Yonsei Med J.
2017 Nov;58(6):1177-1185. 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.6.1177.
Effect of Sagittal Balance on Risk of Falling after Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery Combined with Posterior Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Catholic-Kwandong University, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Institue for Bio-Medical Convergence, College of Medicine, Catholic-Kwandong University, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. shmoon@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2418900
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2017.58.6.1177
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To demonstrate the impact of correcting sagittal balance (SB) on functional outcomes of surgical treatment for degenerative spinal disease and actual falls via utilization of new minimally invasive lumbar fusion techniques via a lateral approach.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
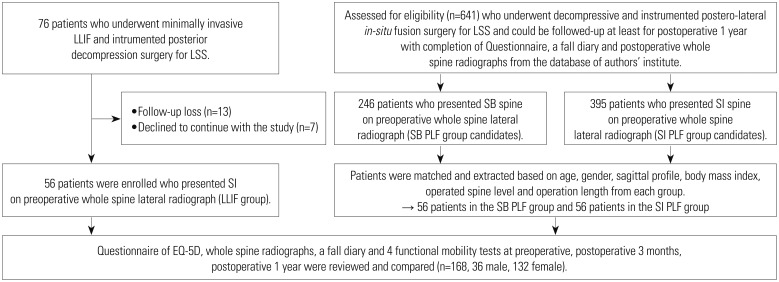
From November 2011 to March 2015, we enrolled 56 patients who underwent minimally invasive lateral lumbar interbody fusion (LLIF) and matched 112 patients receiving decompression/postero-lateral fusion (PLF) surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. According to SB status using C7-plumb line-distance (C7PL) and surgery type, patients were divided into three groups: SB PLF, sagittal imbalance (SI) PLF, and LLIF groups. We then compared their outcomes.
RESULTS
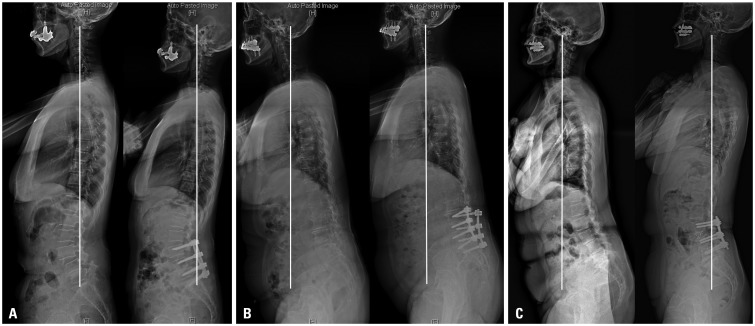
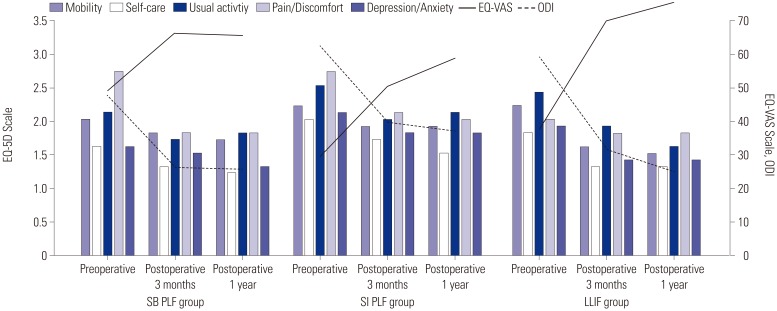
The mean C7PL was 6.2±13.6 mm in the SB PLF group, 72.9±33.8 mm in the SI PLF group, and 74.8±38.2 mm in the LLIF group preoperatively. Postoperatively, C7PL in only the LLIF group improved significantly (p=0.000). Patients in the LLIF group showed greater improvement in fall-related functional test scores than the SI PLF group (p=0.007 for Alternate-Step test, p=0.032 for Sit-to-Stand test). The average number of postoperative falls was 0.4±0.7 in the SB PLF group, 1.1±1.4 in the SI PLF group, and 0.8±1.0 in the LLIF group (p=0.041). Oswestry Disability Index and the Euro-QoL 5 dimension visual analogue scale scores also showed greater improvements in the LLIF group than in the SI PLF group at postoperative 1 year (p=0.003, 0.016).
CONCLUSION
Surgical correction of SI in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis using a combination of minimal invasive LLIF and posterior surgery achieved better surgical outcomes and a lower incidence of actual falls than PLF surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Accidental Falls/*statistics & numerical data
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Decompression, Surgical/*methods
Exercise Test
Female
Humans
Incidence
Lumbar Vertebrae/*diagnostic imaging/*surgery
Male
Middle Aged
Outcome Assessment (Health Care)
Postoperative Period
Postural Balance
Quality of Life
Radiography
Risk
Spinal Fusion/*methods
Spinal Stenosis/*surgery
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berven SH, Deviren V, Smith JA, Hu SH, Bradford DS. Management of fixed sagittal plane deformity: outcome of combined anterior and posterior surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:1710–1715. PMID: 12897497.
Article2. Bayerl SH, Pohlmann F, Finger T, Onken J, Franke J, Czabanka M, et al. The sagittal balance does not influence the 1 year clinical outcome of patients with lumbar spinal stenosis without obvious instability after microsurgical decompression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40:1014–1021. PMID: 25893354.
Article3. Hikata T, Watanabe K, Fujita N, Iwanami A, Hosogane N, Ishii K, et al. Impact of sagittal spinopelvic alignment on clinical outcomes after decompression surgery for lumbar spinal canal stenosis without coronal imbalance. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015; 23:451–458. PMID: 26140404.
Article4. Kawakami M, Tamaki T, Ando M, Yamada H, Hashizume H, Yoshida M. Lumbar sagittal balance influences the clinical outcome after decompression and posterolateral spinal fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:59–64. PMID: 11805637.
Article5. Costanzo G, Zoccali C, Maykowski P, Walter CM, Skoch J, Baaj AA. The role of minimally invasive lateral lumbar interbody fusion in sagittal balance correction and spinal deformity. Eur Spine J. 2014; 23(Suppl 6):699–704. PMID: 25217242.
Article6. Kotwal S, Kawaguchi S, Lebl D, Hughes A, Huang R, Sama A, et al. Minimally invasive lateral lumbar interbody fusion: clinical and radiographic outcome at a minimum 2-year follow-up. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015; 28:119–125. PMID: 22964885.7. Resnick DK, Watters WC 3rd, Mummaneni PV, Dailey AT, Choudhri TF, Eck JC, et al. Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 10: lumbar fusion for stenosis without spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014; 21:62–66. PMID: 24980587.
Article8. Resnick DK, Watters WC 3rd, Sharan A, Mummaneni PV, Dailey AT, Wang JC, et al. Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 9: lumbar fusion for stenosis with spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014; 21:54–61. PMID: 24980586.
Article9. Rampersaud YR, Ravi B, Lewis SJ, Stas V, Barron R, Davey R, et al. Assessment of health-related quality of life after surgical treatment of focal symptomatic spinal stenosis compared with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. Spine J. 2008; 8:296–304. PMID: 17669690.
Article10. Tiedemann A, Shimada H, Sherrington C, Murray S, Lord S. The comparative ability of eight functional mobility tests for predicting falls in community-dwelling older people. Age Ageing. 2008; 37:430–435. PMID: 18487264.
Article11. Villareal DT, Chode S, Parimi N, Sinacore DR, Hilton T, Armamento-Villareal R, et al. Weight loss, exercise, or both and physical function in obese older adults. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1218–1229. PMID: 21449785.
Article12. Lee SM, Yoon MG, Moon MS, Lee BJ, Lee SR, Seo YH. Effect of correction of the contractured flexed osteoarthritic knee on the sagittal alignment by total replacement. Asian Spine J. 2013; 7:204–211. PMID: 24066216.
Article13. Morvan G, Mathieu P, Vuillemin V, Guerini H, Bossard P, Zeitoun F, et al. Standardized way for imaging of the sagittal spinal balance. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20(Suppl 5):602–608. PMID: 21830081.
Article14. Jackson RP, McManus AC. Radiographic analysis of sagittal plane alignment and balance in standing volunteers and patients with low back pain matched for age, sex, and size. A prospective controlled clinical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:1611–1618. PMID: 7939998.15. Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Hecquet J, Marty C. Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J. 1998; 7:99–103. PMID: 9629932.
Article16. Tsutsumimoto T, Shimogata M, Yoshimura Y, Misawa H. Union versus nonunion after posterolateral lumbar fusion: a comparison of long-term surgical outcomes in patients with degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2008; 17:1107–1112. PMID: 18536941.
Article17. Williams AL, Gornet MF, Burkus JK. CT evaluation of lumbar interbody fusion: current concepts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:2057–2066. PMID: 16155160.18. Solberg TK, Olsen JA, Ingebrigtsen T, Hofoss D, Nygaard OP. Health-related quality of life assessment by the EuroQol-5D can provide cost-utility data in the field of low-back surgery. Eur Spine J. 2005; 14:1000–1007. PMID: 15843969.
Article19. Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB. The Oswestry Disability Index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:2940–2952. PMID: 11074683.
Article20. Lee BH, Yang JH, Lee HM, Park JY, Park SE, Moon SH. Surgical outcome predictor in degenerative lumbar spinal disease based on health related quality of life using euro-quality 5 dimensions analysis. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:1214–1221. PMID: 27401654.
Article21. Kellgren JH. Osteoarthrosis in patients and populations. Br Med J. 1961; 2:1–6. PMID: 13752350.
Article22. Binkley N, Krueger D, Gangnon R, Genant HK, Drezner MK. Lateral vertebral assessment: a valuable technique to detect clinically significant vertebral fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2005; 16:1513–1518. PMID: 15834512.
Article23. Kim HJ, Chun HJ, Han CD, Moon SH, Kang KT, Kim HS, et al. The risk assessment of a fall in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:E588–E592. PMID: 21242866.
Article24. Lee BH, Kim TH, Park MS, Lim S, Park JO, Kim HS, et al. Comparison of effects of nonoperative treatment and decompression surgery on risk of patients with lumbar spinal stenosis falling: evaluation with functional mobility tests. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96:e110. PMID: 24990984.25. Ohtori S, Orita S, Yamauchi K, Eguchi Y, Ochiai N, Kishida S, et al. Mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion: oblique lateral interbody fusion for lumbar spinal degeneration disease. Yonsei Med J. 2015; 56:1051–1059. PMID: 26069130.
Article26. Baghdadi YM, Larson AN, Dekutoski MB, Cui Q, Sebastian AS, Armitage BM, et al. Sagittal balance and spinopelvic parameters after lateral lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative scoliosis: a case-control study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39:E166–E173. PMID: 24150436.27. Phan K, Rao PJ, Scherman DB, Dandie G, Mobbs RJ. Lateral lumbar interbody fusion for sagittal balance correction and spinal deformity. J Clin Neurosci. 2015; 22:1714–1721. PMID: 26190218.
Article28. Imagama S, Ito Z, Wakao N, Seki T, Hirano K, Muramoto A, et al. Influence of spinal sagittal alignment, body balance, muscle strength, and physical ability on falling of middle-aged and elderly males. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22:1346–1353. PMID: 23443680.
Article29. Lee BH, Park JO, Kim HS, Suk KS, Lee SY, Lee HM, et al. Spinal sagittal balance status affects postoperative actual falls and quality of life after decompression and fusion in-situ surgery in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016; 148:52–59. PMID: 27398622.
Article30. Jean L. Influence of age and sagittal balance of the spine on the value of the pelvic incidence. Eur Spine J. 2014; 23:1394–1399. PMID: 24509774.
Article31. Lamartina C, Berjano P. Classification of sagittal imbalance based on spinal alignment and compensatory mechanisms. Eur Spine J. 2014; 23:1177–1189. PMID: 24682355.
Article32. Diebo BG, Ferrero E, Lafage R, Challier V, Liabaud B, Liu S, et al. Recruitment of compensatory mechanisms in sagittal spinal malalignment is age and regional deformity dependent: a full-standing axis analysis of key radiographical parameters. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40:642–649. PMID: 25705962.33. Schwab FJ, Blondel B, Bess S, Hostin R, Shaffrey CI, Smith JS, et al. Radiographical spinopelvic parameters and disability in the setting of adult spinal deformity: a prospective multicenter analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:E803–E812. PMID: 23722572.34. Bao H, He S, Liu Z, Zhu Z, Qiu Y, Zhu F. Will immediate postoperative imbalance improve in patients with thoracolumbar/lumbar degenerative kyphoscoliosis? A comparison between Smith-Petersen osteotomy and pedicle subtraction osteotomy with an average 4 years of follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40:E293–E300. PMID: 25901984.
Article35. Kim SJ, Lee YS, Kim YB, Park SW, Hung VT. Clinical and radiological outcomes of a new cage for direct lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Korean J Spine. 2014; 11:145–151. PMID: 25346760.
Article36. Katz JN, Dalgas M, Stucki G, Katz NP, Bayley J, Fossel AH, et al. Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Diagnostic value of the history and physical examination. Arthritis Rheum. 1995; 38:1236–1241. PMID: 7575718.
Article37. Koller H, Pfanz C, Meier O, Hitzl W, Mayer M, Bullmann V, et al. Factors influencing radiographic and clinical outcomes in adult scoliosis surgery: a study of 448 European patients. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25:532–548. PMID: 25917822.
Article38. Chung MM, Chan RW, Fung YK, Fong SS, Lam SS, Lai CW, et al. Reliability and validity of Alternate Step Test times in subjects with chronic stroke. J Rehabil Med. 2014; 46:969–974. PMID: 25167536.
Article39. Barrey C, Roussouly P, Perrin G, Le Huec JC. Sagittal balance disorders in severe degenerative spine. Can we identify the compensatory mechanisms? Eur Spine J. 2011; 20(Suppl 5):626–633. PMID: 21796393.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally Invasive Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Indications, Outcomes and Complications
- Anterolateral and Posterior versus Posterior-Only Approaches for the Correction of Degenerative Adult Spinal Deformity
- Sagittal Balance Correction Following Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Comparison of the Three Approaches
- The Change of Segmental Sagittal angle in Low - grade spondylolisthesis after Pedicular Screw Fixation with or without PLIF - PLIF + PLF versus PLF groups -
- Mini-Open Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Combined with Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Corrective Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity