Infect Chemother.
2018 Sep;50(3):238-251. 10.3947/ic.2018.50.3.238.
Analysis of Klebsiella as a Prognostic Factor of Ocular Outcomes in Endogenous Endophthalmitis with Decision Tree Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea. ksw2kms@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2420908
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2018.50.3.238
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Endogenous endophthalmitis (EE) is a fulminant ocular disease. This study was conducted to explore frequent pathogens and significant prognostic factors associated with poor ocular outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective analysis was performed in a tertiary hospital in Korea. Thirty-nine patients, treated between January 2000 and June 2017, were eligible for the analysis. Ocular outcomes were classified as follows: 1) no light perception (NLP), 2) light perception (LP), 3) hand motion (HM), 4) counting fingers (CF), and 5) 20/200 or better. Logistic regression and decision tree analyses were used to identify risk factors that were associated with poor outcomes.
RESULTS
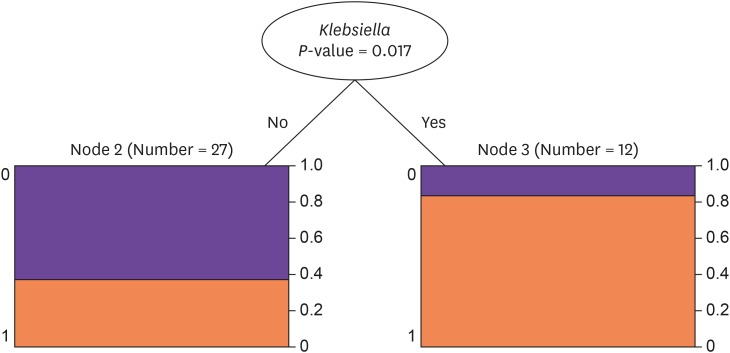
Pathogens were identified in 23 (58.9%) samples from blood, liver aspirate, and/or vitreous humor. Klebsiella pneumoniae was the most frequent organism (12/39, 30.8%), followed by Candida species (3/39, 8.3%). The most common combined infection was liver abscess (16/39, 41.0%). Acute pyelonephritis occurred in 30.8% of cases (12/39). Final ocular outcomes were as follows: 35.9% (14/39) NLP, 15.4% (6/39) LP, 15.4% (6/39) HM, 7.7% (3/39) CF, and 25.6% (10/39) 20/200 or better. K. pneumoniae was a poor prognostic factor in univariate (odds ratio [OR], 13.3; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.1-130.9) and multivariate (OR, 17.5; 95% CI, 2.1-398.8) regression analyses (NLP and LP vs. HM, CF, and 20/200 or better). Other factors did not reach statistical difference. Decision tree analysis identified K. pneumoniae as a node that divided ocular outcomes (P = 0.017).
CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, K. pneumoniae is the most frequent causative pathogen of EE. Considering the poor prognosis and rapid progression of K. pneumoniae EE, physicians should test for K. pneumoniae EE in patients who experience acute systemic infections with ocular signs and symptoms.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chee SP, Jap A. Endogenous endophthalmitis. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2001; 12:464–470. PMID: 11734687.
Article2. Jackson TL, Eykyn SJ, Graham EM, Stanford MR. Endogenous bacterial endophthalmitis: a 17-year prospective series and review of 267 reported cases. Surv Ophthalmol. 2003; 48:403–423. PMID: 12850229.
Article3. Ang M, Jap A, Chee SP. Prognostic factors and outcomes in endogenous Klebsiella pneumoniae endophthalmitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 151:338–344.e2. PMID: 21168820.
Article4. Connell PP, O'Neill EC, Fabinyi D, Islam FM, Buttery R, McCombe M, Essex RW, Roufail E, Clark B, Chiu D, Campbell W, Allen P. Endogenous endophthalmitis: 10-year experience at a tertiary referral centre. Eye (Lond). 2011; 25:66–72. PMID: 20966972.
Article5. Jackson TL, Paraskevopoulos T, Georgalas I. Systematic review of 342 cases of endogenous bacterial endophthalmitis. Surv Ophthalmol. 2014; 59:627–635. PMID: 25113611.
Article6. Lee S, Um T, Joe SG, Hwang JU, Kim JG, Yoon YH, Lee JY. Changes in the clinical features and prognostic factors of endogenous endophthalmitis: fifteen years of clinical experience in Korea. Retina. 2012; 32:977–984. PMID: 22105504.7. Durand ML, Heier JS. Endophthalmitis. Curr Clin Top Infect Dis. 2000; 20:271–297. PMID: 10943529.8. Yoon YH, Lee SU, Sohn JH, Lee SE. Result of early vitrectomy for endogenous Klebsiella pneumoniae endophthalmitis. Retina. 2003; 23:366–370. PMID: 12824838.9. Ishii K, Hiraoka T, Kaji Y, Sakata N, Motoyama Y, Oshika T. Successful treatment of endogenous Klebsiella pneumoniae endophthalmitis: a case report. Int Ophthalmol. 2011; 31:29–31. PMID: 20661624.10. Sallam A, Taylor SR, Khan A, McCluskey P, Lynn WA, Manku K, Pacheco PA, Lightman S. Factors determining visual outcome in endogenous Candida endophthalmitis. Retina. 2012; 32:1129–1134. PMID: 22298012.11. Lim HW, Shin JW, Cho HY, Kim HK, Kang SW, Song SJ, Yu HG, Oh JR, Kim JS, Moon SW. Endogenous endophthalmitis in the Korean population: a six-year retrospective study. Retina. 2014; 34:592–602. PMID: 24056527.12. Hwang JH, Cho NC. Prognostic factors in patients with endogenous endophthalmitis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:858–863.
Article13. Cho H, Shin YU, Siegel NH, Yu HG, Sobrin L, Patel A, Durand ML, Miller JW, Husain D. Endogenous endophthalmitis in the American and Korean population: an 8-year retrospective study. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2018; 26:496–503. PMID: 27459423.
Article14. Wong JS, Chan TK, Lee HM, Chee SP. Endogenous bacterial endophthalmitis: an east Asian experience and a reappraisal of a severe ocular affliction. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:1483–1491. PMID: 10919895.
Article15. Takebayashi H, Mizota A, Tanaka M. Relation between stage of endogenous fungal endophthalmitis and prognosis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006; 244:816–820. PMID: 16331481.
Article16. Wilhelmus KR, Specter S, Wilhelmus KR. Laboratory diagnosis of ocular infections: American Society for Microbiology. 1994.17. Greenwald MJ, Wohl LG, Sell CH. Metastatic bacterial endophthalmitis: a contemporary reappraisal. Surv Ophthalmol. 1986; 31:81–101. PMID: 3541265.
Article18. Chang FY, Chou MY, Fan RL, Shaio MF. A clinical study of Klebsiella liver abscess. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1988; 87:282–287. PMID: 3397725.19. Chee SP, Ang CL. Endogenous Klebsiella endophthalmitis--a case series. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 1995; 24:473–478. PMID: 7574438.20. Chiu CT, Lin DY, Liaw YF. Metastatic septic endophthalmitis in pyogenic liver abscess. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1988; 10:524–527. PMID: 3053874.
Article21. Lee CC, Chen CY, Chen FH, Zimmerman RA, Hsiao HS. Septic metastatic endophthalmitis from Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: CT and MR imaging characteristics--report of three cases. Radiology. 1998; 207:411–416. PMID: 9577489.22. Liu YC, Cheng DL, Lin CL. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess associated with septic endophthalmitis. Arch Intern Med. 1986; 146:1913–1916. PMID: 3532983.23. Wang FD, Wang LS, Liu YC, Liu CY, Lin CL, Wong WW. Successful treatment of metastatic endophthalmitis. Case reports. Ophthalmologica. 1989; 198:124–128. PMID: 2657535.24. Sridhar J, Flynn HW Jr, Kuriyan AE, Dubovy S, Miller D. Endophthalmitis caused by Klebsiella species. Retina. 2014; 34:1875–1881. PMID: 24801652.25. Schiedler V, Scott IU, Flynn HW Jr, Davis JL, Benz MS, Miller D. Culture-proven endogenous endophthalmitis: clinical features and visual acuity outcomes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:725–731. PMID: 15059712.
Article26. Essman TF, Flynn HW Jr, Smiddy WE, Brod RD, Murray TG, Davis JL, Rubsamen PE. Treatment outcomes in a 10-year study of endogenous fungal endophthalmitis. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1997; 28:185–194. PMID: 9076791.
Article27. Ness T, Pelz K, Hansen LL. Endogenous endophthalmitis: microorganisms, disposition and prognosis. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2007; 85:852–856. PMID: 17725616.
Article28. Binder MI, Chua J, Kaiser PK, Procop GW, Isada CM. Endogenous endophthalmitis: an 18-year review of culture-positive cases at a tertiary care center. Medicine (Baltimore). 2003; 82:97–105. PMID: 12640186.29. Fang CT, Lai SY, Yi WC, Hsueh PR, Liu KL, Chang SC. Klebsiella pneumoniae genotype K1: an emerging pathogen that causes septic ocular or central nervous system complications from pyogenic liver abscess. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 45:284–293. PMID: 17599305.30. Liao HR, Lee HW, Leu HS, Lin BJ, Juang CJ. Endogenous Klebsiella pneumoniae endophthalmitis in diabetic patients. Can J Ophthalmol. 1992; 27:143–147. PMID: 1586886.31. Okada AA, Johnson RP, Liles WC, D'Amico DJ, Baker AS. Endogenous bacterial endophthalmitis. Report of a ten-year retrospective study. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:832–838. PMID: 8190467.32. Bohigian GM, Olk RJ. Factors associated with a poor visual result in endophthalmitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986; 101:332–341. PMID: 3485382.
Article33. Chen KJ, Hwang YS, Wang NK, Chao AN. Endogenous Klebsiella pneumoniae endophthalmitis with renal abscess: Report of two cases. Int J Infect Dis. 2010; 14:e429–e432. PMID: 19656711.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Endogenous Endophthalmitis
- Two Cases of Bilateral Endogenous Klebsiella pneumoniae Endophthalmitis in Primary Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscess Patients
- A Case of Endogenous Endophthalmitis Accompanying Orbital Cellulitis Caused by Klebsiella Pneumoniae from Liver Abscess
- Klebsiella pneumoniae Brain Abscess and Endophthalmitis after Acute Epiglottitis
- Two Cases of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Endogenous Endophthalmitis Treated with Sulperazone