Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. djkim@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Etiology Research Center, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 6Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Chosun University Hospital, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- 7Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea.
- 8Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 9Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 10Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea. kimsungrae@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2418706
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.137
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
We evaluated the clinical characteristics of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction in newly diagnosed, drug-naive people with type 2 diabetes by analyzing nationwide cross-sectional data.
METHODS
We collected the clinical data of 912 participants with newly diagnosed diabetes from 83 primary care clinics and hospitals nationwide from 2015 to 2016. The presence of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction was defined as a homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) value ≥2.5 and fasting C-peptide levels < 1.70 ng/mL, respectively.
RESULTS
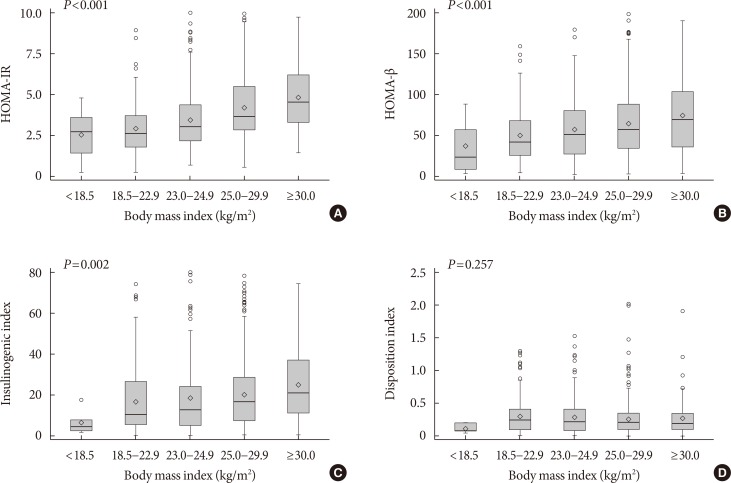
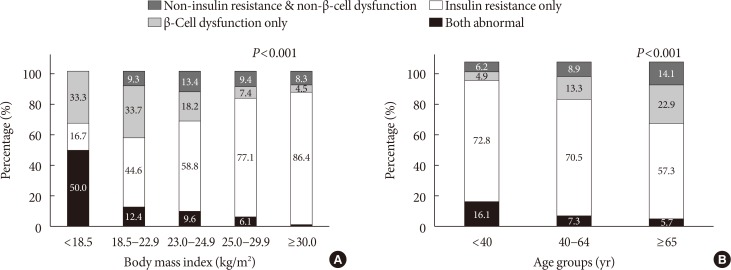
A total of 75.1% and 22.6% of participants had insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction, respectively. The proportion of participants with insulin resistance but no β-cell dysfunction increased, and the proportion of participants with β-cell dysfunction but no insulin resistance decreased as body mass index (BMI) increased. People diagnosed with diabetes before 40 years of age had significantly higher HOMA-IR and BMI than those diagnosed over 65 years of age (HOMA-IR, 5.0 vs. 3.0; BMI, 28.7 kg/m2 vs. 25.1 kg/m2). However, the β-cell function indices were lower in people diagnosed before 40 years of age than in those diagnosed after 65 years of age (homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function, 39.3 vs. 64.9; insulinogenic index, 10.3 vs. 18.7; disposition index, 0.15 vs. 0.25).
CONCLUSION
We observed that the main pathogenic mechanism of type 2 diabetes is insulin resistance in participants with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. In addition, young adults with diabetes are more likely to have higher insulin resistance with obesity and have higher insulin secretory defect with severe hyperglycemia in the early period of diabetes than older populations.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 8 articles
-
Insulin Resistance versus β-Cell Failure: Is It Changing in Koreans?
Mi-kyung Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(2):128-129. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.128.Response: Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index (Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:137-46)
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(3):251-253. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0099.Letter: Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index (Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:137-46)
Ah Reum Khang
Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(3):249-250. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0074.Efficacy and Safety of Pioglitazone versus Glimepiride after Metformin and Alogliptin Combination Therapy: A Randomized, Open-Label, Multicenter, Parallel-Controlled Study
Jeong Mi Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Tae Nyun Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Chang Won Lee, Ja Young Park, Eun Sook Kim, Kwang Jae Lee, Young Sik Choi, Duk Kyu Kim, In Joo Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):67-77. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0274.Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
Han Na Jang, Ye Seul Yang, Seong Ok Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Bo Kyung Koo, Hye Seung Jung
Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(4):382-389. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.382.Rising Incidence of Diabetes in Young Adults in South Korea: A National Cohort Study
Hyun Ho Choi, Giwoong Choi, Hojun Yoon, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):803-807. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0236.A Real-World Study of Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Lobeglitazone in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Bo-Yeon Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Suk Kyeong Kim, Jung-Hyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Hyeong-Kyu Park, Kee-Ho Song, Jong Chul Won, Jae Myung Yu, Mi Young Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sung Wan Chun, In-Kyung Jeong, Choon Hee Chung, Seung Jin Han, Hee-Seok Kim, Ju-Young Min, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):855-865. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0264.Changes in the Epidemiological Landscape of Diabetes in South Korea: Trends in Prevalence, Incidence, and Healthcare Expenditures
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(5):669-677. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.2073.
Reference
-
1. International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas 7th edition. cited 2017 Dec 19. Available from: http://www.diabetesatlas.org.2. Nolan CJ, Damm P, Prentki M. Type 2 diabetes across generations: from pathophysiology to prevention and management. Lancet. 2011; 378:169–181. PMID: 21705072.
Article3. Møller JB, Dalla Man C, Overgaard RV, Ingwersen SH, Tornoe CW, Pedersen M, Tanaka H, Ohsugi M, Ueki K, Lynge J, Vasconcelos NM, Pedersen BK, Kadowaki T, Cobelli C. Ethnic differences in insulin sensitivity, β-cell function, and hepatic extraction between Japanese and Caucasians: a minimal model analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:4273–4280. PMID: 25119313.
Article4. Moller JB, Pedersen M, Tanaka H, Ohsugi M, Overgaard RV, Lynge J, Almind K, Vasconcelos NM, Poulsen P, Keller C, Ueki K, Ingwersen SH, Pedersen BK, Kadowaki T. Body composition is the main determinant for the difference in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology between Japanese and Caucasians. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:796–804. PMID: 24130359.5. Ohn JH, Kwak SH, Cho YM, Lim S, Jang HC, Park KS, Cho NH. 10-Year trajectory of β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in the development of type 2 diabetes: a community-based prospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016; 4:27–34. PMID: 26577716.
Article6. Rattarasarn C, Soonthornpan S, Leelawattana R, Setasuban W. Decreased insulin secretion but not insulin sensitivity in normal glucose tolerant Thai subjects. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:742–743. PMID: 16505544.
Article7. Yabe D, Seino Y, Fukushima M, Seino S. β Cell dysfunction versus insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in East Asians. Curr Diab Rep. 2015; 15:602. PMID: 25944304.
Article8. Ha KH, Kim DJ. Trends in the diabetes epidemic in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2015; 30:142–146. PMID: 26194073.
Article9. Kim DJ, Song KE, Park JW, Cho HK, Lee KW, Huh KB. Clinical characteristics of Korean type 2 diabetic patients in 2005. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007; 77(Suppl 1):S252–S257. PMID: 17459510.
Article10. Son JW, Park CY, Kim S, Lee HK, Lee YS. Insulin Resistance as Primary Pathogenesis in Newly Diagnosed, Drug Naive Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Korea (SURPRISE) Study Group. Changing clinical characteristics according to insulin resistance and insulin secretion in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2015; 39:387–394. PMID: 26566496.
Article11. Ko SH, Kim SR, Kim DJ, Oh SJ, Lee HJ, Shim KH, Woo MH, Kim JY, Kim NH, Kim JT, Kim CH, Kim HJ, Jeong IK, Hong EK, Cho JH, Mok JO, Yoon KH. Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association. 2011 Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:431–436. PMID: 22111032.
Article12. World Health Organization, International Association for the Study of Obesity, International Obesity Task Force. Chapter 2, Assessment/diagnosis. The Asia Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. Sydney: Health Communications;2000. p. 15–21.13. Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972; 18:499–502. PMID: 4337382.
Article14. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985; 28:412–419. PMID: 3899825.15. Utzschneider KM, Prigeon RL, Faulenbach MV, Tong J, Carr DB, Boyko EJ, Leonetti DL, McNeely MJ, Fujimoto WY, Kahn SE. Oral disposition index predicts the development of future diabetes above and beyond fasting and 2-h glucose levels. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:335–341. PMID: 18957530.
Article16. Yamada C, Mitsuhashi T, Hiratsuka N, Inabe F, Araida N, Takahashi E. Optimal reference interval for homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance in a Japanese population. J Diabetes Investig. 2011; 2:373–376.
Article17. Park SW, Yun YS, Ahn CW, Nam JH, Kwon SH, Song MK, Han SH, Cha BS, Son YD, Lee HC, Huh KB. Short Insulin Tolerance Test (SITT) for the determination of in vivo insulin sensitivity-a comparison with euglycemic clamp test. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1998; 22:199–208.18. Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, Fruchart JC, James WP, Loria CM, Smith SC Jr. International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention. Hational Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. American Heart Association. World Heart Federation. International Atherosclerosis Society. International Association for the Study of Obesity. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009; 120:1640–1645. PMID: 19805654.19. Yabe D, Seino Y. Type 2 diabetes via β-cell dysfunction in east Asian people. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016; 4:2–3. PMID: 26577717.
Article20. Kim DJ, Lee MS, Kim KW, Lee MK. Insulin secretory dysfunction and insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2001; 50:590–593. PMID: 11319722.
Article21. Qian L, Xu L, Wang X, Fu X, Gu Y, Lin F, Peng Y, Li G, Luo M. Early insulin secretion failure leads to diabetes in Chinese subjects with impaired glucose regulation. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2009; 25:144–149. PMID: 19116942.
Article22. Park JY, Lee KU, Kim CH, Kim HK, Hong SK, Park KS, Lee HK, Min HK. Past and current obesity in Koreans with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1997; 35:49–56. PMID: 9113475.
Article23. Yoon KH, Ko SH, Cho JH, Lee JM, Ahn YB, Song KH, Yoo SJ, Kang MI, Cha BY, Lee KW, Son HY, Kang SK, Kim HS, Lee IK, Bonner-Weir S. Selective beta-cell loss and alpha-cell expansion in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:2300–2308. PMID: 12727989.24. Beard JC, Ward WK, Halter JB, Wallum BJ, Porte D Jr. Relationship of islet function to insulin action in human obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987; 65:59–64. PMID: 3294880.
Article25. Kahn SE. The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2003; 46:3–19. PMID: 12637977.
Article26. Olefsky J, Farquhar JW, Reaven G. Relationship between fasting plasma insulin level and resistance to insulin-mediated glucose uptake in normal and diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1973; 22:507–513. PMID: 4719190.
Article27. Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2006; 444:840–846. PMID: 17167471.
Article28. Kim CH, Kim HK, Kim EH, Bae SJ, Park JY. Relative contributions of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction to the development of type 2 diabetes in Koreans. Diabet Med. 2013; 30:1075–1079. PMID: 23600561.29. Liu J, Wang Y, Hu Y, Leng S, Wang G. Comparison of β-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance correlating obesity with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. J Diabetes Complications. 2016; 30:898–902. PMID: 27012460.
Article30. Hillier TA, Pedula KL. Characteristics of an adult population with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: the relation of obesity and age of onset. Diabetes Care. 2001; 24:1522–1527. PMID: 11522693.31. Wang J, Geiss LS, Williams DE, Gregg EW. Trends in emergency department visit rates for hypoglycemia and hyperglycemic crisis among adults with Diabetes, United States, 2006-2011. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0134917. PMID: 26252486.
Article32. Song SH. Emerging type 2 diabetes in young adults. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012; 771:51–61. PMID: 23393671.
Article33. Kong AP, Chan NN, Chan JC. The role of adipocytokines and neurohormonal dysregulation in metabolic syndrome. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2006; 2:397–407. PMID: 18220644.34. Kong AP, Luk AO, Chan JC. Detecting people at high risk of type 2 diabetes: how do we find them and who should be treated? Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 30:345–355. PMID: 27432070.
Article35. Wajchenberg BL. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocr Rev. 2000; 21:697–738. PMID: 11133069.
Article36. Maedler K, Sergeev P, Ris F, Oberholzer J, Joller-Jemelka HI, Spinas GA, Kaiser N, Halban PA, Donath MY. Glucose-induced beta cell production of IL-1beta contributes to glucotoxicity in human pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 2002; 110:851–860. PMID: 12235117.37. Drews G, Krippeit-Drews P, Dufer M. Oxidative stress and beta-cell dysfunction. Pflugers Arch. 2010; 460:703–718. PMID: 20652307.
Article38. Rains JL, Jain SK. Oxidative stress, insulin signaling, and diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011; 50:567–575. PMID: 21163346.
Article39. Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korea Health Statistics 2015: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. cited 2017 Dec 19. Available from: http://cdc.go.kr.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter: Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index (Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:137-46)
- Response: Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index (Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:137-46)
- Body Composition Analysis in Newly Diagnosed Diabetic Adolescent Girls
- Comparison of the Efficacy of Dipeptidylpeptidase-4 Inhibitors Between Asian and Non-Asian Populations
- Clinical Characteristics and Laboratory Findings of Children who were Newly Diagnosed with Diabetes Mellitus (From 2001 to 2008)