Asia Pac Allergy.
2018 Jul;8(3):e28. 10.5415/apallergy.2018.8.e28.
Cow's milk oral immunotherapy in real life: 8-year long-term follow-up study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Immunoallergy Department, CUF Descobertas Hospital, Lisbon, Portugal. angela.gaspar@sapo.pt
- KMID: 2417975
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2018.8.e28
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Oral immunotherapy (OIT) has been recognized as a promising treatment for severe and long-lasting cow's milk (CM) allergy. Once maintenance has been achieved, patients should maintain daily intake of CM to ensure desensitization. Clinical experience concerning long-term follow-up is scarce.
OBJECTIVE
The authors aimed to assess long-term efficacy and safety of a maintenance phase of OIT in real life.
METHODS
Prospective study of all children and adolescents, who underwent CM-OIT and were subsequently followed at our allergy center on maintenance dose (200 mL daily) for at least 36 months after reaching the maintenance phase (from 2009 to 2016).
RESULTS
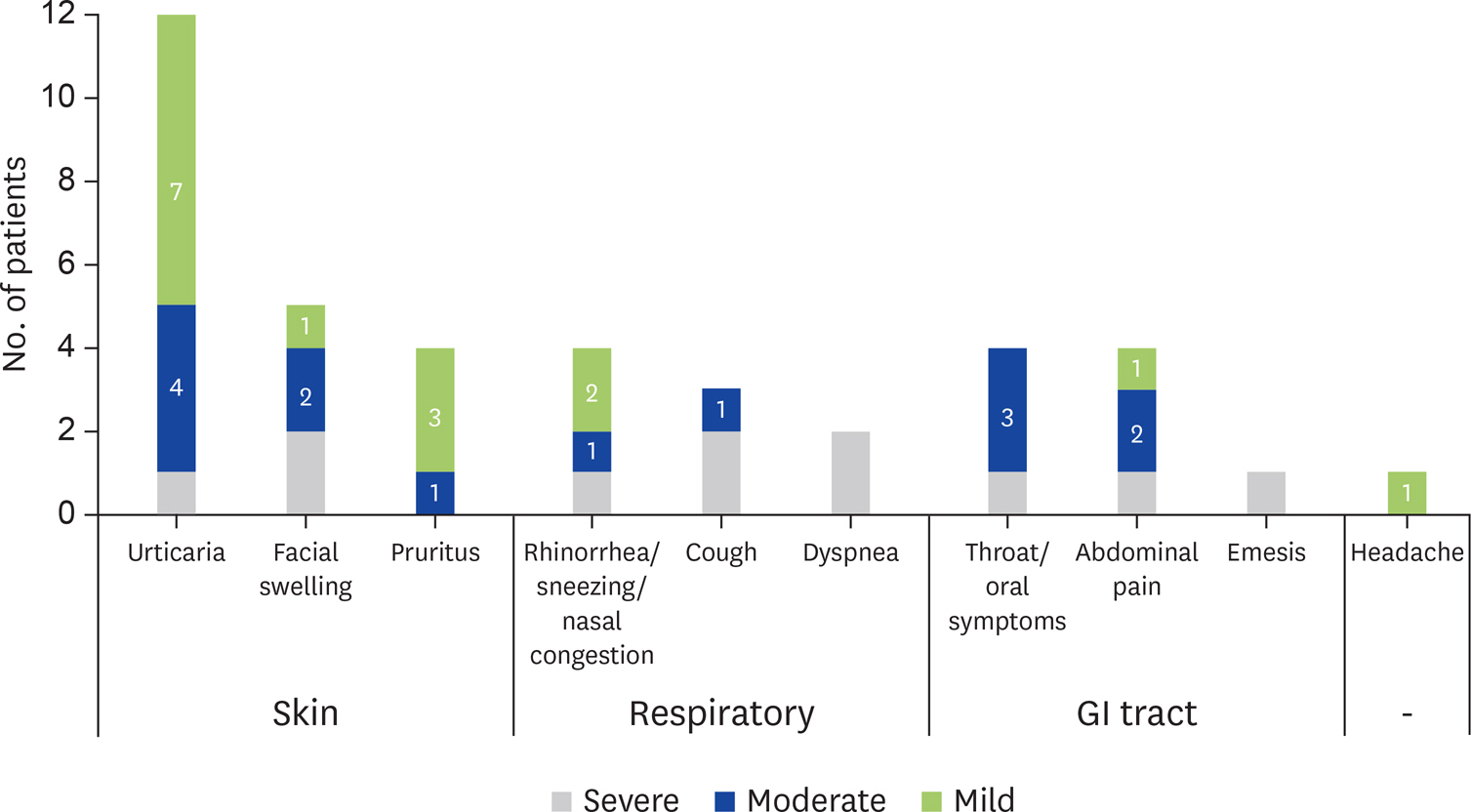
Forty-two patients were enrolled: 60% male, 36% with history of anaphylaxis and 57% with asthma. The median time of follow-up was 69 months (range, 39-105 months) and the median age at the last clinical evaluation was 13 years (range, 6-23 years). Regarding adherence to the protocol: 92% are on free diet (at least 200 mL of CM daily; 7-g protein); 14% had transient interruptions and 7% definitely withdrawn with loss of tolerance. During maintenance, 45% developed mild to severe allergic reactions, and 7% had more than 3 episodes. A positive correlation between the occurrence of allergic reactions and history of anaphylaxis (p < 0.001) was found. The coexistence of asthma was risk factor for the occurrence of allergic reactions during maintenance.
CONCLUSION
This real-life study supports long-term efficacy and safety of CM-OIT. Despite daily intake, 41% had symptoms at some moment during the complete follow-up period; a total of 33 symptomatic days in patients with mean follow-up time of 67.5 months. Clinical tolerance depends on daily intake. The protective effect reached can be lost after CM withdrawal. History of anaphylaxis was a risk factor for the occurrence of allergic reactions during the maintenance phase.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
In this July
Yoon-Seok Chang
Asia Pac Allergy. 2018;8(3):. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2018.8.e32.
Reference
-
References
1. Nwaru BI, Hickstein L, Panesar SS, Roberts G, Muraro A. Sheikh AEAACI Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Guidelines Group. Prevalence of common food allergies in Europe: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy. 2014; 69:992–1007.
Article2. Skripak JM, Matsui EC, Mudd K, Wood RA. The natural history of IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:1172–7.
Article3. Yeung JP, Kloda LA, McDevitt J, Ben-Shoshan M, Alizadehfar R. Oral immunotherapy for milk allergy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 11:CD009542.
Article4. Martorell Calatayud C, Muriel García A, Martorell Aragonés A, De La Hoz Caballer B. Safety and efficacy profile and immunological changes associated with oral immunotherapy for IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy in children: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2014; 24:298–307.5. Santos N, Gaspar A, Borrego LM, Morais-Almeida M. Successful oral tolerance induction to cow's milk in a child with allergy to extensively hydrolysed formula. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2015; 43:216–8.
Article6. Longo G, Barbi E, Berti I, Meneghetti R, Pittalis A, Ronfani L, Ventura A. Specific oral tolerance induction in children with very severe cow's milk-induced reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:343–7.
Article7. Pajno GB, Caminiti L, Ruggeri P, De Luca R, Vita D, La Rosa M, Passalacqua G. Oral immunotherapy for cow's milk allergy with a weekly up-dosing regimen: a randomized single-blind controlled study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010; 105:376–81.
Article8. González Jiménez D, Larrea Tamayo E, Díaz Martin JJ, Molinos Norniella C, Pérez Solis D, Menéndez Arias C, Jiménez Treviño S, Bousoño García C. Oral rush desensitization for cow milk allergy: clinical and immunological follow-up. An Pediatr (Barc). 2013; 79:346–51.9. Pajno GB, Cox L, Caminiti L, Ramistella V, Crisafulli G. Oral Immunotherapy for treatment of immunoglobulin E-mediated food allergy: the transition to clinical practice. Pediatr Allergy Immunol Pulmonol. 2014; 27:42–50.
Article10. Passalacqua G, Landi M, Pajno GB. Oral immunotherapy for cow's milk allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 12:271–7.
Article11. Sato S, Yanagida N, Ogura K, Asaumi T, Okada Y, Koike Y, Iikura K, Syukuya A, Ebisawa M. Immunotherapy in food allergy: towards new strategies. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2014; 32:195–202.12. Rolinck-Werninghaus C, Staden U, Mehl A, Hamelmann E, Beyer K, Niggemann B. Specific oral tolerance induction with food in children: transient or persistent effect on food allergy? Allergy. 2005; 60:1320–2.
Article13. Keet CA, Frischmeyer-Guerrerio PA, Thyagarajan A, Schroeder JT, Hamilton RG, Boden S, Steele P, Driggers S, Burks AW, Wood RA. The safety and efficacy of sublingual and oral immunotherapy for milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:448–55. 455.e1-5.
Article14. Pajno GB, Caminiti L, Salzano G, Crisafulli G, Aversa T, Messina MF, Wasniewska M, Passalacqua G. Comparison between two maintenance feeding regimens after successful cow's milk oral desensitization. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2013; 24:376–81.
Article15. Morais-Almeida M, Piedade S, Couto M, Sampaio G, Santa-Marta C, Gaspar A. Innovation in specific oral tolerance induction in children with anaphylaxis to cow's milk proteins. Rev Port Imunoalergologia. 2011; 19:161–9.16. Nurmatov U, Devereux G, Worth A, Healy L, Sheikh A. Effectiveness and safety of orally administered immunotherapy for food allergies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. 2014; 111:12–22.
Article17. Alonso-Lebrero E, Fuentes V, Zapatero L, Pérez-Bustamante S, Pineda F, Martinez-Molero MI. Goat's milk allergies in children following specific oral tolerance induction to cow's milk. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2008; 36:180–1.
Article18. Staden U, Rolinck-Werninghaus C, Brewe F, Wahn U, Niggemann B, Beyer K. Specific oral tolerance induction in food allergy in children: efficacy and clinical patterns of reaction. Allergy. 2007; 62:1261–9.
Article19. Meglio P, Giampietro PG, Gianni S, Galli E. Oral desensitization in children with immunoglobulin E-mediated cow's milk allergy–follow-up at 4 yr and 8 months. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2008; 19:412–9.20. Vázquez-Ortiz M, Alvaro-Lozano M, Alsina L, Garcia-Paba MB, Piquer-Gibert M, Giner-Muñoz MT, Lozano J, Domínguez-Sánchez O, Jiménez R, Días M, Martín-Mateos MA, Plaza-Martín AM. Safety and predictors of adverse events during oral immunotherapy for milk allergy: severity of reaction at oral challenge, specific IgE and prick test. Clin Exp Allergy. 2013; 43:92–102.
Article21. Martorell A, Alonso E, Echeverría L, Escudero C, García-Rodríguez R, Blasco C, Bone J, Borja-Segade J, Bracamonte T, Claver A, Corzo JL, De la Hoz B, Del Olmo R, Dominguez O, Fuentes-Aparicio V, Guallar I, Larramona H, Martín-Muñoz F, Matheu V, Michavila A, Ojeda I, Ojeda P, Piquer M, Poza P, Reche M, Río PRD, Rodríguez M, Ruano F, Sánchez-García S, Terrados S, Valdesoiro L, Vazquez-Ortiz MExpert panel selected from members of the Spanish Societies of Pediatric Allergology, Asthma and Clinical Immunology (SEICAP) and Allergology and Clinical Immunology (SEAIC). Oral immunotherapy for food allergy: A Spanish guideline. Egg and milk immunotherapy Spanish guide (ITEMS GUIDE). Part 2: Maintenance phase of cow milk (CM) and egg oral immunotherapy (OIT), special treatment dosing schedules. Models of dosing schedules of OIT with CM and EGG. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2017; 45:508–18.
Article22. Meglio P, Caminiti L, Pajno GB, Dello Iacono I, Tripodi S, Verga MC. Martelli ASIAIP Group. The oral food desensitization in the Italian allergy centres. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 47:68–76.23. Keet CA, Seopaul S, Knorr S, Narisety S, Skripak J, Wood RA. Long-term follow-up of oral immunotherapy for cow's milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 132:737–739. e6.
Article24. Elizur A, Appel MY, Goldberg MR, Yichie T, Levy MB, Nachshon L, Katz Y. Clinical and laboratory 2-year outcome of oral immunotherapy in patients with cow's milk allergy. Allergy. 2016; 71:275–8.
Article25. Barbi E, Longo G, Berti I, Matarazzo L, Rubert L, Saccari A, Lenisa I, Ronfani L, Radillo O, Ventura A. Adverse effects during specific oral tolerance induction: in home phase. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2012; 40:41–50.
Article26. Couto M, Gaspar A, Santa-Marta C, Morais-Almeida M. Cow's milk dependent exercise-induced urticaria after oral tolerance induction in an adolescent. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2012; 40:67–8.
Article27. Piedade S, Morais-Almeida M. Indução de tolerância em alergia alimentar. In: Castro FF, Galvão CE, editors. Imunoterpia. São Paulo: Editora Manole Lda;2011. p. 125–47.28. Caminiti L, Passalacqua G, Vita D, Ruggeri P, Barberio G, Pajno GB. Food-exercise-induced anaphylaxis in a boy successfully desensitized to cow milk. Allergy. 2007; 62:335–6.
Article29. Ansley L, Bonini M, Delgado L, Del Giacco S, Du Toit G, Khaitov M, Kurowski M, Hull JH, Moreira A, Robson-Ansley PJ. Pathophysiological mechanisms of exercise-induced anaphylaxis: an EAACI position statement. Allergy. 2015; 70:1212–21.
Article30. Saarinen KM, Pelkonen AS, Mäkelä MJ, Savilahti E. Clinical course and prognosis of cow's milk allergy are dependent on milk-specific IgE status. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 116:869–75.
Article31. Elizur A, Goldberg MR, Levy MB, Nachshon L, Katz Y. Oral immunotherapy in cow's milk allergic patients: course and long-term outcome according to asthma status. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015; 114:240–4. e1.
Article32. Savilahti EM, Kuitunen M, Valori M, Rantanen V, Bardina L, Gimenez G, Mäkelä MJ, Hautaniemi S, Savilahti E, Sampson HA. Use of IgE and IgG4 epitope binding to predict the outcome of oral immunotherapy in cow's milk allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2014; 25:227–35.
Article33. Kuitunen M, Englund H, Remes S, Movérare R, Pelkonen A, Borres MP, Mäkelä MJ. High IgE levels to α-lactalbumin, β-lactoglobulin and casein predict less successful cow's milk oral immunotherapy. Allergy. 2015; 70:955–62.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cow's Milk Allergy with Atopic Dermatitis
- Butter Tolerance in Children Allergic to Cow's Milk
- A Follow-up Study of Intractable Diarrhea in Early Infancy: Clinical Features of Cow's Milk Allergy and Cow Milk-Sensitive Enteropathy
- Cow mild allergy in infant who neonatal onset
- Oral immunotherapy for the treatment of immediate type food allergy