Ann Lab Med.
2019 Jan;39(1):31-35. 10.3343/alm.2019.39.1.31.
Evaluation of the SD Bioline Strep A Ultra Test in Relation With Number of Colony Forming Units and Color Intensity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Changwon Fatima Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing Science, Kyungsung University, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. sjkim8239@hanmail.net
- 5Gyeongsang Institute of Health Sciences, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2420268
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2019.39.1.31
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The SD Bioline Strep A Ultra (SD, Yongin, Korea) is a recently developed rapid antigen detection test (RADT) for diagnosing bacterial pharyngitis caused by Group A Streptococcus, We evaluated the performance of SD Bioline Strep A Ultra, using the number of colony forming units and color intensity.
METHODS
Three throat swabs each were taken from 343 children with pharyngitis who visited pediatric clinics. We evaluated the performance of SD Bioline Strep A Ultra and compared its positive rate with the number of colony forming units, using the Fisher exact test.
RESULTS
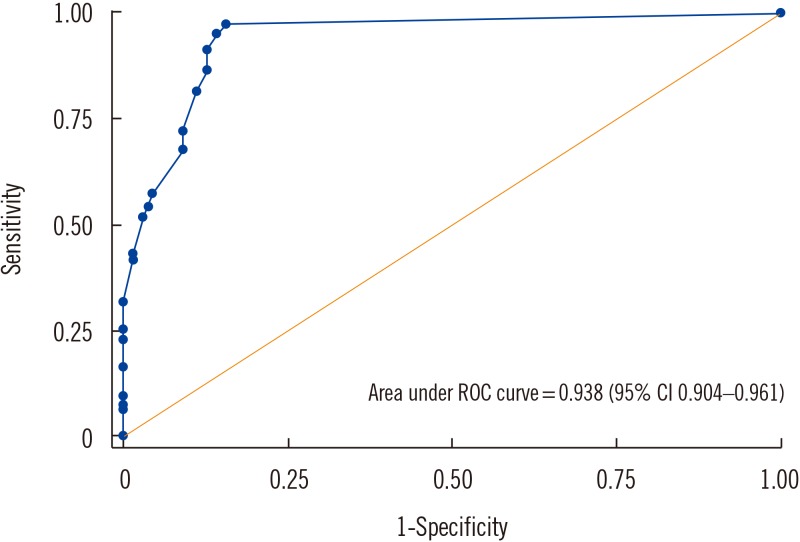
The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value (95% confidence interval) were 97.4% (94.0-99.1%), 90.8% (85.0-94.9%), 93.0% (88.5-96.1%), and 96.5% (92.0-98.9%), respectively. Positive rate significantly differed by number of colony forming units (P=0.021). ROC plot for color intensity showed 0.938 of AUC (area under curve).
CONCLUSIONS
SD Bioline Strep A Ultra showed excellent performance, and its positive rate differed by the number of colony counts. This RADT could be used as a sensitive and semi-quantitative method detecting bacterial pharyngitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison and Recommendation of Diagnostic Tools for Bacterial Pharyngitis at Primary Care Clinics
Seon A Jo, Sunjoo Kim
Lab Med Online. 2020;10(4):307-313. doi: 10.47429/lmo.2020.10.4.307.
Reference
-
1. Choby BA. Diagnosis and treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis. Am Fam Physician. 2009; 79:383–390. PMID: 19275067.2. Edmonson MB, Farwell KR. Relationship between the clinical likelihood of group A streptococcal pharyngitis and the sensitivity of a rapid antigen-detection test in a pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 2005; 115:280–285. PMID: 15687433.3. Kalra MG, Higgins KE, Perez ED. Common questions about streptococcal pharyngitis. Am Fam Phys. 2016; 94:24–31.4. Wessels MR. Clinical practice. Streptococcal pharyngitis. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:648–655. PMID: 21323542.5. Gerber MA. Diagnosis and treatment of pharyngitis in children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2005; 52:729–747. vi. PMID: 15925660.6. Shulman ST, Bisno AL, Clegg HW, Gerber MA, Kaplan EL, Lee G, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis: 2012 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 55:1279–1282. PMID: 23091044.7. Webb KH, Needham CA, Kurtz SR. Use of a high-sensitivity rapid strep test without culture confirmation of negative results: 2 years’ experience. J Fam Pract. 2000; 49:34–38. PMID: 10678338.8. Cohen JF, Bertille N, Cohen R, Chalumeau M. Rapid antigen detection test for group A streptococcus in children with pharyngitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016; 7:CD010502. PMID: 27374000.9. Lean WL, Arnup S, Danchin M, Steer AC. Rapid diagnostic tests for group A streptococcal pharyngitis: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2014; 134:771–781. PMID: 25201792.10. Hall MC, Kieke B, Gonzales R, Belongia EA. Spectrum bias of a rapid antigen detection test for group A β-hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis in a pediatric population. Pediatrics. 2004; 114:182–186. PMID: 15231926.11. Kim S. The evaluation of SD Bioline Strep A rapid antigen test in acute pharyngitis in pediatric clinics. Korean J Lab Med. 2009; 29:320–323. PMID: 19726894.12. Kurtz B, Kurtz M, Roe M, Todd J. Importance of inoculum size and sampling effect in rapid antigen detection for diagnosis of Streptococcus pyogenes pharyngitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2000; 38:279–281. PMID: 10618101.13. Gieseker KE, Mackenzie T, Roe MH, Todd JK. Comparison of two rapid Streptococcus pyogenes diagnostic tests with a rigorous culture standard. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2002; 21:922–927. PMID: 12394813.14. Bisno AL. Acute pharyngitis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:205–211. PMID: 11172144.15. Lieu TA, Fleisher GR, Schwartz JS. Clinical evaluation of a latex agglutination test for streptococcal pharyngitis: performance and impact on treatment rates. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988; 7:847–854. PMID: 3062561.16. Dunne EM, Marshall JL, Baker CA, Manning J, Gonis G, Danchin MH, et al. Detection of group A streptococcal pharyngitis by quantitative PCR. BMC Infect Dis. 2013; 13:312. PMID: 23844865.17. Hernes SS, Quarsten H, Hagen E, Lyngroth AL, Pripp AH, Bjorvatn B, et al. Swabbing for respiratory viral infections in older patients: a comparison of rayon and nylon flocked swabs. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011; 30:159–165. PMID: 20853014.18. Dube FS, Kaba M, Whittaker E, Zar HJ, Nicol MP. Detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae from different types of nasopharyngeal swabs in children. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e68097. PMID: 23840817.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of SD Bioline Strep A for Rapid Antigen Testing in Elementary Schoolchildren
- The Evaluation of SD Bioline Strep A Rapid Antigen Test in Acute Pharyngitis in Pediatric Clinics
- Evaluation of SD BIOLINE Tetanus Kit
- Comparison of SD BIOLINE Rapid Influenza Antigen Test Using Two Different Specimens, Nasopharyngeal Swabs and Nasopharyngeal Aspirates
- Effect of Topical Povidone-Iodine during the First Week after Cataract Surgery