.
2018 Sep;29(3):121-127. 10.14734/PN.2018.29.3.121.
Newborn Hearing Screening Test: A Comparison between Infants in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit versus Nursery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yschang@skku.ed
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2421577
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/PN.2018.29.3.121
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study is to compare the clinical characteristics of newborn hearing test results between infants in well-baby nursery (WBN) versus neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) and to determine the optimal strategies of hearing screening for each group.
METHODS
A total of 2,161 newborns admitted to WBN and NICU were enrolled in this retrospective cohort study. Automated audio brainstem response was used for hearing screening test. The screening rates, referral rates, prevalence rates, false positive rates and predictive positive value (PPV) were analyzed for infants in WBN and NICU.
RESULTS
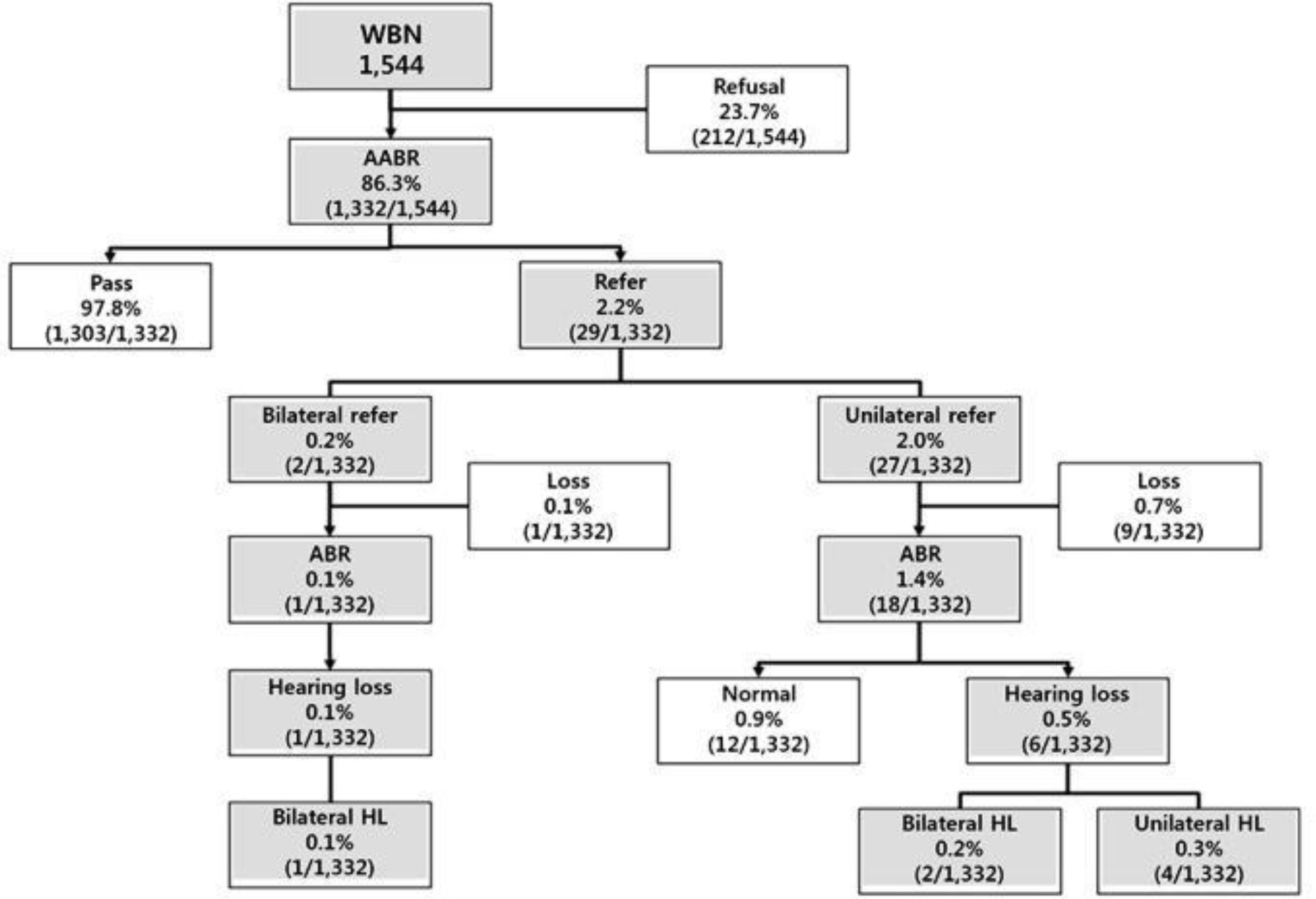
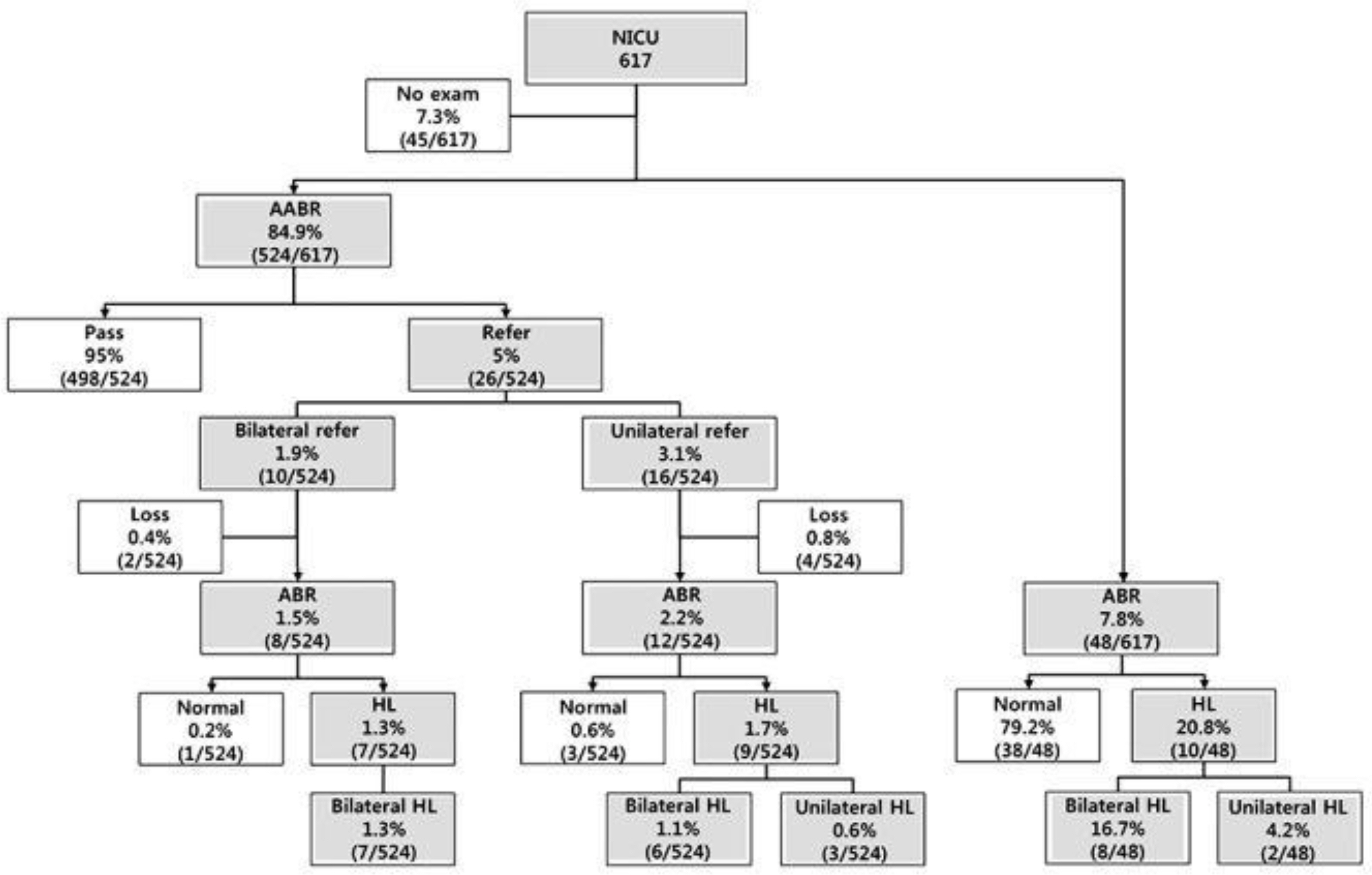
The referral rates of the screening test were 2.2% and 5.0% in WBN and NICU groups (P < 0.01); the prevalence rate of congenital hearing loss (HL) were 0.5% and 4.6% in the WBN and NICU groups (P < 0.01). The false positive rates and PPV of screening test were 0.9% and 36.8% in WBN; 0.8% and 80% in NICU. Infants with bilateral refer results in both WBN and NICU were at the higher risk of congenital HL, compared with infants with unilateral refer results in WBN who were mostly confirmed to have false positive.
CONCLUSION
The infants in WBN showed high unilateral referral rate with low prevalence rate of HL. However, the infants with bilateral refer results in WBN and uni- or bi-lateral refer results in NICU had higher prevalence rate of HL, compared with those with unilateral refer results in WBN. Different strategies for hearing screening might be considered in infants in WBN and NICU.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Wroblewska-Seniuk KE., Dabrowski P., Szyfter W., Mazela J. Universal newborn hearing screening: methods and results, obstacles, and benefits. Pediatr Res. 2017. 81:415–22.
Article2). Clemens CJ., Davis SA., Bailey AR. The false-positive in universal newborn hearing screening. Pediatrics. 2000. 106:E7.
Article3). Hessel F., Grill E., Schnell-Inderst P., Siebert U., Kunze S., Nickisch A, et al. Economic evaluation of newborn hearing screening: modelling costs and outcomes. Ger Med Sci. 2003. 1:Doc09.4). Lemons J., Fanaroff A., Stewart EJ., Bentkover JD., Murray G., Diefendorf A. Newborn hearing screening: costs of establishing a program. J Perinatol. 2002. 22:120–4.
Article5). Joint Committee on Infant Hearing, American Academy of Audiology, American Academy of Pediatrics, American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, Directors of Speech and Hearing Programs in State Health and Welfare Agencies. Year 2000 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Joint Committee on Infant Hearing, American Academy of Audiology, American Academy of Pediatrics, American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, and Directors of Speech and Hearing Programs in State Health and Welfare Agencies. Pediatrics. 2000. 106:798–817.6). Li PC., Chen WI., Huang CM., Liu CJ., Chang HW., Lin HC. Comparison of newborn hearing screening in well-baby nursery and NICU: a study applied to reduce referral rate in NICU. PLoS One. 2016. 11:e0152028.
Article7). Lim HW., Han MW., Lee HS., Kim KS., Chung JW., Kim YJ, et al. The validity using two-stage automated auditory brainstem response as a universal newborn hearing screening protocol: experiences in Asan medical center. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2007. 50:108–14.8). Colella-Santos MF., Hein TA., de Souza GL., do Amaral MI., Casali RL. Newborn hearing screening and early diagnostic in the NICU. Biomed Res Int. 2014. 2014:845308.
Article9). van Dommelen P., van Straaten HL., Verkerk PH. Dutch NICU Neonatal Hearing Screening Working Group. Ten-year quality assurance of the nationwide hearing screening programme in Dutch neonatal intensive care units. Acta Paediatr. 2011. 100:1097–103.
Article10). Wood SA., Sutton GJ., Davis AC. Performance and characteristics of the newborn hearing screening programme in England: the first seven years. Int J Audiol. 2015. 54:353–8.
Article11). Korean Audiological Society, Korean Otologic Society. Korean Clinical Practice Guildline: Newborn Hearing Screening 2010. Seoul: ML Communications;2011. p. 1–80.12). American Academy of Pediatrics, Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2007 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics. 2007. 120:898–921.13). Stein LK., Jabaley T., Spitz R., Stoakley D., McGee T. The hearing-impaired infant: patterns of identification and habilitation revisited. Ear Hear. 1990. 11:201–5.14). Coplan J. Deafness: ever heard of it? Delayed recognition of permanent hearing loss. Pediatrics. 1987. 79:206–13.
Article15). Pimperton H., Kennedy CR. The impact of early identification of permanent childhood hearing impairment on speech and language outcomes. Arch Dis Child. 2012. 97:648–53.
Article16). Erenberg A., Lemons J., Sia C., Trunkel D., Ziring P. Newborn and infant hearing loss: detection and intervention. American academy of pedia-trics. Task force on newborn and infant hearing, 1998-1999. Pediatrics. 1999. 103:527–30.17). American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Fetus Newborn. Levels of neonatal care. Pediatrics. 2012. 130:587–97.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Newborn Hearing Screening: 3 Years of Experience
- Changes in the Hearing Thresholds of Infants Who Failed the Newborn Hearing Screening Test and in Infants Treated in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Neonatal Hearing Screening in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Graduate
- Evaluation of Transient Evoked Otoacoustic Emission in the Newborn Hearing Screening Program in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Incidence of hearing loss and importance of risk factors in the neonatal intensive care unit